Scientists study the immortal jellyfish to learn about its DNA reproduction, life cycle and telomeres. New research reveals its special genes.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Will we ever define the conscious mind?
Some neuroscientists believe we will never solve the hard problem. Just as a goldfish will never be able to read a newspaper or write a sonnet, Homo sapiens, these scholars argue, are cognitively closed to such knowledge. It is a great but impenetrable mystery. The psychologist Steven Pinker calls the hard problem “the ultimate tease… orever beyond our conceptual grasp.” Echoing the view that consciousness remains outside the limits of human comprehension, one of the best entries in Ambrose Bierce’s The Devil’s Dictionary is the following:
“Mind, n. A mysterious form of matter secreted by the brain. Its chief activity consists in the endeavor to ascertain its own nature, the futility of the attempt being due to the fact that it has nothing but itself to know itself.”
Others believe that if we just keep solving the easy problems, the hard problem will disappear. By locating and understanding what we call the neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) — neural mechanisms that researchers say are responsible for consciousness, typically gleaned using brain scans or neurosurgery to compare conscious and unconscious states — we will march ever closer to solving the mystery, until one day there is nothing left to solve. Defining an NCC starts as a process of elimination: the spinal cord and cerebellum can be ruled out, for instance, because if both are lost to stroke or trauma, nothing happens to the victim’s consciousness. They still perceive and experience their surroundings as they did before. The best candidates for NCC (so far) are a subset of neurons in a posterior hot zone of the brain that comprises the parietal, occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. When the posterior hot zone is electrically stimulated, as it sometimes is during surgery for brain tumors, a person will report experiencing a menagerie of thoughts, memories, sensations, visual and auditory hallucinations, and an eerie feeling of surrealism or familiarity. So if the consciousness illusion is located anywhere, it might be in this mysterious region of the posterior cortex.

Making Computer Chips Act More like Brain Cells
The human brain is an amazing computing machine. Weighing only three pounds or so, it can process information a thousand times faster than the fastest supercomputer, store a thousand times more information than a powerful laptop, and do it all using no more energy than a 20-watt lightbulb.
Researchers are trying to replicate this success using soft, flexible organic materials that can operate like biological neurons and someday might even be able to interconnect with them. Eventually, soft “neuromorphic” computer chips could be implanted directly into the brain, allowing people to control an artificial arm or a computer monitor simply by thinking about it.
Like real neurons — but unlike conventional computer chips — these new devices can send and receive both chemical and electrical signals. “Your brain works with chemicals, with neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. Our materials are able to interact electrochemically with them,” says Alberto Salleo, a materials scientist at Stanford University who wrote about the potential for organic neuromorphic devices in the 2021 Annual Review of Materials Research.
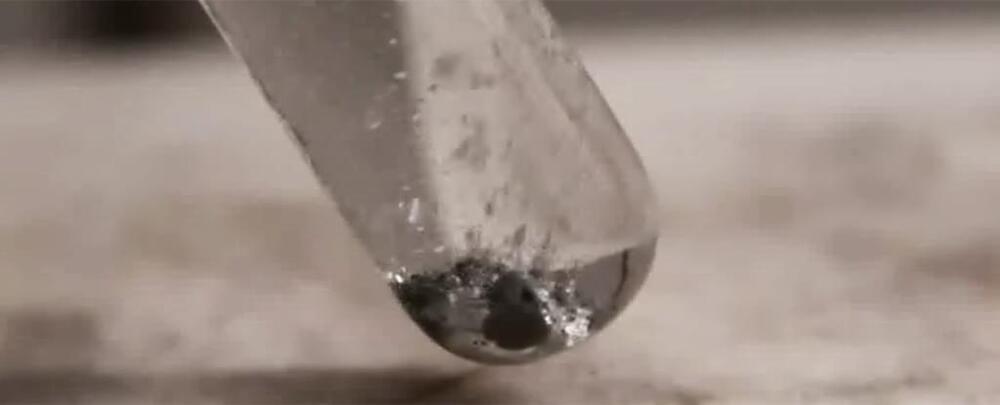


Clean Fuel Breakthrough Turns Water Into Hydrogen at Room Temperature
Hydrogen fuel promises to be a clean and abundant source of energy in the future – as long as scientists can figure out ways to produce it practically and cheaply, and without fossil fuels.
A new study provides us with another promising step in that direction.
Scientists have described a relatively simple method involving aluminum nanoparticles that are able to strip the oxygen from water molecules and leave hydrogen gas.
Chariots of the Gods
https://youtube.com/watch?v=HouRC6PaoR4&feature=share
1973 movie. This German film explores the theory that aliens visited Earth thousands of years ago. NTSC analog broadcast on WHYY-TV 12, January 1, 1990, midnight — 1:30 a.m. SLP-mode VHS recording. Digitized on a Sony DVD+RW disc at SP mode. Transferred to MP4 using Handbrake H.265, 30 frames, peak frame rate, 18 RF, Fast encoding, Decomb filter at default setting.
