The man was walking along a river when he made the amazing discovery, which experts estimate to be around 84 million years old.
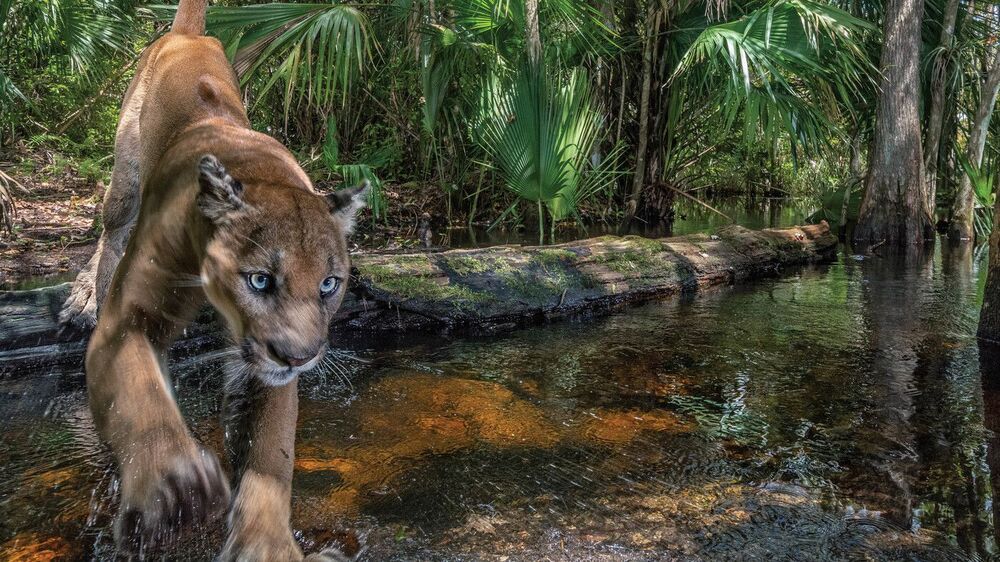
Kelly and photographer Carlton Ward Jr. are featured in the April issue of National Geographic magazine. The article provides a glimpse into the life of the Florida panther, whose population once dwindled to below two dozen but has since rebounded to more than 200. Still, serious risks remain. In the past few weeks alone, two more endangered animals were killed after being struck by vehicles. Those deaths highlight a problem — as well as a success story for the cat the Cherokee once called “Lord of the forest.”
To capture panthers on camera, Kelly and Ward first had to find them. That’s not an easy task on Florida’s sandy soil, which makes them hard to track. You have to find really fresh tracks, Kelly said.
“First things first is identifying the track and knowing if it’s a panther or not. And then the real trick is following it,” he said. “So because they go so far, like in any given night, a panther might walk oh, a couple of miles. Maybe more. To actually follow panther tracks to find the panther itself — it’s way harder than it is for any of those African animals. Way harder.”
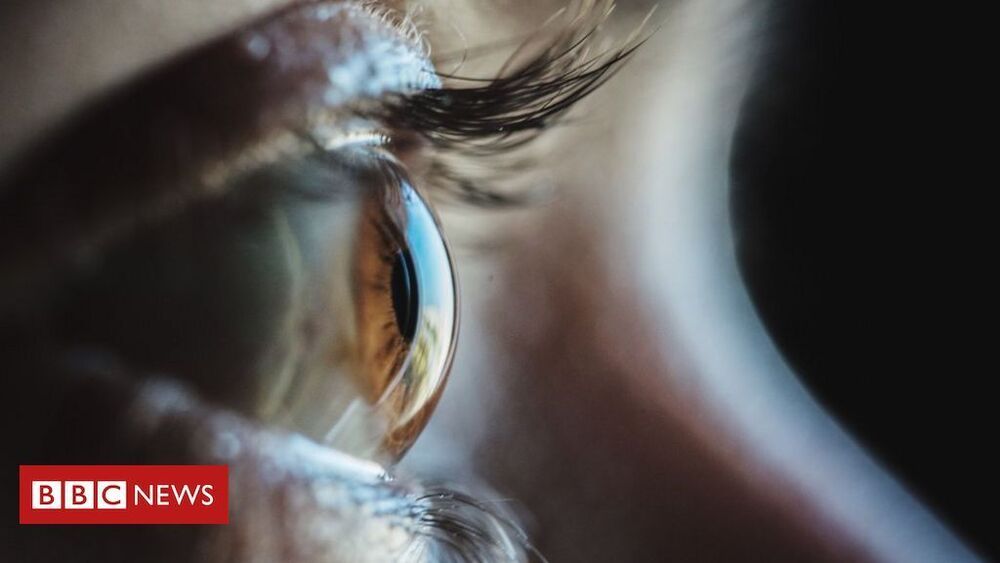
The patient was completely blind before the treatment — now he can see and count objects on a table.
