Europe’s new Digital Markets Act aims to make larger messaging platforms ‘interoperable’ with smaller ones. No wonder the tech titans are running scared.


NOTE FROM TED: Research around aging discussed in this talk remains an ongoing field of study. Please do not look to this talk for health advice. TEDx events are independently organized by volunteers. The guidelines we give TEDx organizers are described in more detail here: http://storage.ted.com/tedx/manuals/tedx_content_guidelines.pdf.
Have you ever wondered how long you will live? And if so, how could you change that number to live drastically longer? The science might be in your favor: follow David Sinclair, Australian biologist and professor of genetics at Harvard University, as he shares his research on slowing and reversing the process of aging in mice, and how the same technology may someday be transferable to humans. David Sinclair, Australian biologist and professor of genetics at Harvard Universityhis insightful research into the science of age reversal and anti-aging medicine.
David Sinclair, Australian biologist and professor of genetics at Harvard Universityhis insightful research into the science of age reversal and anti-aging medicine. This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.
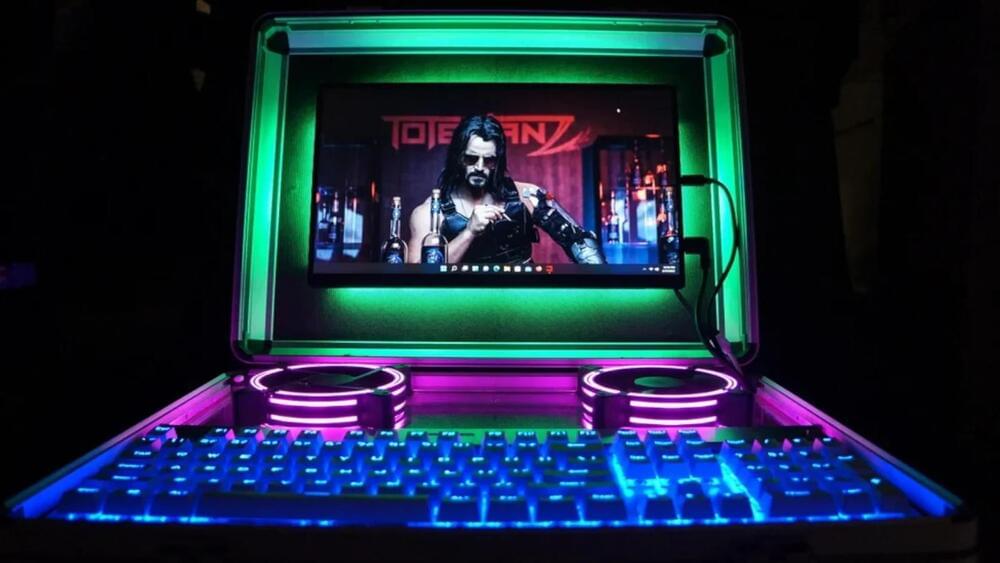

There are plenty of gaming laptops on the market these days, but none quite fit the requirements of one [ParticularlyPippin]. Thus, they set out on building their own portable computer, ending up with a rig in a briefcase with a decidedly cyberpunk feel.
The design relies on desktop components, with the idea being to make a machine with better upgradability than a typical laptop. The briefcase itself is a nice deep-shell unit, and was given a wooden baseboard to hold all the components. It was then provided with standoffs and mountings for a Mini-ITX motherboard, as well as all the necessary add-ons like fans and storage. As in many odd-form-factor builds, a PCI-E riser cable comes in handy to hook up the GPU.
As for the user interface, a USB portable monitor is paired with a mechanical keyboard for the appropriate amount of clackity-clack when hacking out in the field. The icing on the cake, however, are the RGB strip backlights controlled via MSI’s software that really make the final result pop.
A new method of identifying gravitational wave signals using quantum computing could provide a valuable new tool for future astrophysicists.
A team from the University of Glasgow’s School of Physics & Astronomy have developed a quantum algorithm to drastically cut down the time it takes to match gravitational wave signals against a vast databank of templates.
This process, known as matched filtering, is part of the methodology that underpins some of the gravitational wave signal discoveries from detectors like the Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory (LIGO) in America and Virgo in Italy.
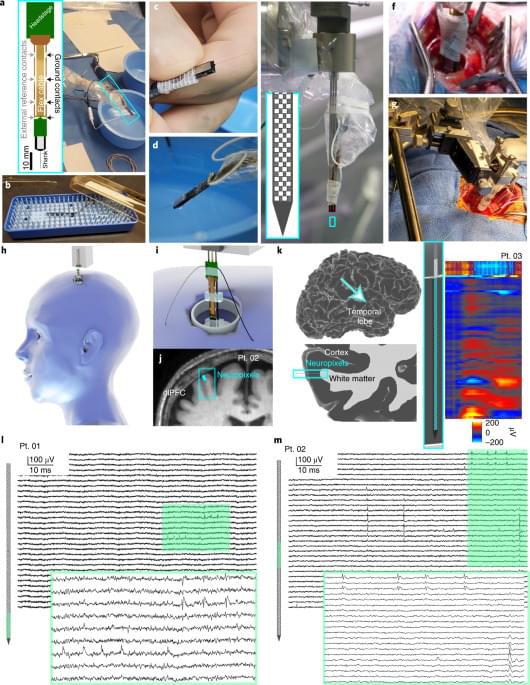
Recent advances in multi-electrode array technology have made it possible to monitor large neuronal ensembles at cellular resolution in animal models. In humans, however, current approaches restrict recordings to a few neurons per penetrating electrode or combine the signals of thousands of neurons in local field potential (LFP) recordings. Here we describe a new probe variant and set of techniques that enable simultaneous recording from over 200 well-isolated cortical singl… See more.
Neuropixels probes were used to simultaneously record from more than 200 cortical neurons in human participants during neurosurgical procedures. The approach could reveal insights underlying human cognition and pathology.


