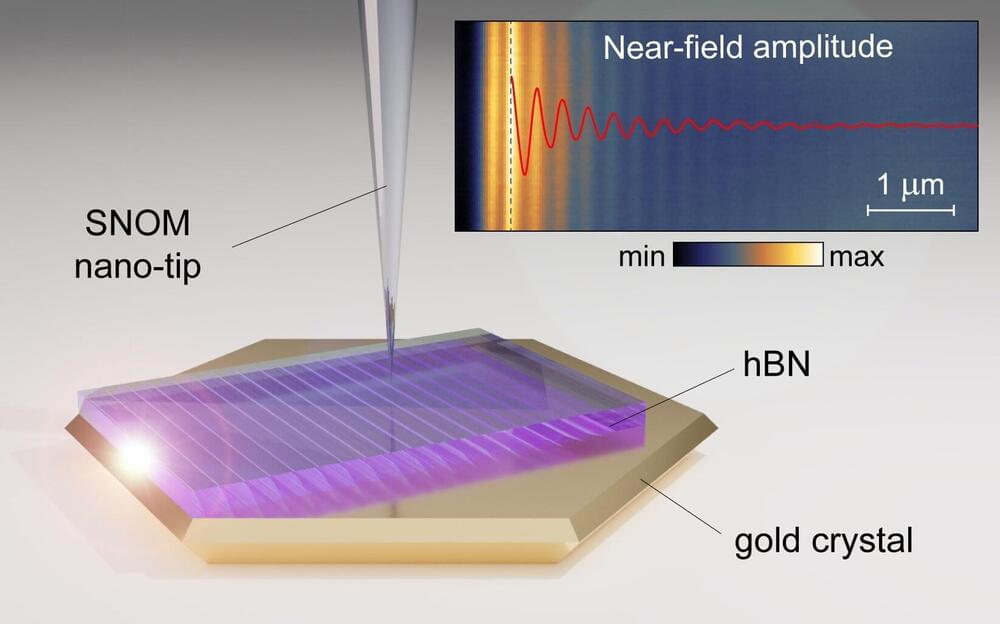
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
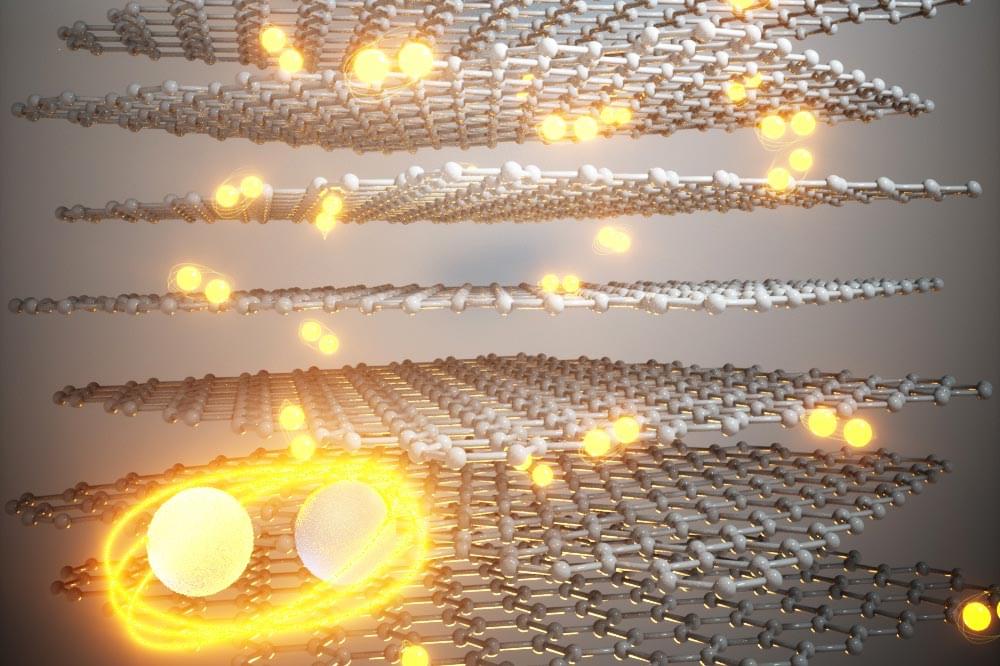
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.