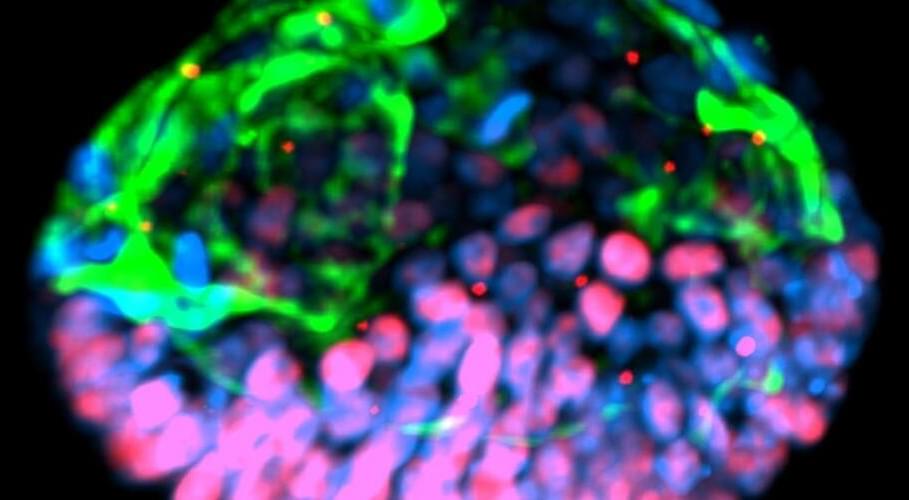
What drew his attention was that the cells seemed to change much faster than expected—they arranged themselves rapidly over a few days into a lopsided circle.
What was it? Shao startled Googling to see if he could identify the structure. That’s when he landed on a website called The Virtual Human Embryo and found some microscope photos of ten-day old human embryos shortly after implantation, fused to the uterine wall. There was the beginning of the amniotic sac and, inside it, the embryonic disc, or future body. They matched what he was seeing.
Shao informed his coworkers, a mixed team of biologists and engineers, at the University of Michigan. “When I showed the image to the team, everyone said, ” Wow, we need to figure out what to do,” says Shao. Had they somehow made a real human embryo from stem cells? ” At that point, we started to be more cautious.”