I subtitled this post “Why we’re all in denial about the robot apocalypse”. I say that because I believe that society at large is completely, utterly, and woefully unprepared for the advent of sentient, living artificial general intelligence. I think the singularity is coming much sooner than most people expect, and I think it’s going to cause a great deal of upset when it arrives — for better and for worse.
Take for instance the common religious belief that people possess some unmeasurable, undefinable soul, and that this soul is what separates us from inanimate objects and non-sentient animals. Furthermore, some people believe that these souls come from deity. I have spoken with friends who believe that AGI is impossible because “robots can’t have souls, humans aren’t God”. For these people, like Caleb says in Ex Machina (paraphrasing), removing the line between man and machine also removes the line between god and man.
Now, this isn’t to say that AGI will destroy religion or anything — it may even be used to strengthen some sects (as taken to the extreme in HBO’s Raised By Wolves). No, religion has been around for millennia and I’m sure it will continue to be around for many more millennia. I’m simply predicting that a subset of religious people are going to experience lots of cognitive dissonance when the first AGI arrives.
AI will completely take over game development by the early 2030s. To a point where there will be almost no human developers. Just people telling AI what they want to play and it builds it in real time.
Over the past few years we’ve seen massive improvements in AI technology, from GPT-3, AI picture generation to self-driving cars and drug discovery. But can machine learning progress change games?
Note: AI has many subsets, in this article when I say AI I’m referring to machine learning algorithms.
First important question to ask is, will AI even change anything? Why use machine learning when you can just hardcode movement and dialogues? The answer to this question can be found in replayability and immersive gameplay.
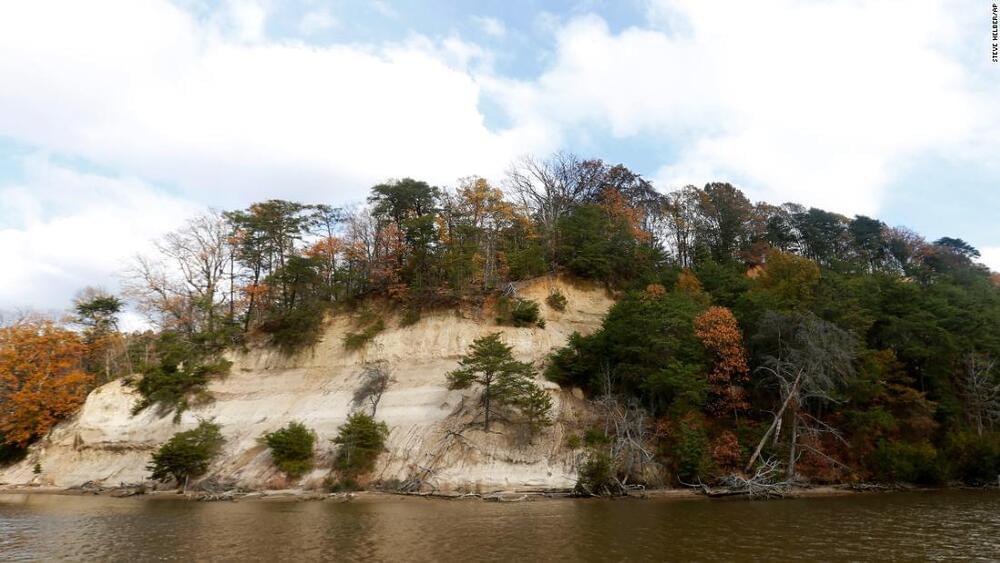

Will they able to make good use of this land?🤔🤔.
The Rappahannock Tribe, a Native Tribe in Virginia, has reacquired 465 acres of sacred land at Fones Cliff.
Secretary of the Interior Deb Haaland and US Fish and Wildlife Service Director Martha Williams celebrated the tribe’s reacquisiton of the land Friday, according to a press release from the Department of the Interior.
“We have worked for many years to restore this sacred place to the Tribe,” said Rappahannock Tribe Chief Anne Richardson, according to the Chesapeake Conservancy. “With eagles being prayer messengers, this area where they gather has always been a place of natural, cultural and spiritual importance.”