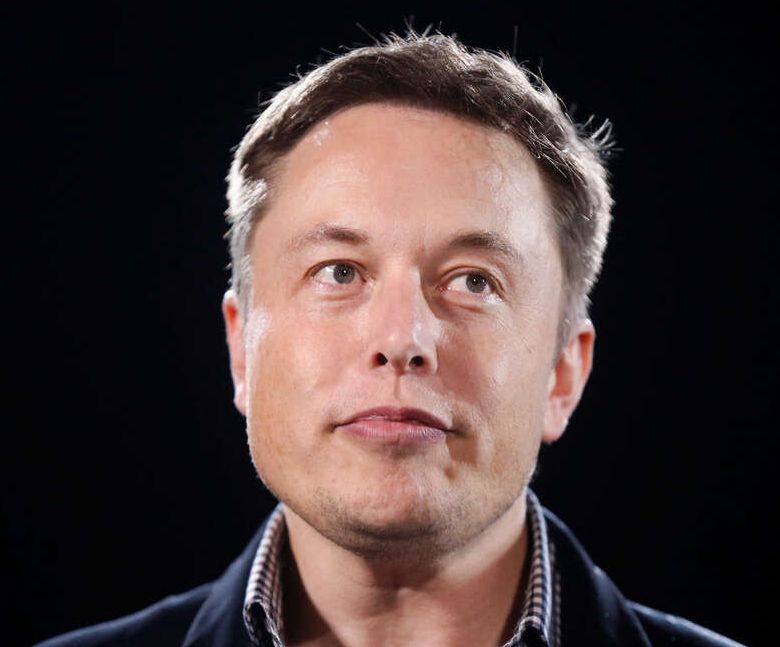
The price of bitcoin jumped about 4% Monday afternoon after Tesla CEO Elon Musk tweeted that he was having active discussions regarding the sustainability of the digital coin.
Bitcoin was trading around $38074, according to Coindesk, when at about 3:42 p.m. ET Musk posted on Twitter: “Spoke with North American Bitcoin miners. They committed to publish current & planned renewable usage & to ask miners WW to do so. Potentially promising.”
Within minutes, the price had shot up to more than $39500. Overall, the coin is up more than 17% in the last 24 hours.
Iowa high school senior Dasia Taylor has invented color-changing sutures that can catch an infection early.
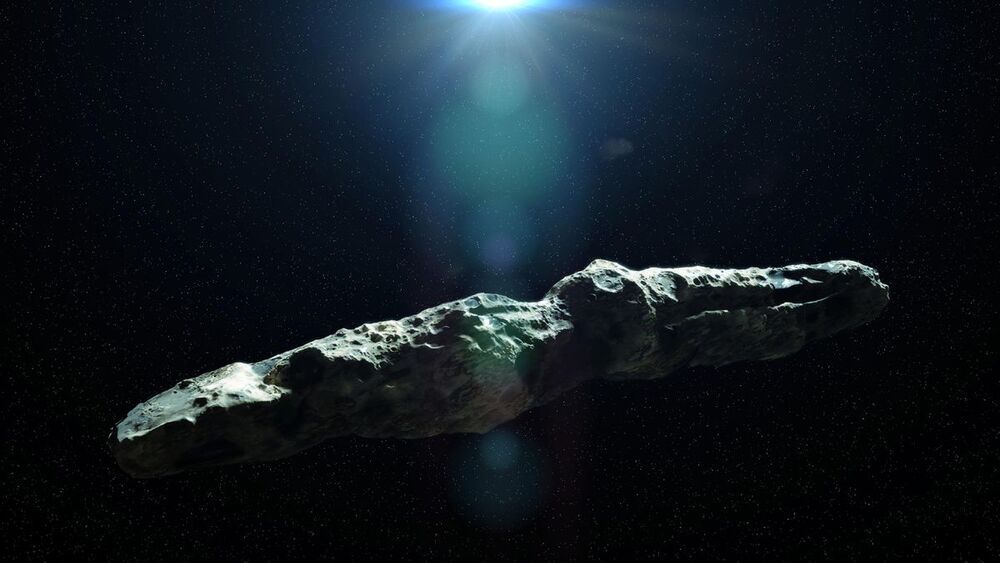
Even if the interstellar object known as Oumuamua were an interstellar lightsail, it could never travel fast enough to be practical, says a new paper.
