PipeMagic exploits CVE-2025–29824 in Windows, enabling RansomExx attacks in Saudi Arabia and Brazil.




A state-sponsored espionage campaign is targeting foreign embassies in South Korea to deploy XenoRAT malware from malicious GitHub repositories.
According to Trellix researchers, the campaign has been running since March and is ongoing, having launched at least 19 spearphishing attacks against high-value targets.
Although infrastructure and techniques match the pllaybook of North Korean actor Kimsuky (APT43), there are signs that better match China-based operatives, the researchers say.

The source code for version 3 of the ERMAC Android banking trojan has been leaked online, exposing the internals of the malware-as-a-service platform and the operator’s infrastructure.
The code base was discovered in an open directory by Hunt.io researchers while scanning for exposed resources in March 2024.
They located an archive named Ermac 3.0.zip, which contained the malware’s code, including backend, frontend (panel), exfiltration server, deployment configurations, and the trojan’s builder and obfuscator.

A recent ruling from Germany’s Federal Supreme Court (BGH) has revived a legal battle over whether browser-based ad blockers infringe copyright, raising fears about a potential ban of the tools in the country.
The case stems from online media company Axel Springer’s lawsuit against Eyeo — the maker of the popular Adblock Plus browser extension.
Axel Springer says that ad blockers threaten its revenue generation model and frames website execution inside web browsers as a copyright violation.


IN A NUTSHELL ⚡ China’s CFR-1000 reactor could supply electricity to one million homes, highlighting a major step in nuclear technology. 🔬 Utilizing fast neutrons, the reactor enhances fuel efficiency and supports sustainable energy solutions. 🌊 Innovative use of liquid sodium coolant allows for higher operational temperatures and improved efficiency. 🌍 Global implications arise as
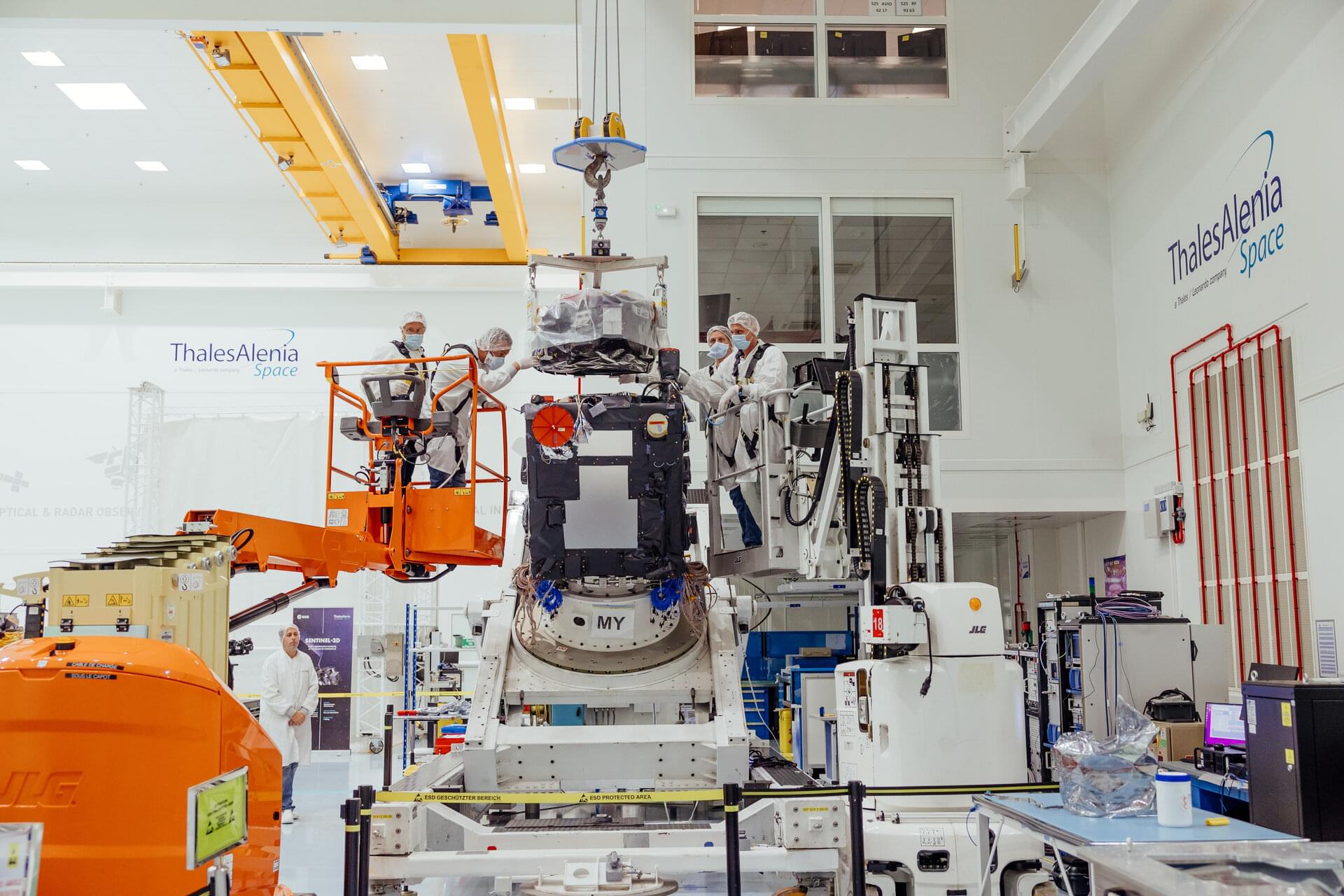

The development of ESA’s Earth Explorer FLEX mission has recently passed a significant milestone: the mission’s all-important, single instrument has been joined to its satellite platform.
This delicate operation was carried out by spacecraft engineers at Thales Alenia Space in Cannes, France, following the delivery of the instrument from Leonardo in Florence, Italy.
FLEX’s fluorescence imaging spectrometer is called FLORIS for short and designed to map vegetation fluorescence around the globe and quantify photosynthetic activity and plant stress.
The Electric Viking
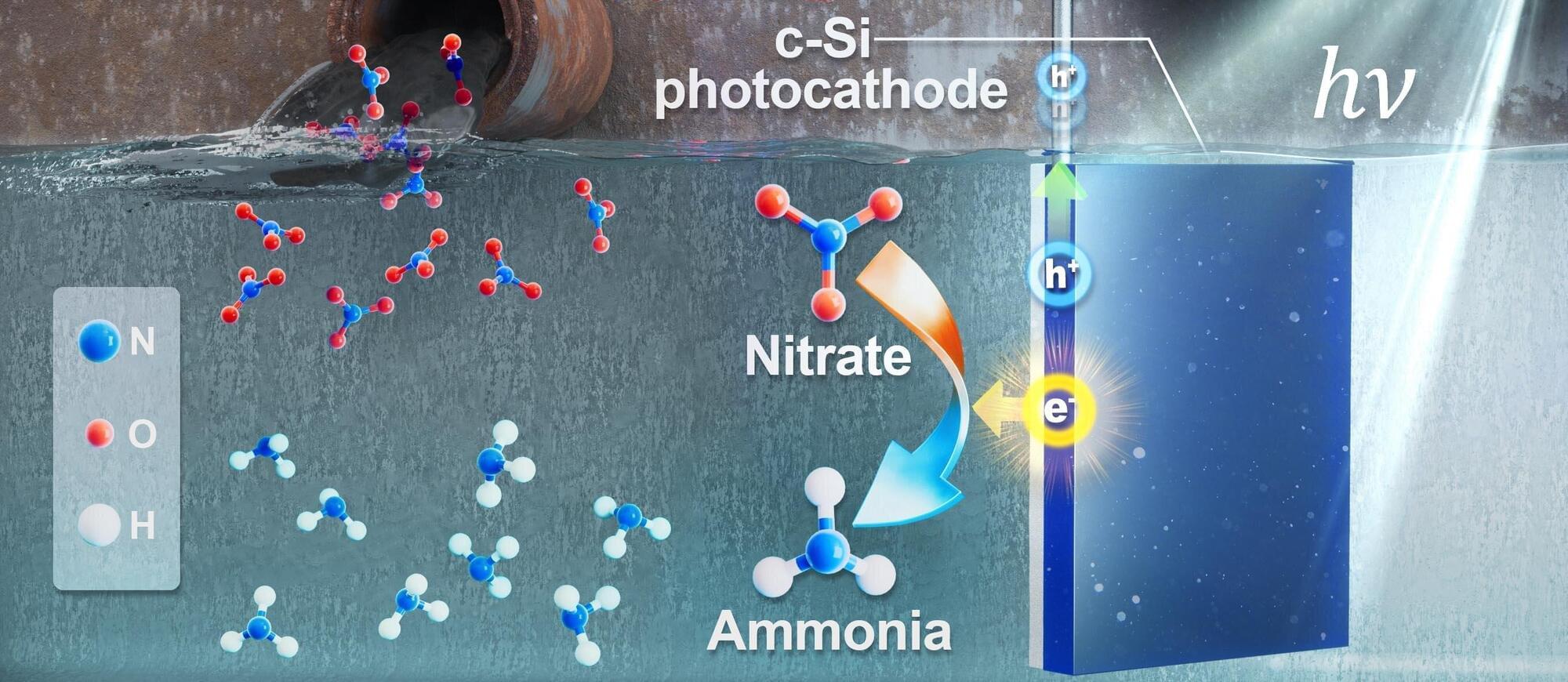
A research team affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a technology that transforms nitrates found in wastewater into ammonia, a vital chemical and promising energy carrier, without carbon emissions. This advancement not only offers a sustainable method for ammonia production but also contributes to wastewater purification efforts.