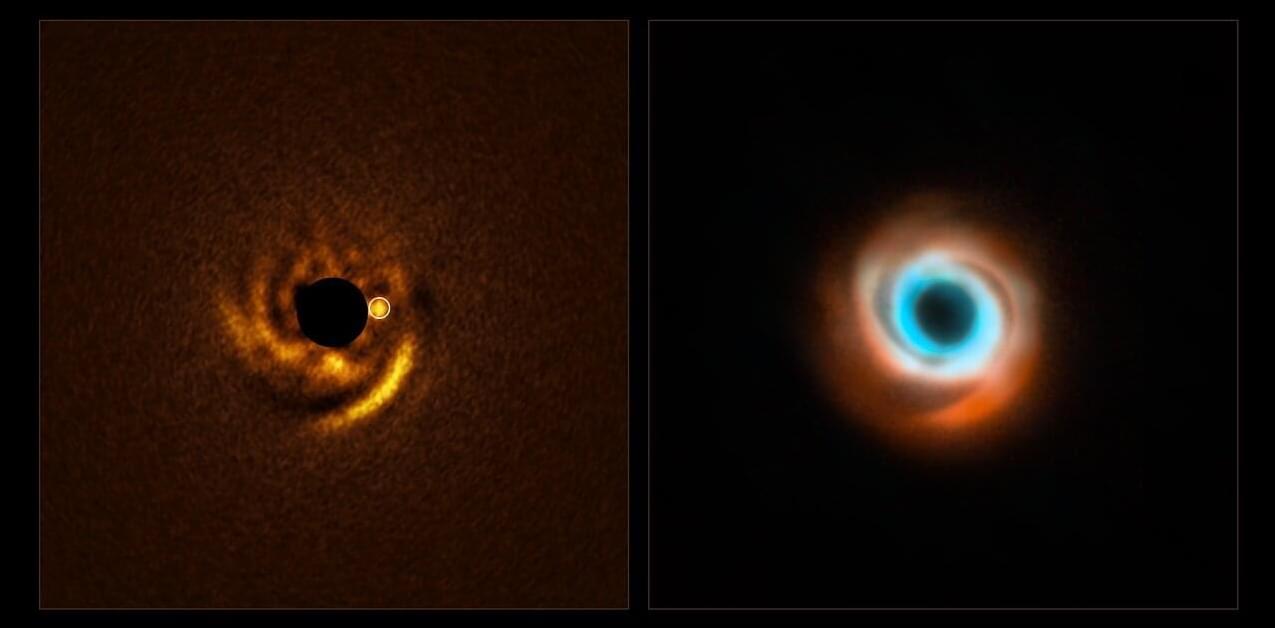
Astronomers may have caught a still-forming planet in action, carving out an intricate pattern in the gas and dust that surrounds its young host star. Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), they observed a planetary disk with prominent spiral arms, finding clear signs of a planet nestled in its inner regions. This is the first time astronomers have detected a planet candidate embedded inside a disk spiral.
“We will never witness the formation of Earth, but here, around a young star 440 light-years away, we may be watching a planet come into existence in real time,” says Francesco Maio, a doctoral researcher at the University of Florence, Italy, and lead author of this study, published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The potential planet-in-the-making was detected around the star HD 135344B, within a disk of gas and dust around it called a protoplanetary disk. The budding planet is estimated to be twice the size of Jupiter and as far from its host star as Neptune is from the sun. It has been observed shaping its surroundings within the protoplanetary disk as it grows into a fully formed planet.