There are an estimated ~2 trillion galaxies within the observable Universe. Most are already unreachable, and the situation only gets worse.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Software may be eating the world, but low code could eat software
Were you unable to attend Transform 2022? Check out all of the summit sessions in our on-demand library now! Watch here.
Marc Andreesen famously claimed in 2011 that “software is eating the world” in an op-ed article in the Wall Street Journal.
His point was that software was the new engine of value creation.
An Alzheimer’s-Proof Brain: Ground-Breaking Case Provides Clues to Treatment and Prevention of Dementia
Due to a rare genetic mutation, Aliria Rosa Piedrahita de Villegas should have had Alzheimer’s.
Alzheimer’s disease is a disease that attacks the brain, causing a decline in mental ability that worsens over time. It is the most common form of dementia and accounts for 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases. There is no current cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but there are medications that can help ease the symptoms.

The Romance of Reality: How the Universe Organizes Itself to Create Life, Consciousness, and Cosmic Complexity
Bobby Azarian is a cognitive neuroscientist and science journalist. His work can be found in publications including The Atlantic, the New York Times, Scientific American, and BBC Future. He has also authored academic papers for prestigious peer-reviewed journals, such as Human Brain Mapping and Cognition & Emotion.
Below, Bobby shares 5 key insights from his new book, Listen to the audio version—read by Bobby himself—in the Next Big Idea App.
If you’re listening to this then congratulations, you’re lucky enough to be alive during the most exciting time in history. We are on the verge of a paradigm shift of unparalleled magnitude. Such a shift occurs when new science forces us to adopt a different overall framework and perspective.
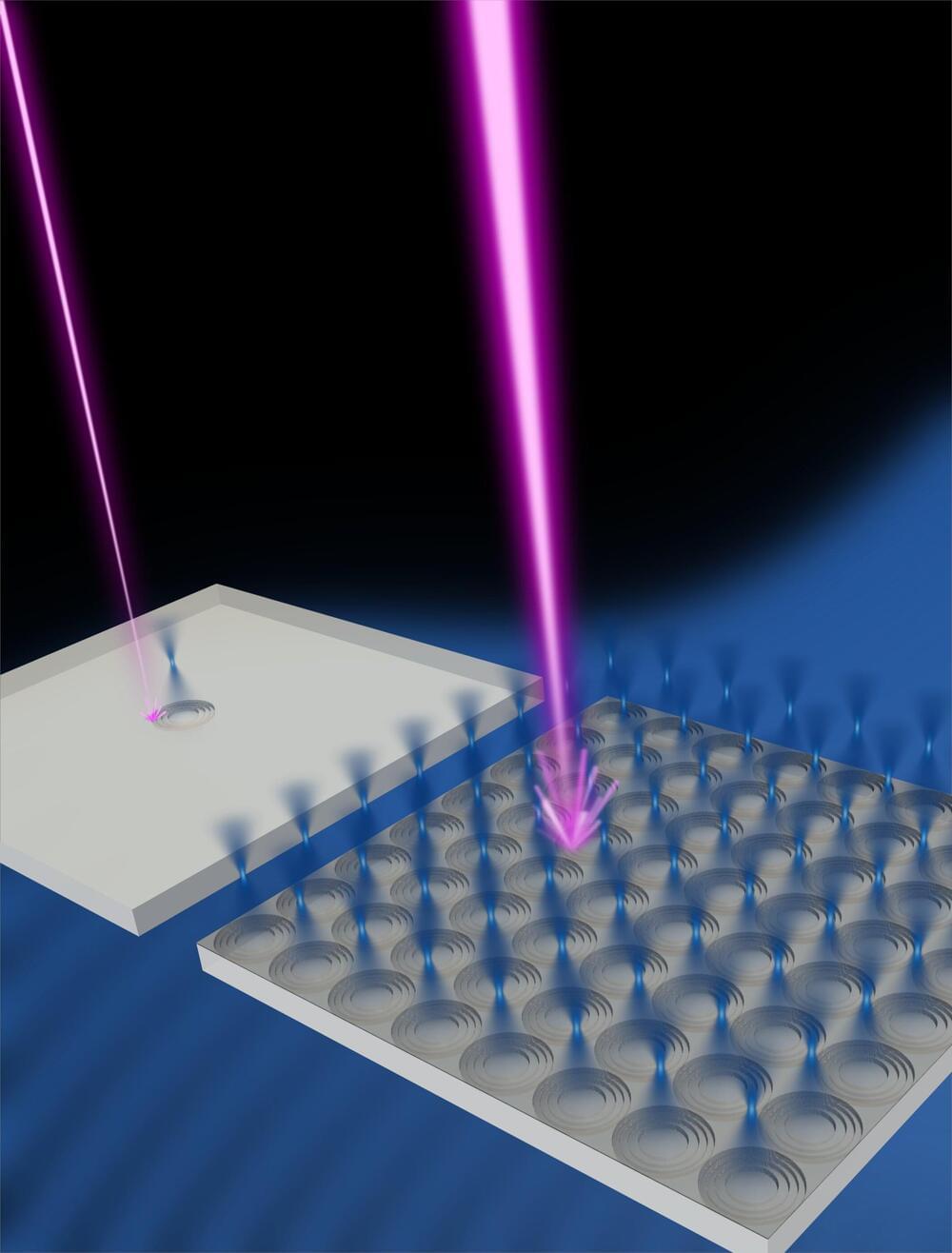
A superfast process for nanoscale machining
Cutting intricate patterns as small as several billionths of a meter deep and wide, the focused ion beam (FIB) is an essential tool for deconstructing and imaging tiny industrial parts to ensure they were fabricated correctly. When a beam of ions, typically of the heavy metal gallium, bombards the material to be machined, the ions eject atoms from the surface—a process known as milling—to sculpt the workpiece.
