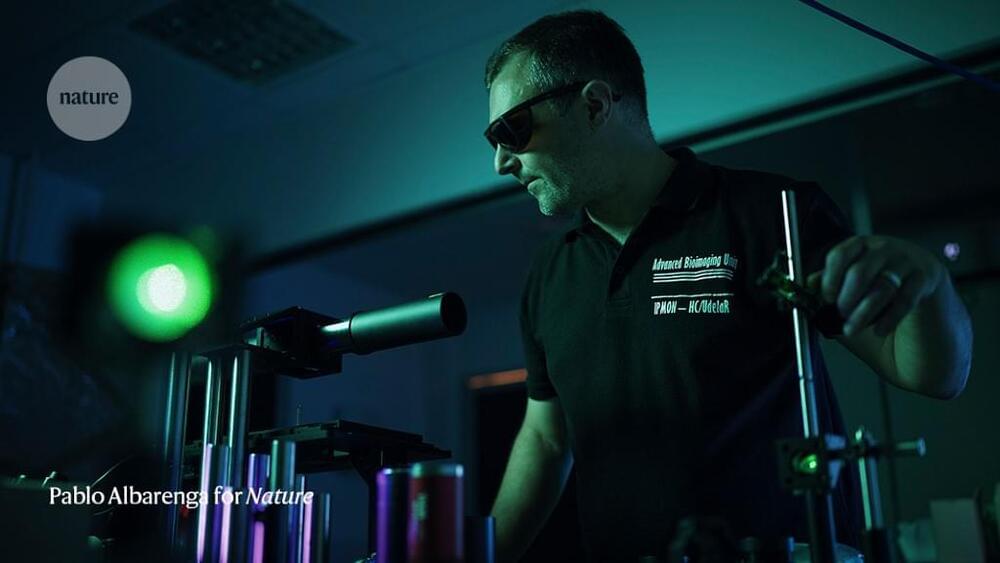
Leonel Malacrida hopes that his lab’s imaging technology will advance cancer diagnosis and research in Uruguay and across Latin America.



If anyone has a tiktok you are welcome to follow me or if you want to view some videos I created a Playlist. Just click on the links:
Psychology:
Robert Sapolsky: https://www.tiktok.com/t/ZTRP33D38/
Neuroscience: https://www.tiktok.com/t/ZTRP3P9kC/
Neurological Disorders: https://www.tiktok.com/t/ZTRP3vBs9/
LSD and the Brain: https://www.tiktok.com/t/ZTRP3g1nG/
Did they unlock one of the vital keys to stop aging?
According to a recent National Eye Institute (NEI) study in mice, loss of the protein pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), which protects retinal support cells, may promote age-related changes in the retina.
Age-related retinal diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), can cause blindness since the retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The new information could help develop medicines to stop AMD and other aging conditions of the retina. The research was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
“People have called PEDF the ‘youth’ protein because it is abundant in young retinas, but it declines during aging,” said Patricia Becerra, Ph.D., chief of NEI’s Section of Protein Structure and Function and senior author of the study. “This study showed for the first time that just removing PEDF leads to a host of gene changes that mimic aging in the retina.”
There will be No Plan of course, and barring a WW3, i can guess the outcome.
There’s a scene in the movie I, Robot where a robot-hating police officer, played by Will Smith, is questioning the manufacturer of a robot suspected of murdering a human. The conversation gets testy, and the robot maker, played by Bruce Greenwood, looks Smith in the eye and says, “I suppose your father lost his job to a robot. I don’t know, maybe you would have simply banned the internet to keep the libraries open.”
Art imitating life? To a degree, yes. Automation, artificial intelligence, and robots are costing people their jobs. But no, none are suspected of committing a homicide as a result. And the last time we checked, none were known to be organizing an AI insurrection, which was the premise behind I, Robot’s plot.
That’s fantasy. What’s real is that this country isn’t doing enough to prepare for a future where millions of Americans with outdated skills won’t be able to compete for jobs when a less expensive, automated alternative is available to their employers. There’s no better time than Labor Day to ask Washington to come up with a more definitive plan to assist employees who are in jeopardy of becoming obsolete.
