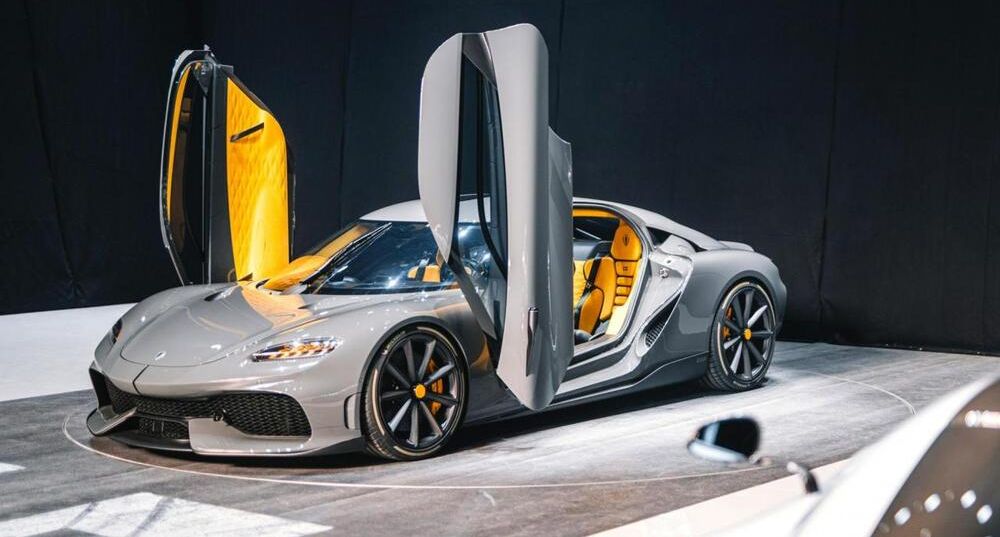
One critical part of the Koenigsegg Gemera’s brain-scrambling powertrain is its ‘Freevalve’ petrol engine. You might have glossed over it while trying to compute the outputs, and they way that engine combines with three electric motors to produce, er, 1700bhp in all. Or in metric, 1.27 Megawatts. Or the power draw of a couple of hundred houses cooking dinner.
Christian von Koenigsegg, though, will talk for hours about this engine. He’s so affectionate about the thing he’s got a nickname rather than the usual dreary car-business habit of codenames. This, then, is the Tiny Friendly Giant.
Giant because 600bhp. Tiny because it’s just two litres and three cylinders. Maybe two litres isn’t that tiny in displacement (though CvK’s cars have mostly had big V8s) but it’s physically very small and easy to package. It has just the three cylinders, and no overhead camshaft casings, and no camshaft drive on the front.