Beyond its traditional uses in the semiconductor industry, the FIB has also become a critical tool for fabricating prototypes of complex three-dimensional devices, ranging from lenses that focus light to conduits that channel fluid. Researchers also use the FIB to dissect biological and material samples to image their internal structure.
However, the FIB process has been limited by a trade-off between high speed and fine resolution. On the one hand, increasing the ion current allows a FIB to cut into the workpiece deeper and faster. On the other hand, the increased current carries a larger number of positively charged ions, which electrically repel each other and defocus the beam. A larger, diffuse beam, which can be about 100 nanometers in diameter or 10 times wider than a typical narrow beam, not only limits the ability to fabricate fine patterns but can also damage the workpiece at the perimeter of the milled region. As a result, the FIB has not been the process of choice for those trying to machine many tiny parts in a hurry.
How does classical, Newtonian inertia emerge from quantum mechanics?
From my understanding, inertia is typically taken as an axiom rather than something that can be explained by some deeper phenomenon. However, it’s also my understanding that quantum mechanics must reduce to classical, Newtonian mechanics in the macroscopic limit.
By inertia, I mean the resistance to changes in velocity — the fact of more massive objects (or paticles, let’s say) accelerating more slowly given the same force.
What is the quantum mechanical mechanism that, in its limit, leads to Newtonian inertia? Is there some concept of axiomatic inertia that applies to the quantum mechanical equations and explains Newtonian inertia, even if it remains a fundamental assumption of quantum theory?
It’s finally here: Lockheed Martin delivers 60+ kW laser to the US Navy
Enhancing overall combat system effectiveness
“Lockheed Martin and the U.S. Navy share a common vision and enthusiasm for developing and providing disruptive laser weapon systems,” said in the statement Rick Cordaro, vice president of Lockheed Martin Advanced Product Solutions.
