Qualcomm AI Research explores fundamental research to combine causality with AI.
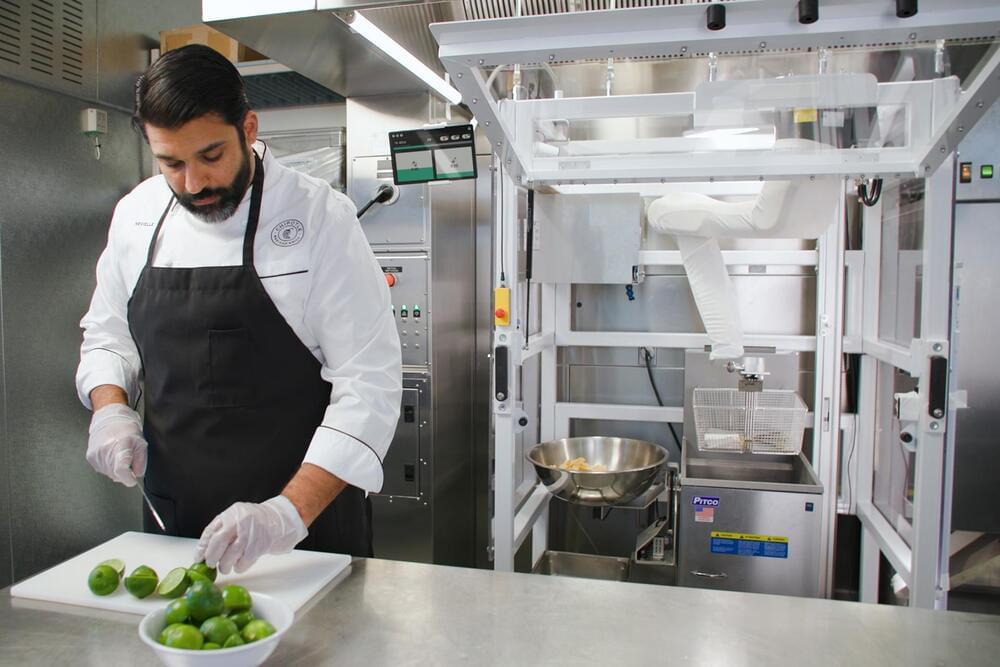


Kitchen robots are making more than just sliders and pizzas. Chipotle is testing Chippy, a version of Miso Robotics’ arm-based automaton (already in use at White Castle) customized to make tortilla chips. The bot not only knows how to replicate Chipotle’s recipe, but is smart enough to add “subtle variations” to keep things interesting — you might get a little more lime or salt.
The test is currently limited a Chipotle “innovation hub” in Irvine, California. However, the Mexican-themed restaurant chain also plans to use Chippy in a southern California restaurant later this year. Feedback from customers and workers will help shape any potential national rollout.
People will still be involved in making most of your burrito or taco, Chipotle said. Like an earlier rollout of the Pepper chat bot, Chippy will be there to “improve the human experience” rather than replace back-of-house cooks. You might get your meals sooner and with more consistent quality, particularly during busy hours.

In molecules, the atoms vibrate with characteristic patterns and frequencies. Vibrations are therefore an important tool for studying molecules and molecular processes such as chemical reactions. Although scanning tunneling microscopes can be used to image individual molecules, their vibrations have so far been difficult to detect.
Physicists at Kiel University (Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, CAU) have now invented a method with which the vibration signals can be amplified by up to a factor of 50. Furthermore, they increased the frequency resolution considerably. The new method will improve the understanding of interactions in molecular systems and further simulation methods. The research team has now published the results in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The discovery by Dr. Jan Homberg, Dr. Alexander Weismann and Prof. Dr. Richard Berndt from the Institute of Experimental and Applied Physics, relies on a special quantum mechanical effect, so-called “inelastic tunneling”. Electrons that pass through a molecule on their way from a metal tip to the substrate surface in the scanning tunneling microscope can release energy to the molecule or take energy up from it. This energy exchange occurs in portions determined by the properties of the respective molecule.

https://youtube.com/watch?v=P_GO2IS_yBQ&feature=share
A great overview of the current state of the space industry and where it is headed in the near future.
A revolution in the history of space travel took off on 20 July 2021. Amazon founder Jeff Bezos flew in his rocket 106 kilometers into outer space. It may have only lasted around 10 minutes, but the trip was the precursor to commercial passenger flights into space.
The Bezos flight, as well as the one billionaire Richard Branson took just a few days earlier, herald a new era of space travel. This looks to be just the beginning of a rekindled space race. Observers suspect it could open up a lucrative market for space tourism. They’re also convinced that the next step will be inevitable: the establishment of human colonies in space. At some point, the day may come when the first person is born in space — or perhaps when humans reach Mars.
The film explores the fluctuations in space technology and the hype around commercial space flights — a topic that’s of great interest to Tesla founder Elon Musk, who founded the aerospace company SpaceX. Predicting the outcome of these developments is tricky. Musk has, in any case, announced plans to make humanity “multiplanetary. According to him, that involves colonizing Mars and enabling life on other planets. Branson and Bezos, on the other hand, are “more interested in how we can use space to help Earth.
Billionaires going on trips into space — is this really progress? Or is it all just about spending lots and lots money? These are questions we’re not yet able to answer.

Desalination will be key to success in maintaining civilizations. Also other technologies like water from air machines. But I also do believe that creating water with some sorta light into matter device like from star trek will make us able to travel anywhere even the stars. Furthermore fusion is key to maintaining civilization as well as it will stem the need for oil or even natural gas which finite and fusion is near infinite.
For years, the energy sector, and almost every other sector, has taken water for granted, viewing it as an abundant resource. But as we move into a new era of renewable energy, the vast amounts of water required to power green energy operations may not be so easy to find. And it’s not just renewables that are under threat from water scarcity, as it also hinders fossil fuel production and threatens food security.
In recent months, we have seen extreme droughts across Europe and the U.S., which are finally making people realise the significance of water security. Stefano Venier, CEO of the Italian energy infrastructure company Snam, highlights the huge impact recent droughts have had on both food security and energy production. Labelled as ‘Europe’s worst drought in 500 years’, the low water levels have restricted shipping capabilities, as well as drying up soil and reducing summer crop yields.
Venier explains, “For a long time, water was considered [as being] for free, as something that is fully available in any quantity.” He went on to say, “Now, we are discovering that with climate change … water can become scarce.” And so, “we have to regain the perception of importance, and the value [that] … the water has, also, with respect to … energy production… we have discovered that without water, enough water, we cannot produce the energy we need, or we can’t ship the fuels for filling the power plants,” he added.

O.o! Circa 2021
False teeth could one day be a thing of the past, thanks to the discovery of an antibody that sparks the regeneration of lost teeth. By inhibiting the action of a gene called USAG-1, the antibody increases the availability of certain growth factors, and could eventually be used to help people grow a new set of pearly whites.
Publishing their work in the journal Science Advances, a team of researchers describes how they genetically modified mice to suffer from tooth agenesis, where some teeth fail to develop. Injecting pregnant mice from this line with the USAG-1 antibody, however, resulted in normal tooth development among their offspring. Moreover, a single administration of the antibody caused the growth of a whole new tooth in regular mice.
The researchers decided to target the USAG-1 gene because it is known to inhibit two signaling molecules known as BMP and Wnt, both of which are involved in tooth development. However, because these compounds also control the growth of a wide range of other organs, interfering with them can produce an array of serious side-effects.