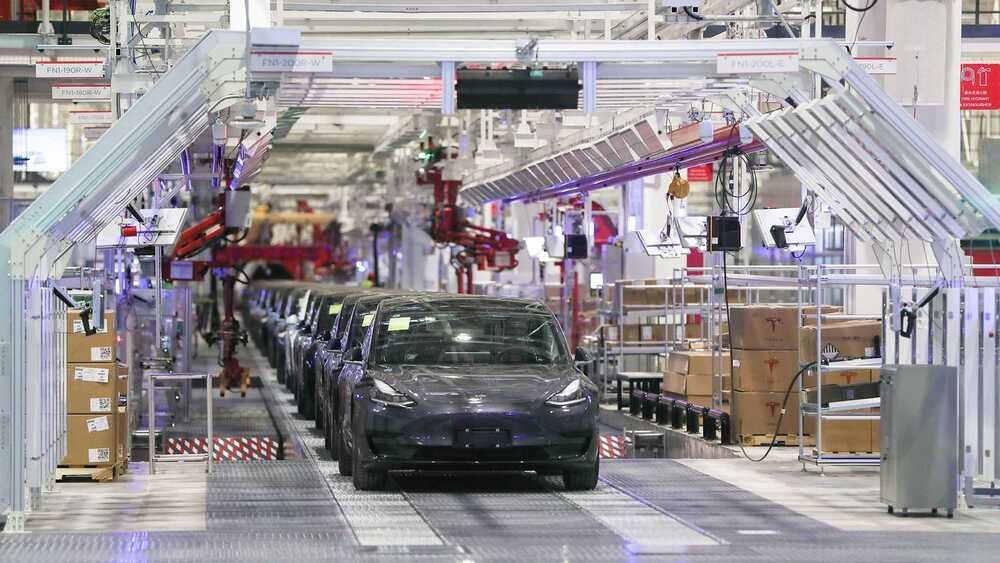
Tesla is considering several sites in Canada for its next Gigafactory according to reports. This comes as Francois-Philippe Champagne, Canada’s industry and innovation minister, recently confirmed talks with Tesla over a new factory. He stated the following (via Reuters):
“Yes, I’m talking to them,” Champagne said, in response to a question about reports of Tesla looking to build a factory in Canada. “I’m talking also to all the automakers around the world.”
Tesla CEO Elon Musk has hinted at a Canadian Gigafactory on numerous occasions, most recently at the automaker’s annual shareholders’ meeting last month. And now reports from Canada suggest representatives from Tesla have already visited numerous locations in Ontario and Quebec. Moreover, Tesla is currently looking for a high-volume recruiter in the Quebec area, indicating the automaker could be on the verge of hiring several thousand Canadian workers.