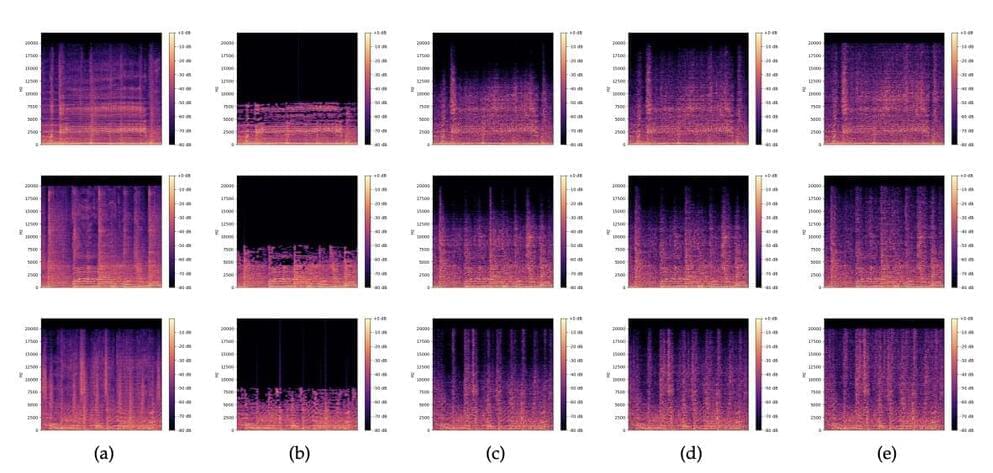
Using a GAN architecture to restore heavily compressed music files
Over the past few decades, computer scientists have developed increasingly advanced technologies and tools to store large amounts of music and audio files in electronic devices. A particular milestone for music storage was the development of MP3 (i.e., MPEG-1 layer 3) technology, a technique to compress sound sequences or songs into very small files that can be easily stored and transferred between devices.
The encoding, editing and compression of media files, including PKZIP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, MP3, AAC, Cinepak and MPEG-2 files, is achieved using a set of technologies known as codecs. Codecs are compression technologies with two key components: an encoder that compresses files and a decoder that decompresses them.
There are two types of codecs, the so-called lossless and lossy codecs. During decompression, lossless codecs, such as PKZIP and PNG codecs, reproduce the exact same file as original files. Lossy compression methods, on the other hand, produce a facsimile of the original file that sounds (or looks) like the original but takes up less storage space in electronic devices.
Preventing an AI-related catastrophe
Why do we think that reducing risks from AI is one of the most pressing issues of our time? There are technical safety issues that we believe could, in the worst case, lead to an existential threat to humanity.
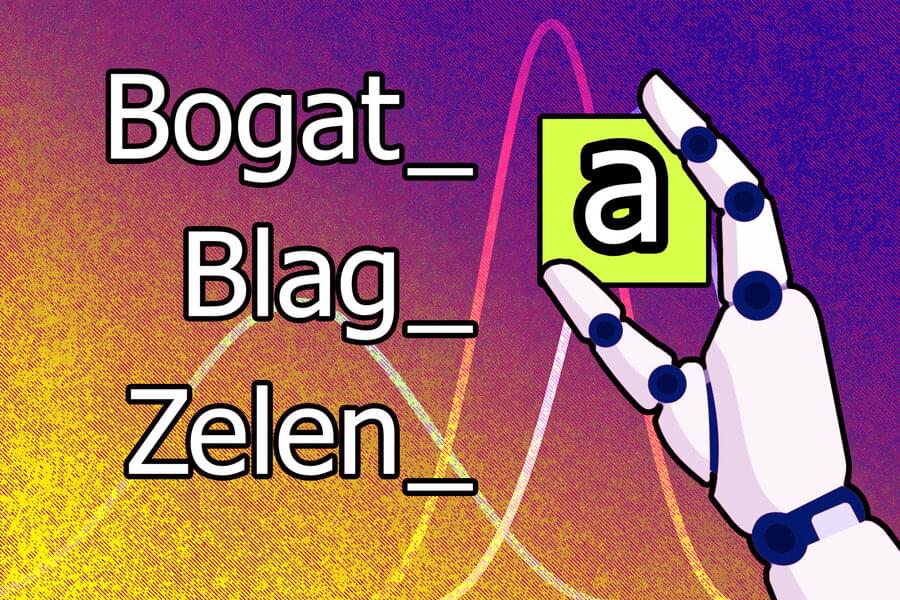
AI that can learn the patterns of human language
Human languages are notoriously complex, and linguists have long thought it would be impossible to teach a machine how to analyze speech sounds and word structures in the way human investigators do.
But researchers at MIT, Cornell University, and McGill University have taken a step in this direction. They have demonstrated an artificial intelligence system that can learn the rules and patterns of human languages on its own.
When given words and examples of how those words change to express different grammatical functions (like tense, case, or gender) in one language, this machine-learning model comes up with rules that explain why the forms of those words change. For instance, it might learn that the letter “a” must be added to end of a word to make the masculine form feminine in Serbo-Croatian.
KRIA Robotic Starter Kit — Robotic Arm
How to create a Robotic Arm under the control of the new KRIA Robotic Starter Kit By Adam Taylor.