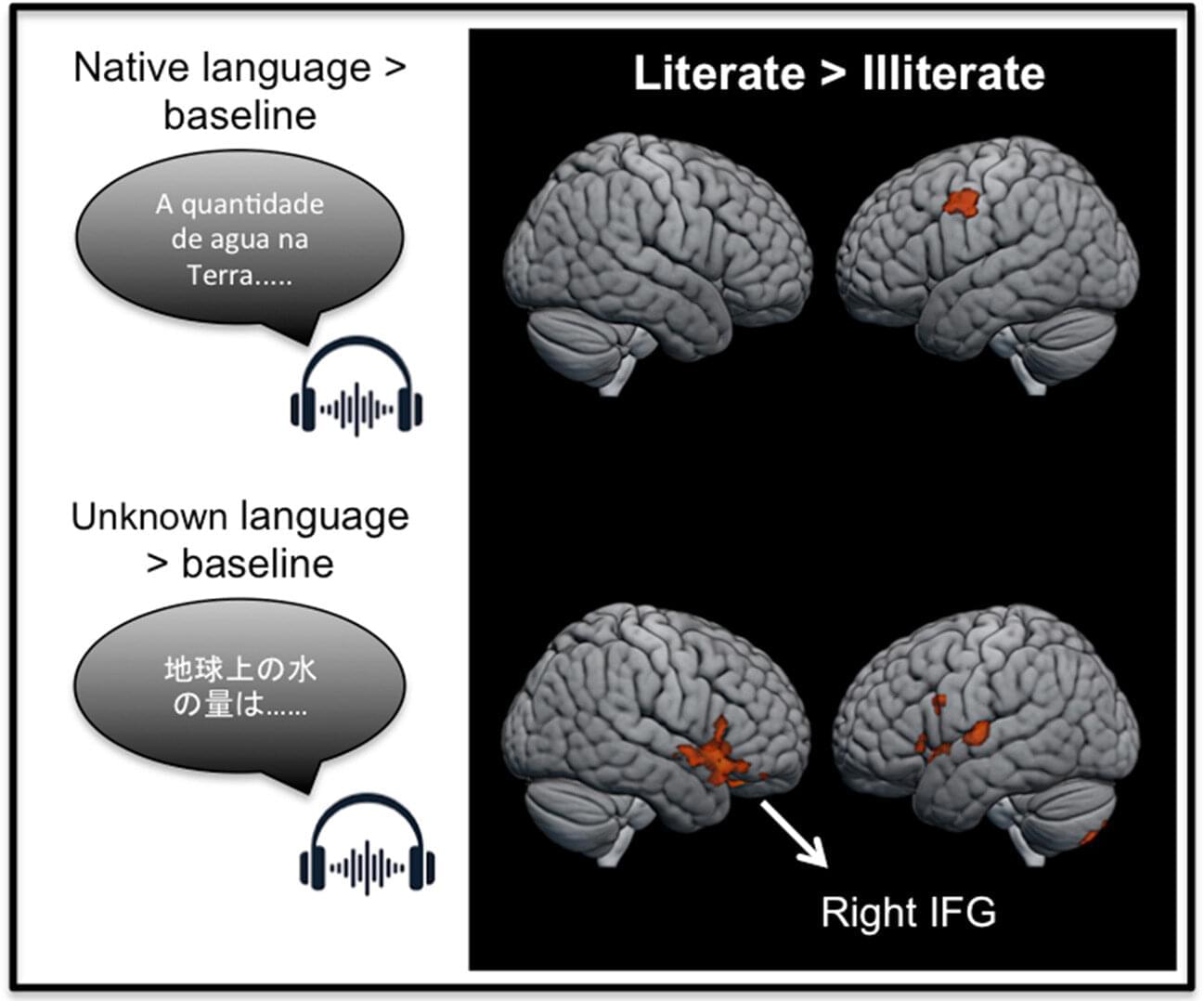
Learning to read reshapes how the brain processes language. New research from Baycrest and the University of São Paulo shows that learning to read fundamentally changes how the brain responds to spoken language, even when no written words are present. While previous brain imaging studies have demonstrated that literacy strongly affects how the brain responds to written words, this study is among the first to show differences in brain activity during listening alone.
The findings confirm that as people learn to read, they develop a skill known as phonemic awareness, the ability to hear and manipulate the individual sounds that make up spoken words, a core foundation of reading. The study shows that learning to read improves how the brain processes spoken language by increasing sensitivity to these component sounds. This, in turn, strengthens short-term verbal memory, supporting the ability to learn complex skills and manage the cognitive demands of daily life.
The work is published in the journal Cortex.