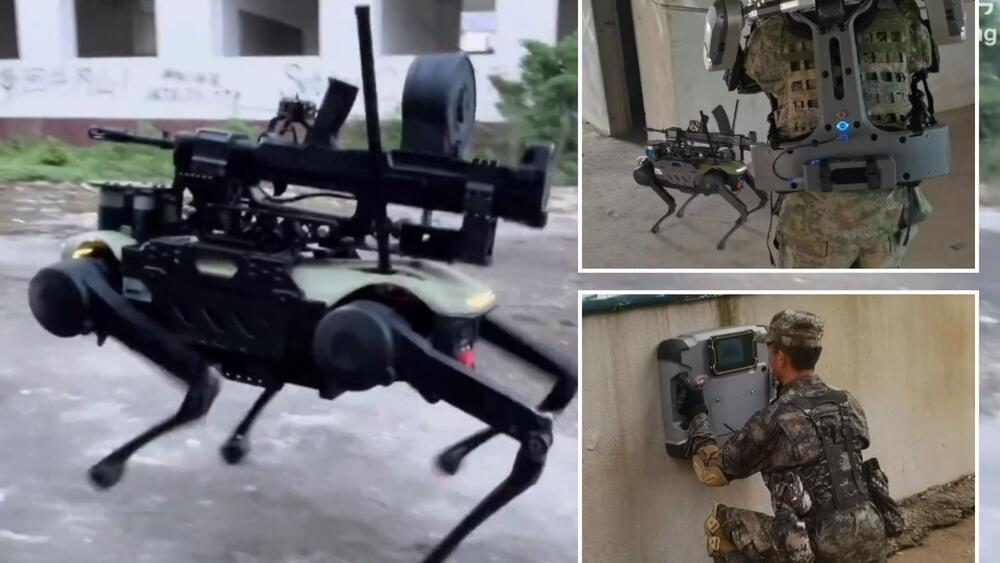

Robo-Dog Assault Droids 😲
CHILLING video shows the Chinese military unveiling more of their high-tech weapons as tensions continue to rage with the West.
Beijing flaunted its military tech in the new video which shows a machine-gun armed robot dog, a small ball scout drone and a soldier wearing an exoskeleton.
It is understood the technology is made by Chinese defence firm Kestrel and the clips from the exercises were shared on Beijing’s state-monitored social media site Weibo.
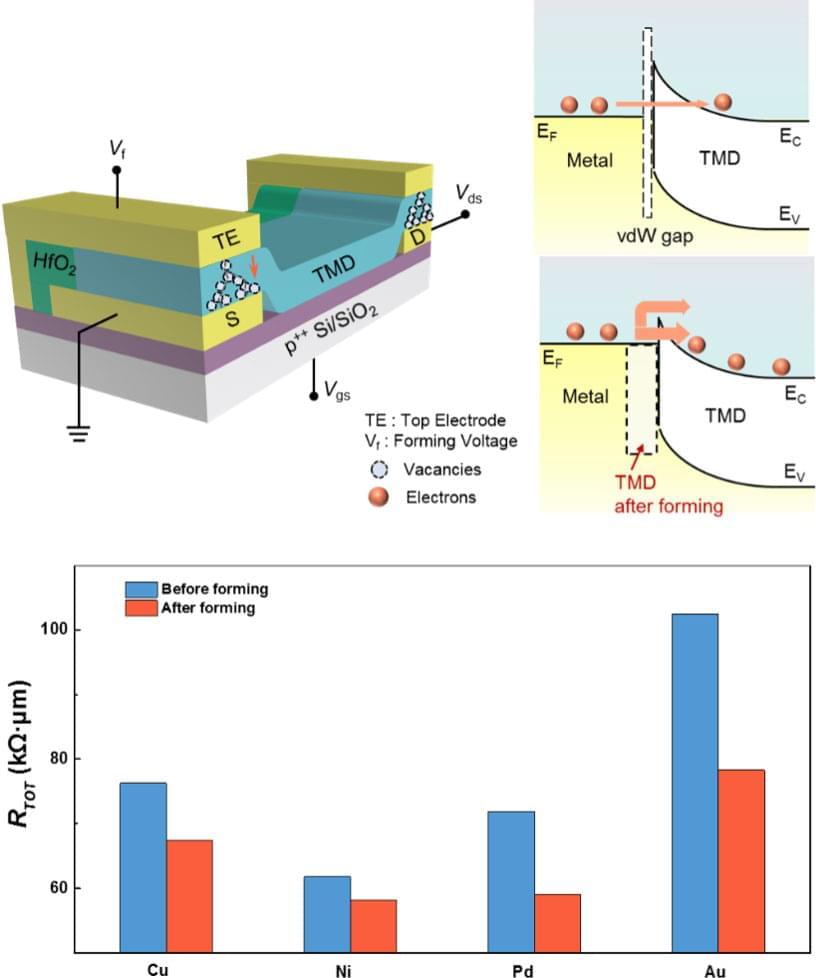
Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors, like transition-metal dichalcogenides, have become a competitive alternative to traditional semiconducting materials in the post-Moore era, and caused worldwide interest. However, before they can be used in practical applications, some key obstacles must be resolved. One of them is the large electrical contact resistances at the metal-semiconductor interfaces. Researchers have proposed a brand-new contact resistance lowering strategy of 2D semiconductors with a good feasibility, a wide generality and a high stability.

