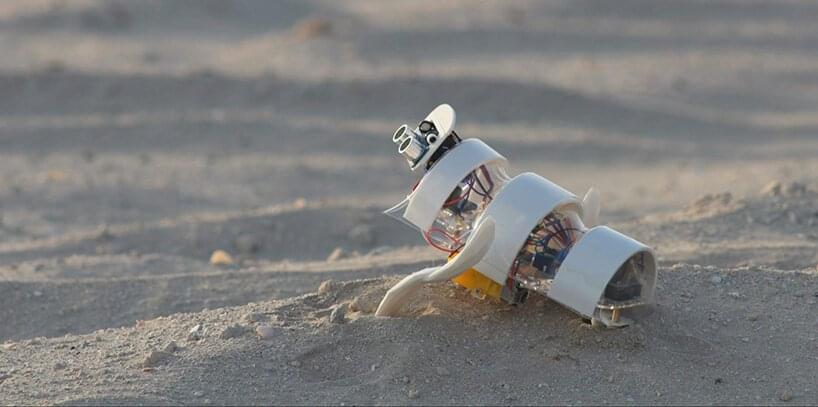
A’seedbot is a tiny autonomous robot that aims to convert the uninhabitable sandy desert soil into a verdant landscape.
A documentary and journey into the future exploring the possibilities and predictions of artificial intelligence. This timelapse of the future explores what is coming, from robots that are too fast for humans to see, to A.I. bots from Microsoft (bringing back loved ones to life) and Google’s laMDA (replacing the need for online searches).
Elon Musk’s Neuralink goes from a medical and healthcare device, to helping people become superhuman – with intelligence amplification, and add-ons that connect to the brain chip.
Artificial general intelligence begins to design an A.I. more powerful than itself. People begin to question if humanity has reached the technological singularity. Artificial Super Intelligence emerges from the AGI.
And further into the deep future. Human consciousness becomes digitized and uploaded into a metaverse simulation. It is merged with A.I. creating hybrid consciousness – which spreads across the cosmos. Matrioshka brains and Dyson Spheres host humanity’s consciousness in a cosmic simulation network.
Quotes about the future from: James J Hughes.
Additional footage sourced from: Neuralink, Tesla.
It was a big year. Fermilab discovered possible evidence of new physics with the muon G-2 experiment. Physicists created a time crystal, a new phase of matter that appears to violate one of nature’s most cherished laws. And we got a glimpse of an enormous pair of bubbles towering over the Milky Way. Read the articles in full at Quanta: https://www.quantamagazine.org/the-year-in-physics-20211222/
Quanta Magazine is an editorially independent publication supported by the Simons Foundation.
Time to have another go at reanimation?
Interview with James Lovelock 101 years old-scientist inventor.
I found an article that said “The microwave was invented to heat hamsters humanely in 1950s experiments.” And I thought, no it wasn’t…was it?
Pull down the description for thorough references and credits.
Thanks to James Lovelock for his time! His latest book is Novacene: https://amzn.to/3hmKsWz [that is, of course, an Amazon affiliate link]
Over-the-counter antioxidants 🤔
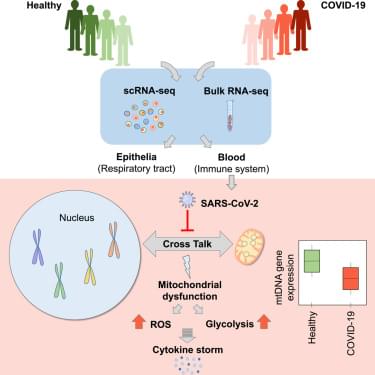
Mitochondria are pivotal for bioenergetics, as well as in cellular response to viral infections. Nevertheless, their role in COVID-19 was largely overlooked. Here, we analyzed available bulk RNA-seq datasets from COVID-19 patients and corresponding healthy controls (three blood datasets, N = 48 healthy, 119 patients; two respiratory tract datasets, N = 157 healthy, 524 patients). We found significantly reduced mtDNA gene expression in blood, but not in respiratory tract samples from patients. Next, analysis of eight single-cells RNA-seq datasets from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, nasopharyngeal samples, and Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (N = 1,192,243 cells), revealed significantly reduced mtDNA gene expression especially in immune system cells from patients. This is associated with elevated expression of nuclear DNA-encoded OXPHOS subunits, suggesting compromised mitochondrial-nuclear co-regulation. This, together with elevated expression of ROS-response genes and glycolysis enzymes in patients, suggest rewiring toward glycolysis, thus generating beneficial conditions for SARS-CoV-2 replication. Our findings underline the centrality of mitochondrial dysfunction in COVID-19.
DataRobot ‘s new DataRobot Core platform is designed to deliver improved AI design tools to enterprises in a range of industries.
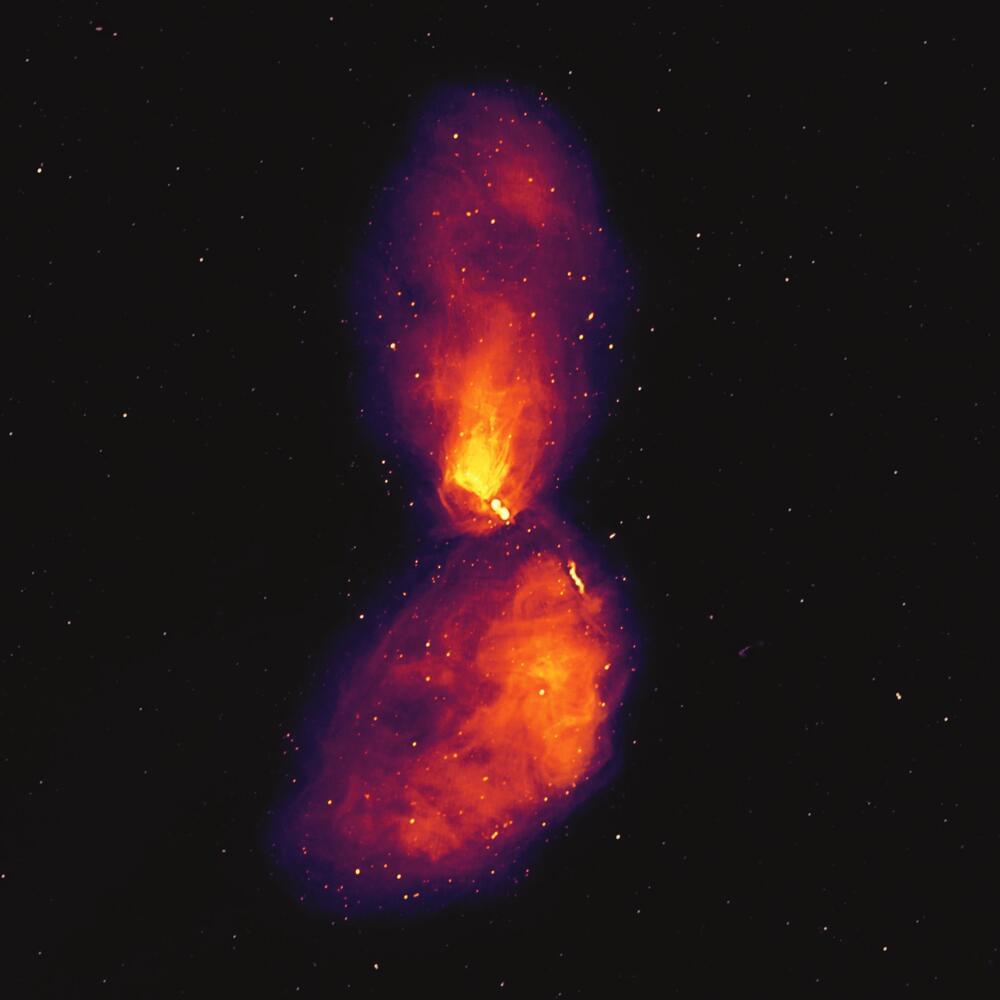
Astronomers have produced the most comprehensive image of radio emission from the nearest actively feeding supermassive black hole to Earth.
The emission is powered by a central black hole in the galaxy Centaurus A, about 12 million light years away.
As the black hole feeds on in-falling gas, it ejects material at near light-speed, causing ‘radio bubbles’ to grow over hundreds of millions of years.
Reducing its carbon emissions by 80% compared to conventional designs.
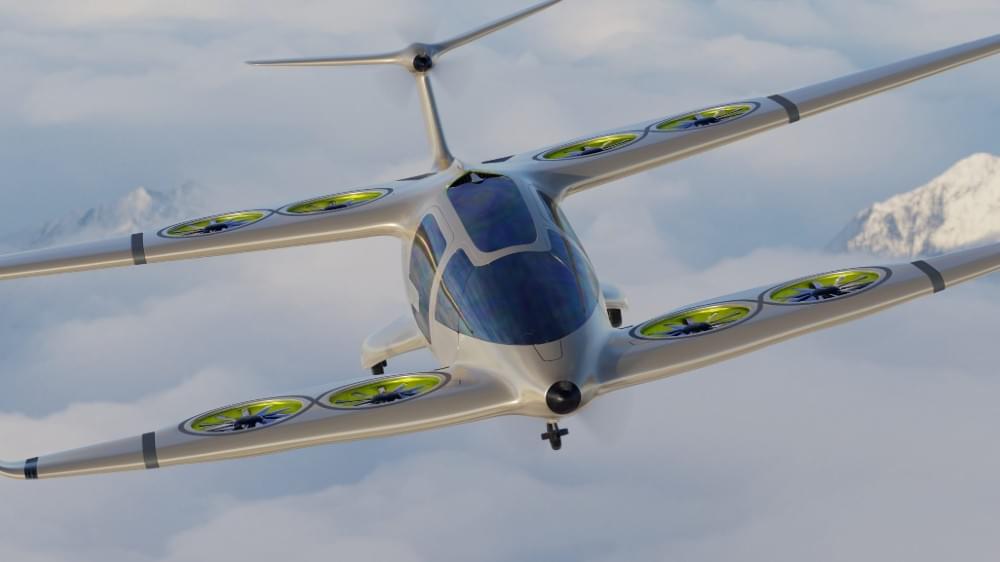
Ascendance Flight Technologies, based in Toulouse, France, has unveiled the striking design of its new hybrid-electric VTOL aircraft, ATEA, according to a press release.
The ATEA is a five-seat hybrid-electric aircraft that can perform vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL). The concept stands out from the rest since it has a tandem wing configuration with rotors incorporated into them, giving it a strikingly unusual appearance.
The concept is the result of three years of research and development, and it’s called the “tomorrow’s aircraft” since it reflects the company’s goal of assisting in the decarbonization of aviation: The aircraft aims to reduce carbon emissions by 80 percent compared to traditional helicopter designs.
The French-designed Ascendance AETA uses hybrid propulsion, with electric for vertical take off and landing, and diesel for forward flight.
At the turn of the 20th Century, Thomas Edison invented a battery with the unusual quirk of producing hydrogen. Now, 120 years later, the battery is coming into its own.