The new system uses molten salts instead of traditional fuel rods.
The world is rethinking nuclear power plants in the face of climate change. Your average plant produces 8,000 times more power than fossil fuels and is environmentally friendly. There’s one massive caveat, though, in the form of nuclear disasters, such as the 1986 Chernobyl incident and the 2011 Fukushima disaster.
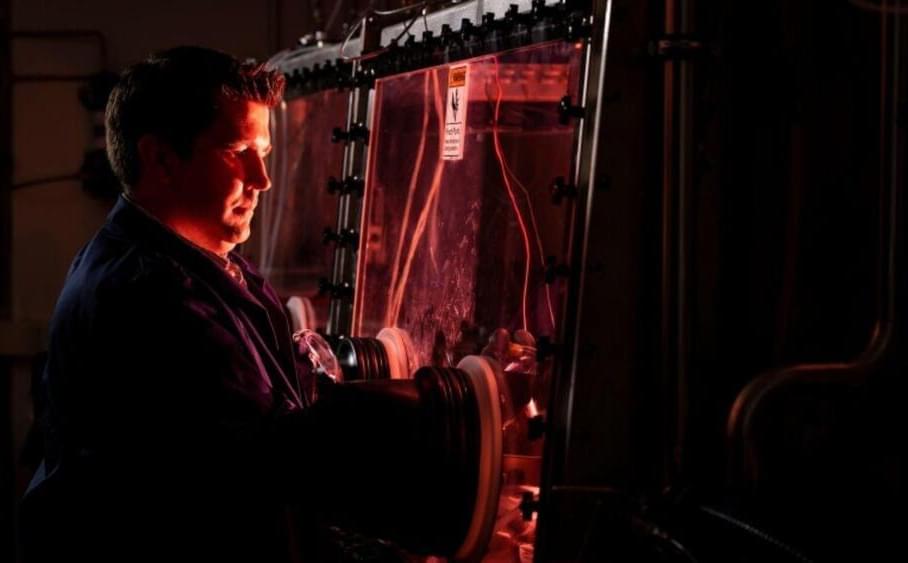
Now, professor Matthew Memmott and colleagues from Bingham Young University (BYU) announced that they designed a new molten salt micro-reactor system that allows for safer nuclear energy production. As per a press release, it may also solve a number of other key issues related to nuclear energy production.
Photo by brooklyn jarvis kelson/byu photo.
Your average plant produces 8,000 times more power than fossil fuels and is environmentally friendly. There’s one massive caveat, though, in the form of nuclear disasters, such as the 1986 Chernobyl incident and the 2011 Fukushima disaster.