Hydrogen (H 2) is currently discussed as an ideal energy carrier in a world requiring renewable energies. Hydrogen has the highest gravimetric energy density of all chemical fuels (141 MJ/kg), which is three times higher than gasoline (46 MJ/kg). However, its low volumetric density restricts its widespread use in transportation applications —as current storage options require a lot of space.
At ambient temperature, hydrogen is a gas, and one kilogram of hydrogen occupies a volume of 12,000 liters (12 cubic meters). In fuel-cell vehicles, hydrogen is stored under a very high pressure of 700 times the atmospheric pressure, which reduces the volume to 25 liters per kilogram of H 2.
Liquid hydrogen shows a higher density resulting in 14 liters per kilogram, but it requires extremely low temperatures since the boiling point of hydrogen is minus 253 °C.
Two-dimensional van der Waals materials have been the focus of work by numerous research groups for some time. Standing just a few atomic layers thick, these structures are produced in the laboratory by combining atom-thick layers of different materials (in a process referred to as “atomic Lego”).
Interactions between the stacked layers allow the heterostructures to exhibit properties that the individual constituents lack.
The coupling of two different electron-hole pairs leads to a fusion of their properties. (Image: L. Sponfeldner, SNI and Department of Physics, University of Basel)
A Turkish entity going by the name of Nitrokod has been accused of running a campaign by spoofing a desktop version of Google Translate to actively mine cryptocurrency from its more than 111,000 users across eleven countries (UK, US, Sri Lanka, Greece, etc., Israel, Germany, Turkey, Cyprus, Australia, Mongolia, and Poland) in 2019.
In addition to Google Translate, there are five other fake desktop applications on the Nitrokod website. Most of them impersonate programs that are not officially available as desktop applications, but as web or mobile applications, which makes the desktop version created by the attackers particularly attractive. In any case, they are popular applications that can be found on websites such as Softpedia and UpToDown.
Six fake applications available on the Nitrokod website. When installing any of these programs, the malicious effects do not manifest until after a sequence of dropper for almost a month after installation, in order to hide such effects from the antiviruses.
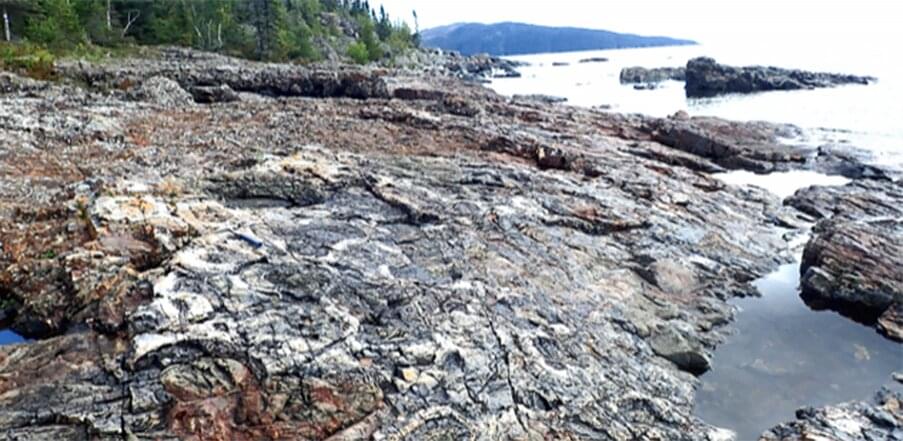

Scientists have long pondered how and when the evolution of prokaryotes to eukaryotes occurred. A collaborative research team from Tohoku University and the University of Tokyo may have provided some answers after discovering new types of microfossils dating 1.9 billion years.
Details of their findings were published in the journal Precambrian Research on August 19, 2022.
The Gunflint Formation traverses the northern part of Minnesota into Ontario, along the northwestern shores of Lake Superior. The first bacterial microfossils were discovered there in 1954, with Gunflint microfossils now recognized as a “benchmark” in the field of life evolution.