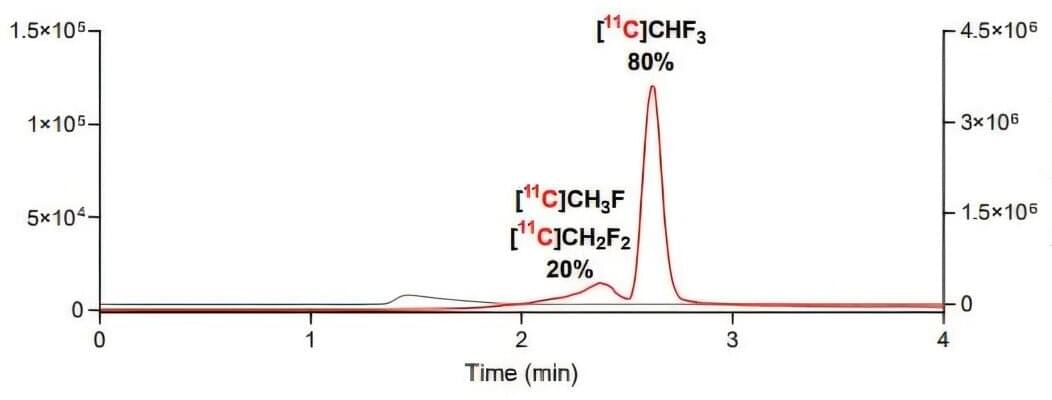
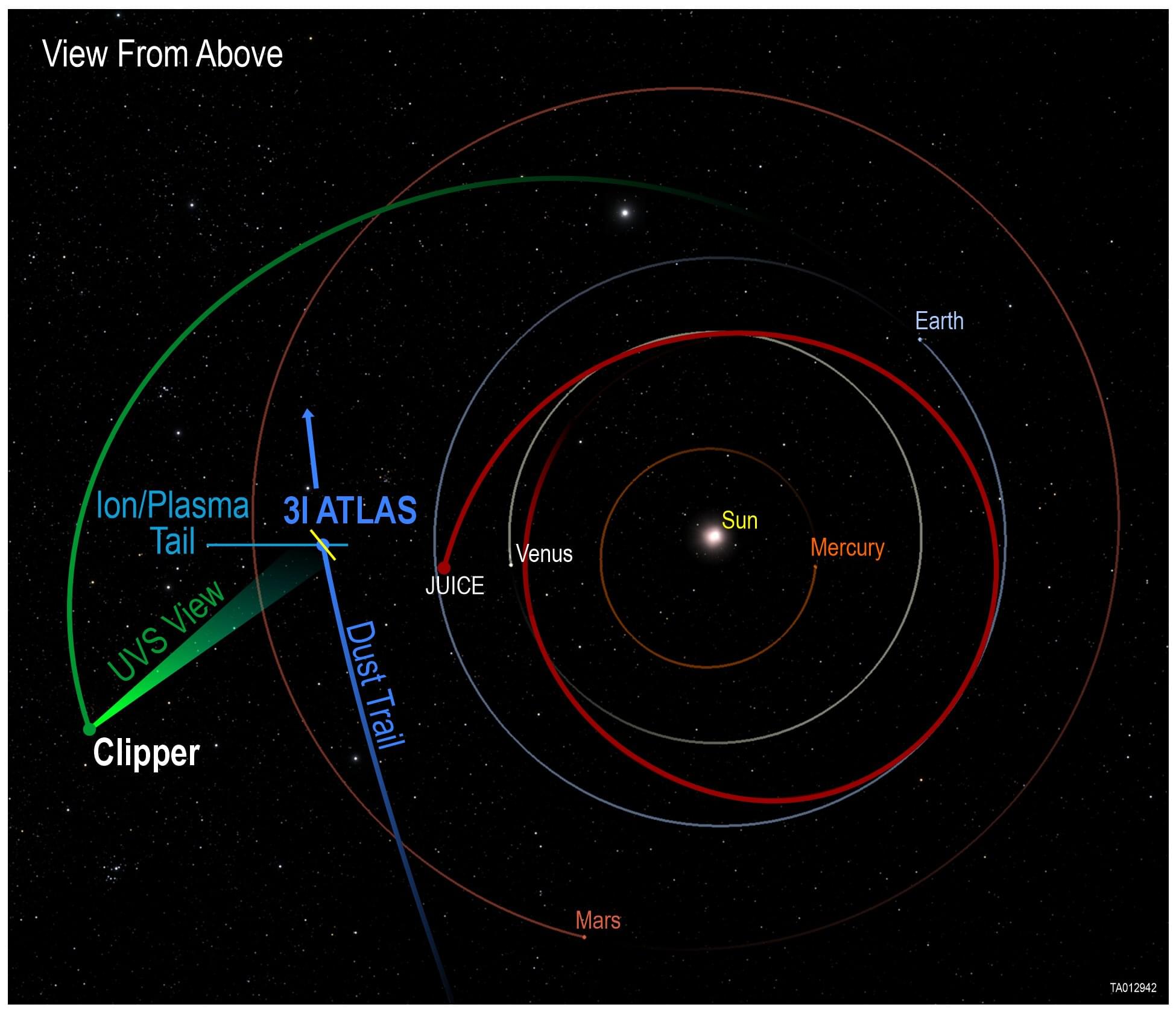
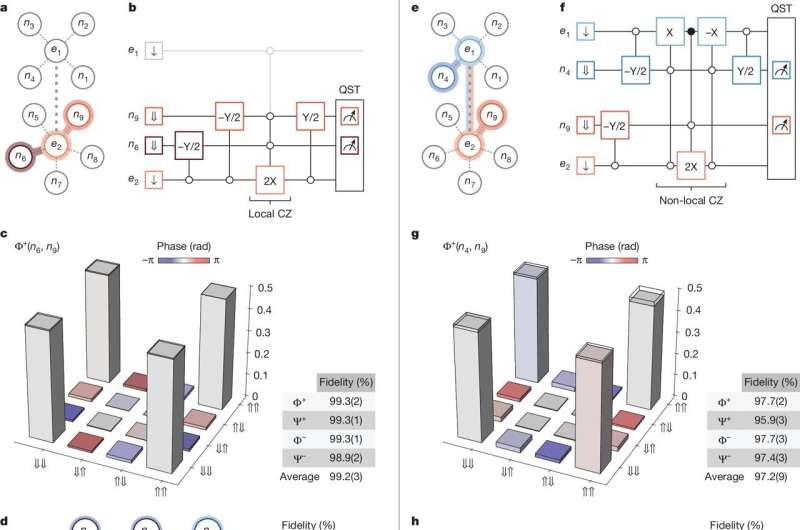
Launched in March, NASA’s SPHEREx space telescope has completed its first infrared map of the entire sky in 102 colors.
While not visible to the human eye, these 102 infrared wavelengths of light are prevalent in the cosmos, and observing the entire sky this way enables scientists to answer big questions, including how a dramatic event that occurred in the first billionth of a trillionth of a trillionth of a second after the big bang influenced the 3D distribution of hundreds of millions of galaxies in our universe.
In addition, scientists will use the data to study how galaxies have changed over the universe’s nearly 14 billion-year history and learn about the distribution of key ingredients for life in our own galaxy.