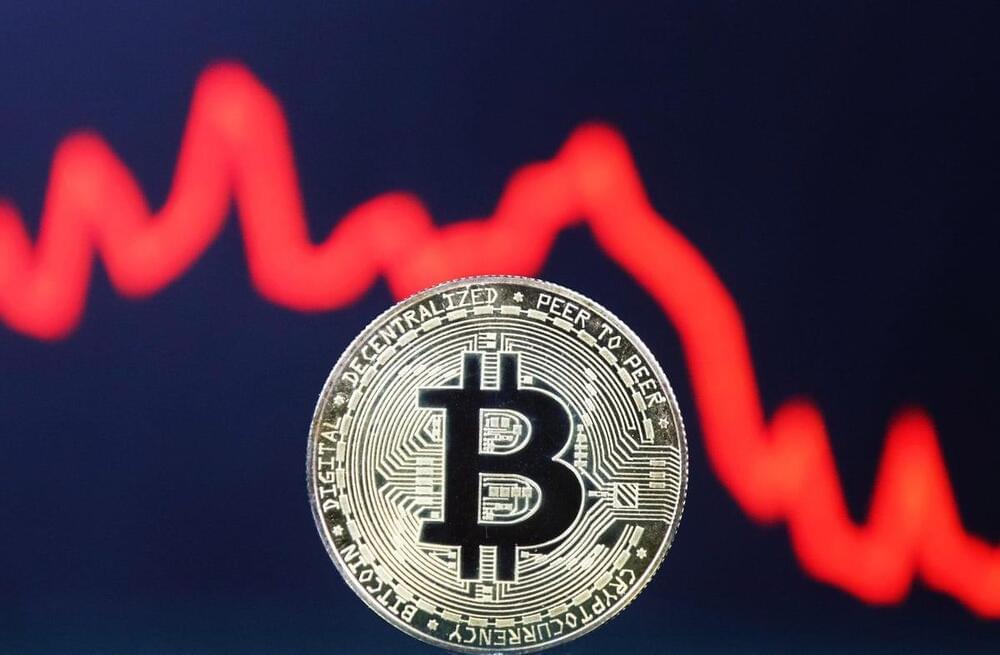
A congressman proposes a game-changing crypto bill, which could be a catalyst for the price of bitcoin, ethereum, bnb, solana, cardano, XRP.



The use of trojanized USB devices for keystroke injection is not a new technique, even for FIN7. Typically the attack targets specific persons with access to the computer systems of the intended victim company. As FIN7 has recently ventured into ransomware, it makes sense for them to look for alternative avenues of infecting computers that are monitored by layers of protective systems, such as firewalls, email scanners, proxy servers, and endpoint security. The tactics and techniques involved in trojanized USB attacks enable FIN7 actors to avoid many of these network-level and endpoint protections by dispensing with malware transmission over the network, minimizing the use of files on disk and employing multiple layers of encoding of the malware’s scripts and executable code.
Pertinently, FIN7 recently created “Bastion Secure”, a fake information security company, and employed system administrators to unknowingly assist in system exploitation. It is possible that trojanized USBs are being constructed and used by these administrators for penetration testing. Alternatively, they might also be providing trojanized USBs to clients or prospective clients through some form of ruse (for example, telling the client it contains documentation on the fake company’s services). In either case, the clients or prospective clients could become victims of a trojanized USB attack, resulting in FIN7 gaining unauthorized remote access to systems within victims’ networks.
Gemini Advisory Mission Statement
I respect what vegans intend to do, but I think they will have to find a different food source soon.
To start comparing quotes and simplify insurance-buying, check out https://www.Policygenius.com/Thoughty2 Thanks to Policygenius for sponsoring this video!
Get my new book Bread and Circuses: https://bit.ly/breadandcircusesbook.
Listen to my new podcast Random Interesting Facts: http://bit.ly/RIFThoughty2
Or watch it on YouTube: http://bit.ly/RIFPodcastYT
Thoughty2 Audiobook: https://geni.us/t2audio.