Your genes may have more influence than anything you put into your body when it comes to how iron relates to longevity. Here’s what you need to know.
The recent announcement that scientists have made human-monkey embryos and cultured them in the lab for two weeks made international headlines.
The technology to make animals that contain cells from other species has been available for decades and used extensively in research. These organisms are called “chimeras”.
But this latest advance highlights the need to broaden the discussion around the possible benefits of such research and, specifically, how inter-species chimeric research should be conducted in future.
It’s that time of year where the federal holiday in the United States commemorating the Declaration of Independence of the United States, (on July 4, 1776) is celebrated. To all my American fans I hope you have an awesome day! To celebrate I’m listing my favorite superheroes to rock the “Red, White and Blue”.
Happy Independence Day (Fourth of July)!
The adhesion and colonization or biofilm formation include primary stage in bacterial infections. Major adhesion virulence factors in this step include type I fimbriae (FimH) and pilli structures for attachment to the host cells7,8. Furthermore, numerous bacteria secrete toxins and extracellular enzymes which play a crucial role in the apoptosis or necrosis of epithelial cells or immunocytes. Various virulence factors of A. baumannii such as adhesins genes like kpsMII (group 2 capsule synthesis) and fimH, tratT (serum resistance associated), fyuA (yersiniabactin receptor) and iutA (aerobactin receptor) have been investigated previously9,10. An important polysaccharide for biofilm formation is encoded by pgaABCD locus11. Biofilm production is a strategy to escape from harsh conditions and immune responses, hence play as reservoirs for drug-resistant systemic infections. Biofilm-producing A. baumannii has been isolated from several infectious origins such as pneumonia and devise-associated infections. Bacterial within biofilm can resist significantly more against antibiotics compared to planktonic mode of growth12. Hence, biofilm-mediated infections are in relapse more frequently13.
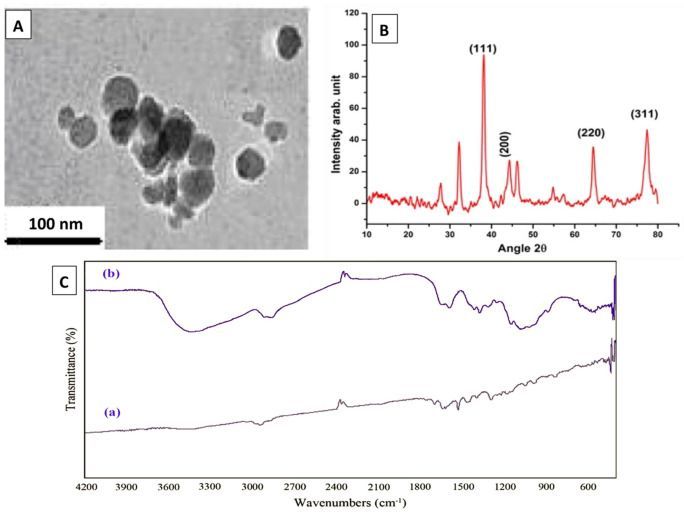
Therefore, there is an urgent need to enhance the effects of antimicrobials against pathogenic bacteria. In recent years, interest has enhanced towards application of nanoparticles as therapeutic regimens14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), which have low toxicity in ecosystems and have high rate of surface capacity, can inhibit accumulation of biofilm materials responsible for evasion and protection22,23,24.
The aim of this study was to isolate A. baumannii from wound infections, determine their resistance and virulence profile, and assess the impact of AgNPs on the bacterial growth, virulence and biofilm-related gene expressions in the isolated strains.