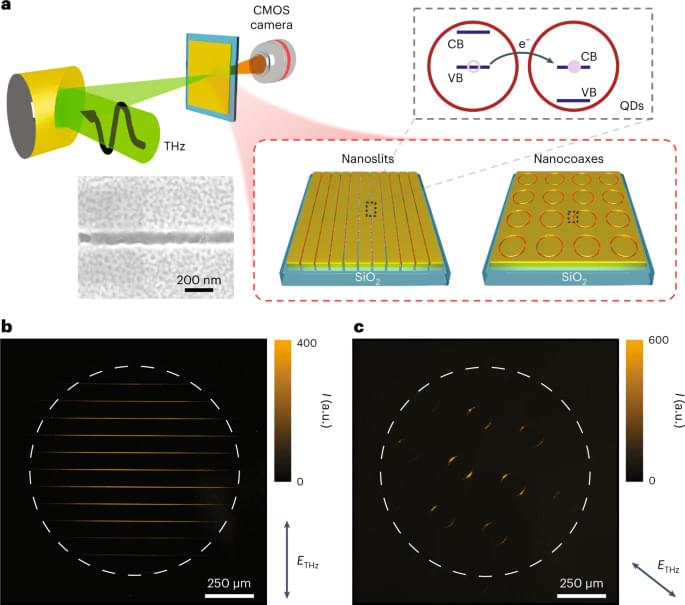
A terahertz camera based on an upconversion mechanism to the visible range can image both THz polarization state and field strength.

Get a free month of Curiosity Stream: https://curiositystream.com/isaacarthur.
Our future in the galaxy is typically envisioned as tied to the stars, be it on planets orbiting them or vast megastructures fueled by the alien suns, and yet the true future of humanity might be to dwell in the vast gulfs between the stars or even in a galaxy in which those stars have ceased to exist.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/exo-stellar-civilizations.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/exo-stellar-ci…ation-only.
Credits:
Exo-Stellar Civilizations.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 281a, March 14, 2021
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Jason Burbank.
Jerry Guern.
Keith Blockus.
S. Kopperud.
Cover Art:
To convert heat into electricity, easily accessible materials from harmless raw materials open up new perspectives in the development of safe and inexpensive so-called “thermoelectric materials.” A synthetic copper mineral acquires a complex structure and microstructure through simple changes in its composition, thereby laying the foundation for the desired properties, according to a study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
The novel synthetic material is composed of copper, manganese, germanium, and sulfur, and it is produced in a rather simple process, explains materials scientist Emmanuel Guilmeau, CNRS researcher at CRISMAT laboratory, Caen, France, who is the corresponding author of the study. “The powders are simply mechanically alloyed by ball-milling to form a precrystallized phase, which is then densified by 600 degrees Celsius. This process can be easily scaled up,” he says.
Thermoelectric materials convert heat to electricity. This is especially useful in industrial processes where waste heat is reused as valuable electric power. The converse approach is the cooling of electronic parts, for example, in smartphones or cars. Materials used in this kind of applications have to be not only efficient, but also inexpensive and, above all, safe for health.

A team of scientists from the University of Sciences and Technology of China has proposed a bold solution for the “measurement problem” in quantum mechanics, suggesting the eventual outcome for states of existence is determined by a “game” between the observer and nature.
For over a century, the quantum realm has imposed an abundance of bizarre obstacles along the road to understanding universal existence.
In the microscopic world of atoms and subatomic particles, nature demonstrates unparalleled strangeness, becoming unpredictable and operating in contrast to how it behaves at the macroscopic scale defined by classical physics.


Summary: Mutations of the PTEN gene cause neurons to grow to twice the size and form four times the number of synaptic connections to other neurons as a normal neuron. Removing the RAPTOR gene, an essential gene in the mTORC1 signaling pathway, prevents the neuronal and synaptic overgrowth associated with PTEN mutations. Using Rapamycin to inhibit mTORC1 rescues all the changes in neuronal overgrowth.
Source: the geisel school of medicine at dartmouth.
Findings from a new study published in Cell Reports, involving a collaborative effort between researchers at the Luikart Laboratory at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine and the Weston Laboratory at the University of Vermont, are providing further insight into the neurobiological basis of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) and pointing to possible treatments.
With her eerily realistic facial expressions and movements, Ameca has been billed as the world’s most advanced humanoid robot.
But if that wasn’t impressive enough, soon she could be walking around too.
That’s because the robot — which has been designed by British company Engineered Arts — has revealed that engineers are working on ‘prototype legs’ which should be ready within the next year.
Detecting cancer early before it spreads throughout the body can be lifesaving. This is why doctors recommend regular screening for several common cancer types, using a variety of methods.
Colonoscopies, for example, screen for colon cancer, while mammograms screen for breast cancer.
While important, getting all these tests done can be logistically challenging, expensive, and sometimes uncomfortable for patients. But what if a single blood test could screen for most common cancer types all at once?

In laboratory mice, pituitary dwarfism caused by genetic reduction or elimination of the activity of growth hormone (GH) significantly extends lifespan. The effects of congenital pituitary dwarfism on human longevity are not well documented. To analyse the effects of untreated pituitary dwarfism on human lifespan, the longevity of a diverse group of widely known little people, the 124 adults who played “Munchkins” in the 1939 movie The Wizard of Oz was investigated. Survival of “Munchkin” actors with those of controls defined as cast members of The Wizard of Oz and those of other contemporary Academy Award winning Hollywood movies was compared. According to the Kaplan–Meier survival curves, survival of female and male “Munchkin” actors was shorter than cast controls and Hollywood controls of respective sexes.
The real origins of Ancient Israel in history is a fascinating area of research. In this interview we discuss ancient Canaan being ruled by Egypt and the conflicts between Philistine peoples and Israel. The God El and Yahweh from Canaan to Israel and its polytheistic origins. We also get into creation accounts prior to Genesis in the ancient Babylonian sources like the Enuma Elish and where Leviathan comes from.
Lester L. Grabbe is a retired American scholar and Emeritus Professor of Hebrew Bible and Early Judaism at the University of Hull, England.
Get Professor Lester L. Grabbe books here 👉 https://amzn.to/35FqNYf.
Sign up for the 7 hour resurrection debate between Dr’s Bart Ehrman & Mike Licona here.
https://www.mythvisionpodcast.com/resurrection.
Sign up for Dr. Bart D. Ehrman’s Genesis “In The Beginning” Webinar here: https://www.mythvisionpodcast.com/genesis.
Sign up for Dr. Bart D. Ehrman’s Christmas Webinar here: