The new Covid variant omicron will likely “overwhelm the whole world” in the coming months, according to Singapore doctor Leong Hoe Nam.
People and companies are betting on life becoming more digitized and the much-hyped, little-understood metaverse taking off; virtual land is becoming as much of an investment as physical land, and if current trends continue, may stand to give early adopters a huge payout. Metaverse Group chose its plot of land very intentionally, and knows exactly what use it will be put to; located in Decentraland’s Fashion Street district, the space will be used “to facilitate fashion shows and commerce within the exploding digital fashion industry.”
Let’s back up a bit. Decentraland is a decentralized virtual world built on the Ethereum blockchain, with “decentralized” obviously being the key word and the platform’s big differentiator. “The people who use Decentraland own Decentraland,” Dave Carr, communications lead for the platform, told Euronews Next. “We have a decentralized autonomous organization in which people can submit proposals and vote on proposals submitted by others. And this effectively determines the future direction of Decentraland.”
Facebook, now Meta, aims to rule the metaverse of the future, but it seems likely that people will gravitate towards platforms like Decentraland precisely because they’re not owned or controlled by a centralized authority. Facebook hasn’t done a great job of earning its users’ trust, and it could take a long time for the company to turn consumer sentiment around. Meanwhile, Decentraland’s emphasis on autonomy and the lack of a single powerful decision-maker may be just what virtual world enthusiasts are looking for.
Go to https://NordVPN.com/sabine to get a 2-year plan plus 4 additional months with a huge discount!
At 2 mins 26 seconds when I say “Peter” I meant “Paul”. Sorry!
Dark energy has got something to do with quantum vacuum fluctuation, whoa, physics. You have probably heard something like that. Alas, that isn’t quite right. In this video I clear up the confusion. Vacuum energy is much easier to understand than you might have been told. And it doesn’t fluctuate.
You can support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/Sabine.
0:00 Intro.
0:27 Vacuum Energy according to Scientific American.
2:07 Vacuum Energy according to Sabine.
7:11 The Gas Analogy for Dark Energy.
10:04 Sponsor Message.
#physics #science
Here’s a quick reminder that one of the expected results of the current pandemic is the slow, controlled, but inevitable destruction of the Canadian economy as government assets are secretly pulled out of circulation and redistributed to international bankers and their wealthiest clients.
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s Liberal government is asking Parliament to approve billions in new spending during a brief four-week sitting in Ottawa, but is facing questions because it has not released a full accounting of how it spent more than $600Bln last year.
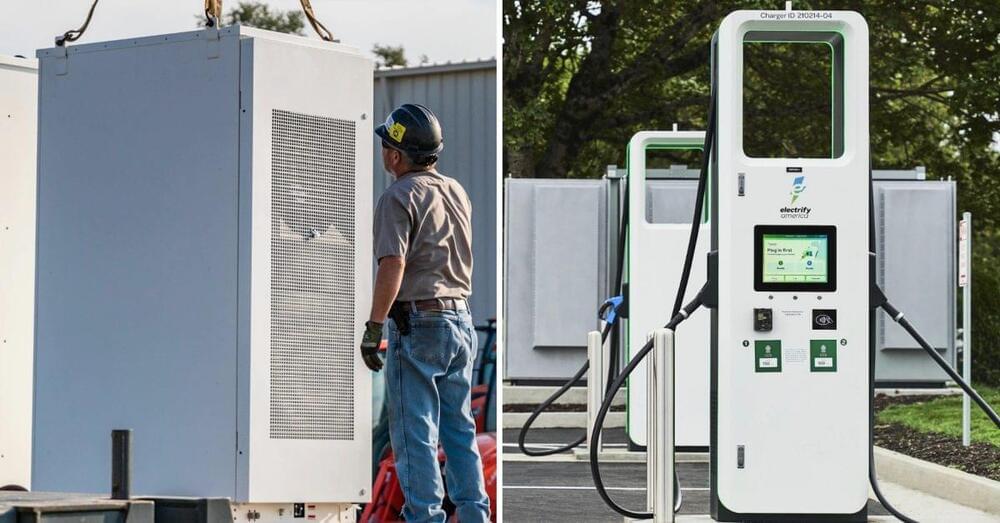
Electrify America announced that it has now deployed over 30 MW of battery capacity using Tesla Powerpacks at over 140 charging stations.
In 2019, Tesla and Electrify America, VW’s electric vehicle charging network, announced that they reached a deal for the former to deploy Powerpacks at more than 100 charging stations operated by the latter.
We have been tracking their progress in deploying those battery systems since it appears to be the largest deployment of energy storage at electric vehicle charging stations.
After Google ditched Qualcomm chips in its Pixel phones, Android chief Hiroshi Lockheimer brings a message of peace to Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Summit.
Harrison.ai, a Sydney-based company that creates medical devices with AI technology, announced today it has raised $129 million AUD (about $92.3 million USD) in what it called one of the largest Series B rounds ever for an Australian startup.
The funding was led by returning investor Horizons Ventures and included participation from new investors Sonic Healthcare and I-MED Radiology Network. Existing backers Blackbird Ventures and Skip Capital also returned for the round, which brings Harrison.ai’s total raised over the past two years to $158 million AUD.
Harrison.ai announced it has also formed a joint venture with Sonic Healthcare, one of the world’s largest medical diagnostics providers, to develop and commercialize new clinical AI solutions in pathology. The partnership will focus first on histopathology, or the diagnosis of tissue diseases.
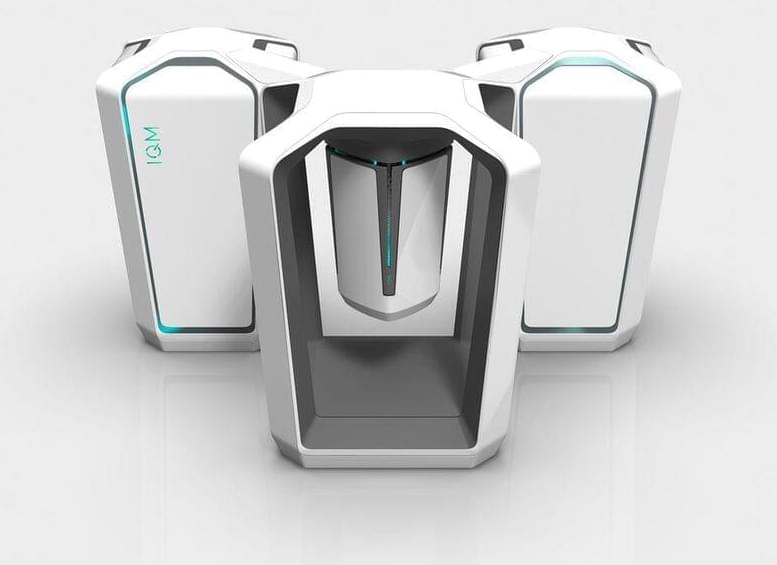
Finland’s first quantum computer was commissioned at a research center near the capital Helsinki, where scientists will use it to study next-generation computing power.
The 5 quantum-bit computer was developed “to learn how to build a quantum computer, how to program one and how to operate one in the future,” Pekka Pursula, research manager at the VTT Technical Research Centre, said by phone on Tuesday. The machine was the joint work of VTT and quantum computing hardware company IQM Finland Oy.
“This 5-qubit computer has relatively low computational power, and it’s not enough to solve practical problems,” Pursula said. The researchers plan to build a 50-qubit machine by 2024 that could be used for applications such as modeling viruses and drugs, and designing materials that today’s technology is ill-equipped to handle.
Scientists say they have made a major step forward in storing information in molecules of DNA.
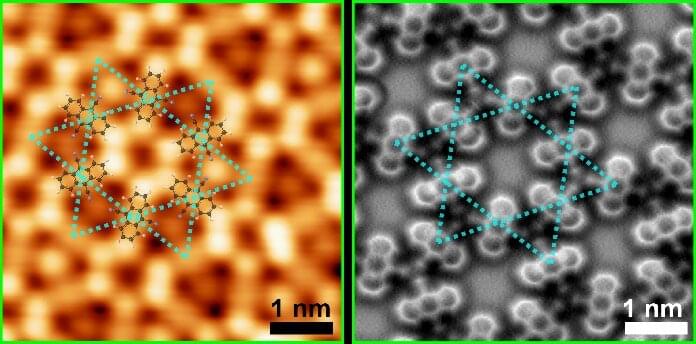
A 2D nanomaterial consisting of organic molecules linked to metal atoms in a specific atomic-scale geometry shows non-trivial electronic and magnetic properties due to strong interactions between its electrons.
A new study, published today, shows the emergence of magnetism in a 2D organic material due to strong electron-electron interactions; these interactions are the direct consequence of the material’s unique, star-like atomic-scale structure.
This is the first observation of local magnetic moments emerging from interactions between electrons in an atomically thin 2D organic material.