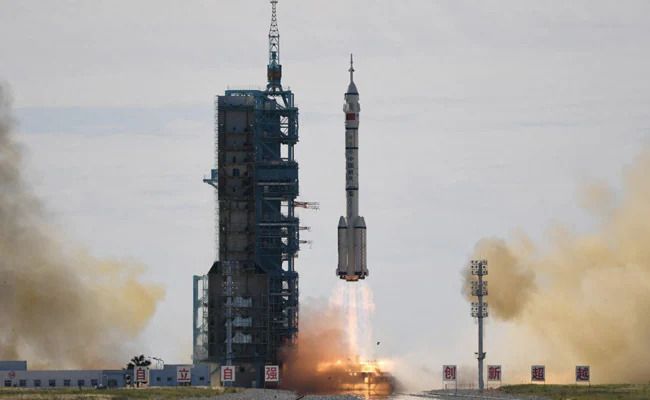
The first astronauts for China’s new space station blasted off Thursday for the country’s longest crewed mission to date, a landmark step in establishing Beijing as a major space power.
In some products it is not listed as an ingredient.
More than half the cosmetics sold in the United States and Canada likely contain high levels of a toxic industrial compound linked to serious health conditions, including cancer and reduced birth weight, according to a new study.
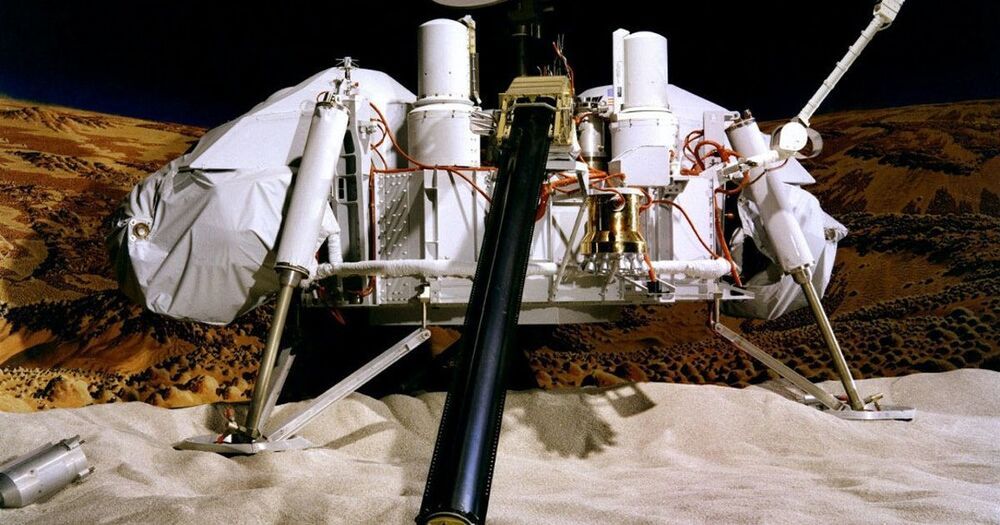
Perseverance, NASA’s rover that landed on Mars in February, is looking for signs of ancient microbial life and determining if the Red Planet is habitable for humans.
From Mariner 4 to Curiosity, these historical missions have shaped our understanding of the Red Planet.
Summary: A new imaging study reveals how the MFSD2A transporter protein provides a gateway for omega-3 fatty acids to enter the brain.
Source: Columbia University.
Spectacular images of a molecule that shuttles omega-3 fatty acids into the brain may open a doorway for delivering neurological therapeutics to the brain.
Big Blue has, for the first time, built a quantum computer that is not physically located in its US data centers. For the company, this is the start of global quantum expansion.
Given the importance of the Kirkwood–Dirac quasiprobability’s nonclassical values, two natural questions arise: Under what conditions does this quasiprobability behave anomalously? And how anomalous can its behaviour get? That’s what we wanted to explore.
What did you do in the paper?
We pinned down conditions under which the Kirkwood–Dirac quasiprobability assumes nonclassical values. Using these conditions, one can calculate which experiments can exhibit certain types of quantum advantages. We also put a “ceiling” on how much nonclassicality one Kirkwood–Dirac quasiprobability distribution can contain.
It was the third round of announcements Scott has made regarding her philanthropy, which rivals the largest of foundations. In 2020, she made two similar surprise announcements and donated about $6bn to causes including Covid relief, gender equity, historically Black colleges and universities and other schools.
Ex-wife of Jeff Bezos gives to 286 groups and says she wants to donate ‘fortune that was enabled by systems in need of change’
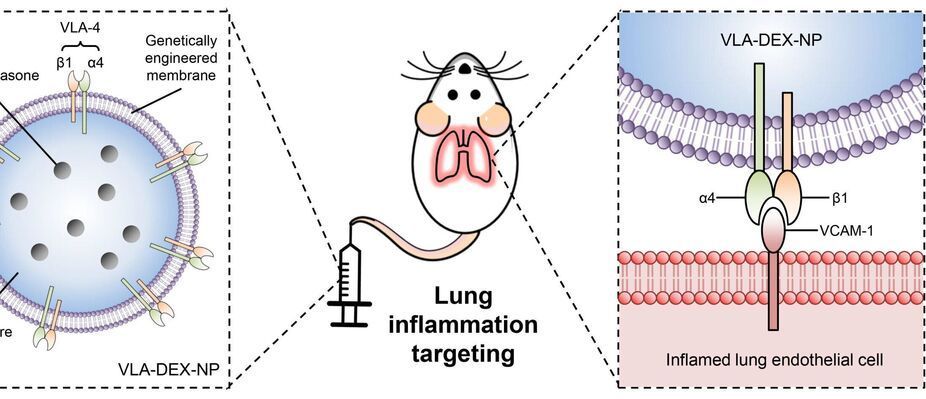
Nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed immune cell-mimicking nanoparticles that target inflammation in the lungs and deliver drugs directly where they’re needed. As a proof of concept, the researchers filled the nanoparticles with the drug dexamethasone and administered them to mice with inflamed lung tissue. Inflammation was completely treated in mice given the nanoparticles, at a drug concentration where standard delivery methods did not have any efficacy.
The researchers reported their findings in Science Advances on June 16.
What’s special about these nanoparticles is that they are coated in a cell membrane that’s been genetically engineered to look for and bind to inflamed lung cells. They are the latest in the line of so-called cell membrane-coated nanoparticles that have been developed by the lab of UC San Diego nanoengineering professor Liangfang Zhang. His lab has previously used cell membrane-coated nanoparticles to absorb toxins produced by MRSA; treat sepsis; and train the immune system to fight cancer. But while these previous cell membranes were naturally derived from the body’s cells, the cell membranes used to coat this dexamethasone-filled nanoparticle were not.