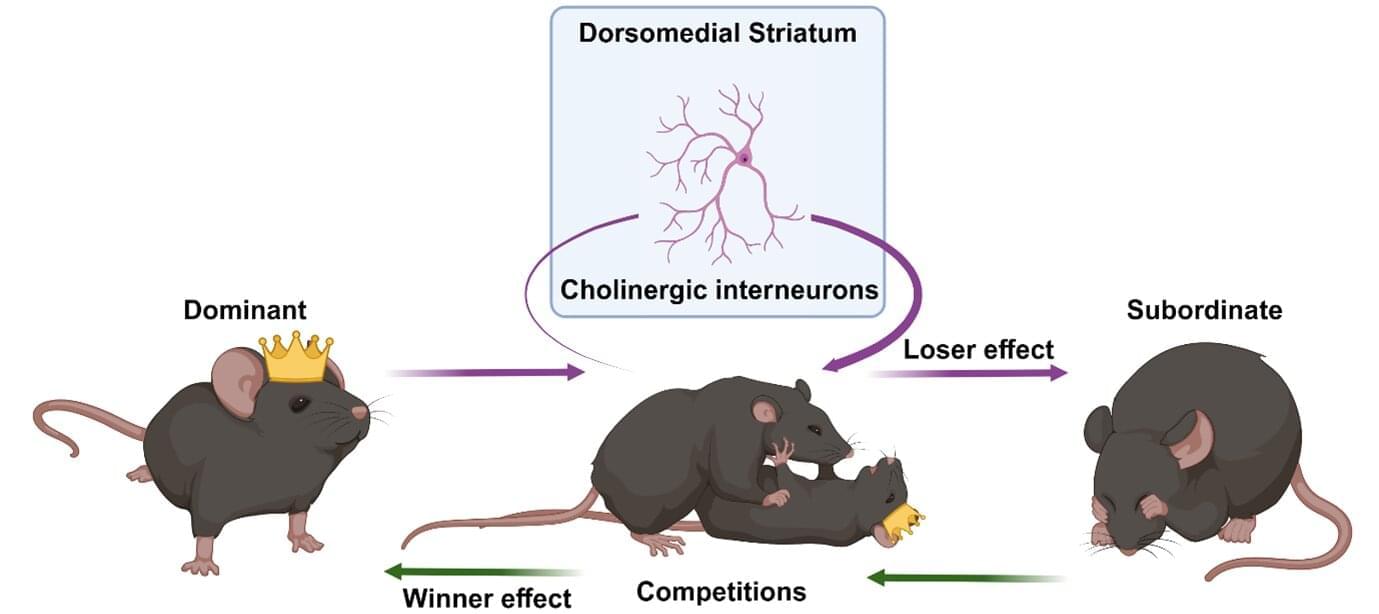
Social hierarchies are everywhere—think of high school dramas, where the athletes are portrayed as the most popular, or large companies, where the CEO makes the important decisions. Such hierarchies aren’t just limited to humans, but span the animal kingdom, with dominant individuals getting faster food access, higher mating priority, and bigger or better territories. While it’s long been thought that winning or losing can influence the position of an individual within a social hierarchy, the brain mechanisms behind these social dynamics have remained a mystery.
In iScience, researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) investigate the neurological basis of social hierarchy in male mice, pinpointing the neurons they believe crucial in determining these social hierarchy dynamics.
“You may think that being dominant in the animal kingdom is all about physical attributes, like size. But interestingly, we’ve found that it seems to be a choice, based on previous experience,” said Professor Jeffery Wickens, head of the Neurobiology Research Unit at OIST and co-author on this study. “The brain circuitry involved in these decisions is well conserved between mice and humans, so there are likely useful parallels to be drawn.”