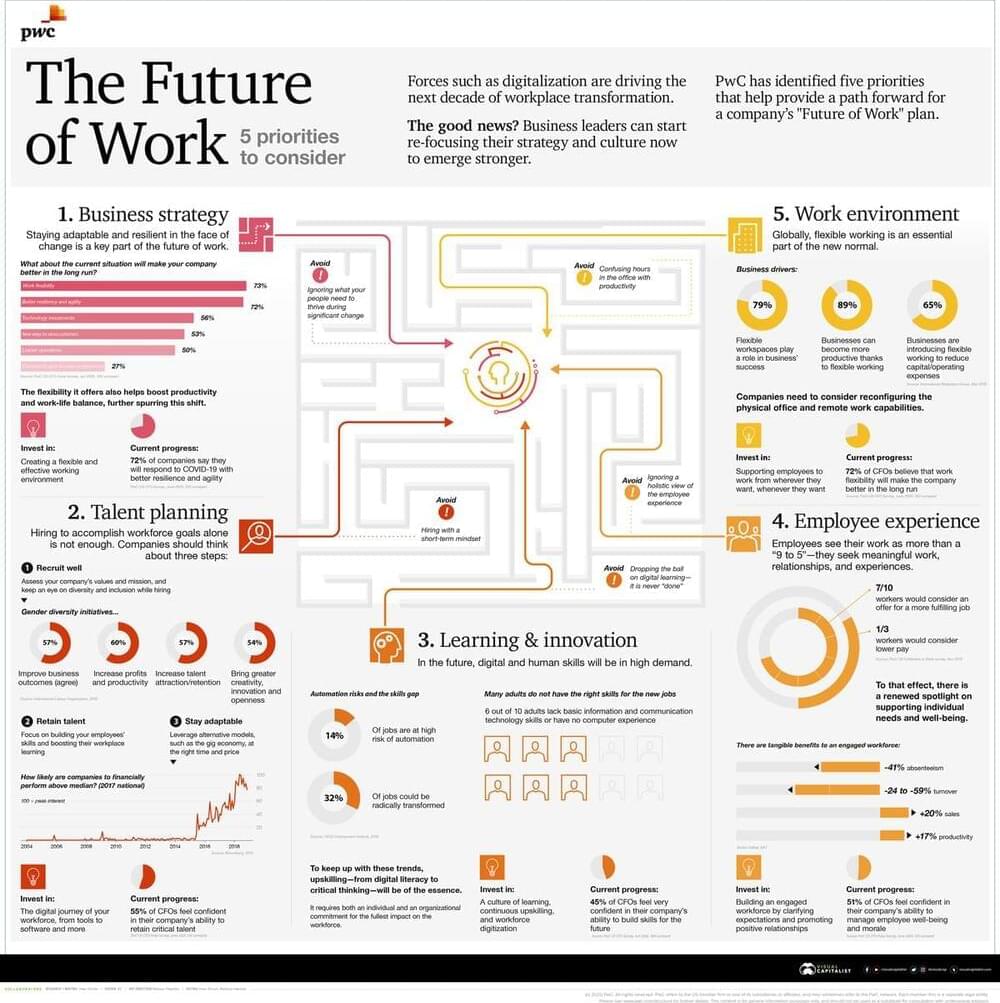
But still there are many areas such as carpenter, electrician e.t.c where remote work is not possible.
As jarring as the transition to remote work was during the coronavirus pandemic, it was modest compared to what’s coming next, says Adam Ozimek, a labor economist at the freelancing platform Upwork. He argues that the next phase of remote work will transform economies, as more companies revise their policies to accommodate employees who have permanently shifted to working remotely, and more workers move to places they’ve always wanted to live but couldn’t.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.


The atomic nucleus is a tough nut to crack. The strong interaction between the protons and neutrons that make it up depends on many quantities, and these particles, collectively known as nucleons, are subject to not only two-body forces but also three-body ones. These and other features make the theoretical modeling of atomic nuclei a challenging endeavor.
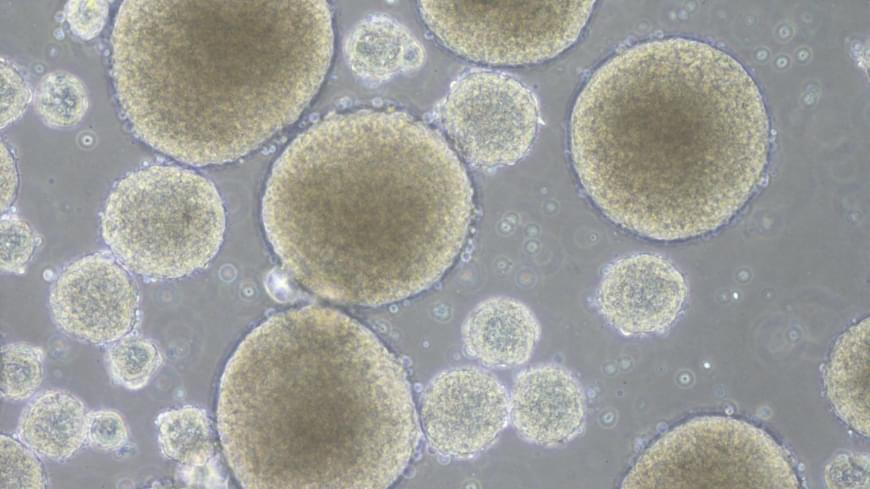
About 2 million cells are transplanted into each patient in the treatment. They were created from iPS cells stored at Kyoto University in western Japan, according to Keio University.
In the future, the university plans to increase the number of cells to be transplanted in order to enhance the effectiveness of the treatment.
Some 5,000 people sustain spinal cord injuries every year in Japan and the number of people living with spinal cord injuries is said to exceed 150,000.
The Chinese manufacturer of flexible and lightweight solar modules has commissioned the first expansion of its production capacity of 500 megawatts. Another 500 megawatts will have been added by June of 2022.