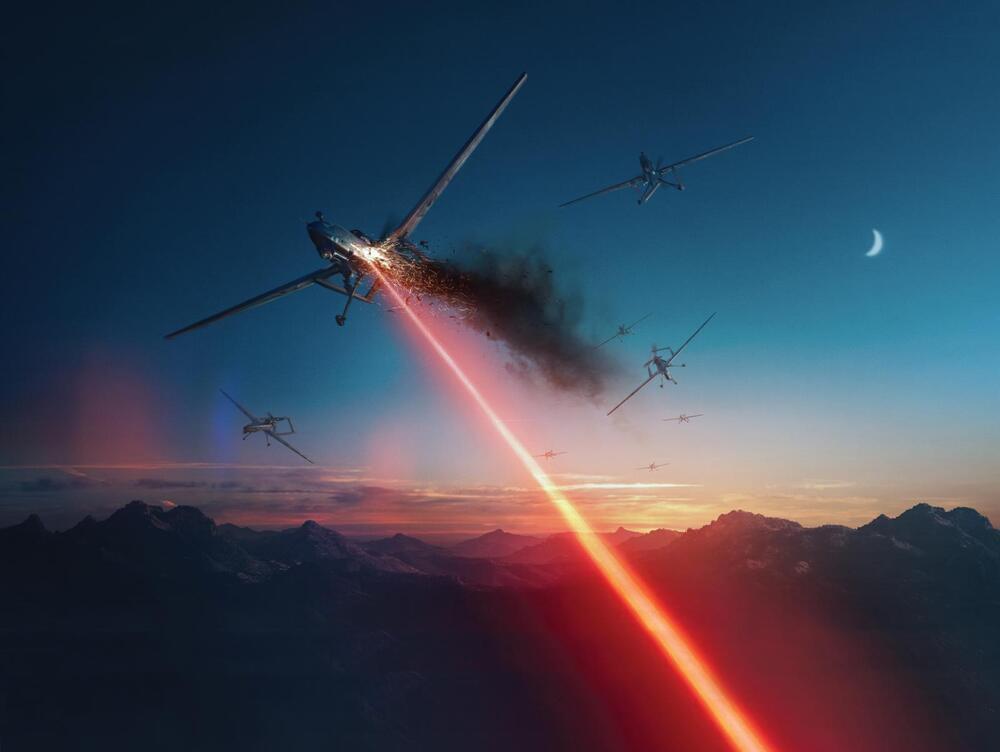

Defenseless Against Hypersonic Missiles, US Navy Turns To ‘Faster & Lethal’ DEWs To Battle China, Russia
The US Navy is exploring the novel technology of Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs) against Chinese and Russian hypersonic weapons in the absence of a potent defense against these highly maneuverable missiles.
The top admiral of the US Navy, Michael Gilday stated that directed energy systems are being developed as a potential countermeasure against hypersonic missiles, calling the advancements made by Russia and China in hypersonic weapon technology “a significant concern.”
The development of devices that would use high-energy lasers or high-power microwaves to remove a threat is a major priority for the Navy, according to Adm. Michael Gilday, Chief of Naval Operations, who is also the Chief of US Missile Defense Agency.
Space Warfare
This episode focuses on the basic concepts and misconceptions of wars fought in space and examines the notions of weapons, defenses, stealth in space, and the distance involved.
Project Rho: http://www.projectrho.com/public_html/rocket/index.php.
Military Science Fiction: http://www.milsf.com.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join the Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Support the Channel on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Visit the sub-reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/space-warfare.
Cover Art by Jakub Grygier: https://www.artstation.com/artist/jakub_grygier

Scientists are unraveling the mystery of the arrow of time
The flow of time from the past to the future is a central feature of how we experience the world. But precisely how this phenomenon, known as the arrow of time, arises from the microscopic interactions among particles and cells is a mystery—one that researchers at the CUNY Graduate Center Initiative for the Theoretical Sciences (ITS) are helping to unravel with the publication of a new paper in the journal Physical Review Letters. The findings could have important implications in a variety of disciplines, including physics, neuroscience, and biology.
Fundamentally, the arrow of time arises from the second law of thermodynamics: the principle that microscopic arrangements of physical systems tend to increase in randomness, moving from order to disorder. The more disordered a system becomes, the more difficult it is for it to find its way back to an ordered state, and the stronger the arrow of time. In short, the universe’s tendency toward disorder is the fundamental reason why we experience time flowing in one direction.
“The two questions our team had were, if we looked at a particular system, would we be able to quantify the strength of its arrow of time, and would we be able to sort out how it emerges from the micro scale, where cells and neurons interact, to the whole system?” said Christopher Lynn, the paper’s first author and a postdoctoral fellow with the ITS program. “Our findings provide the first step toward understanding how the arrow of time that we experience in daily life emerges from these more microscopic details.”