Immortality DNA strands found in humans.
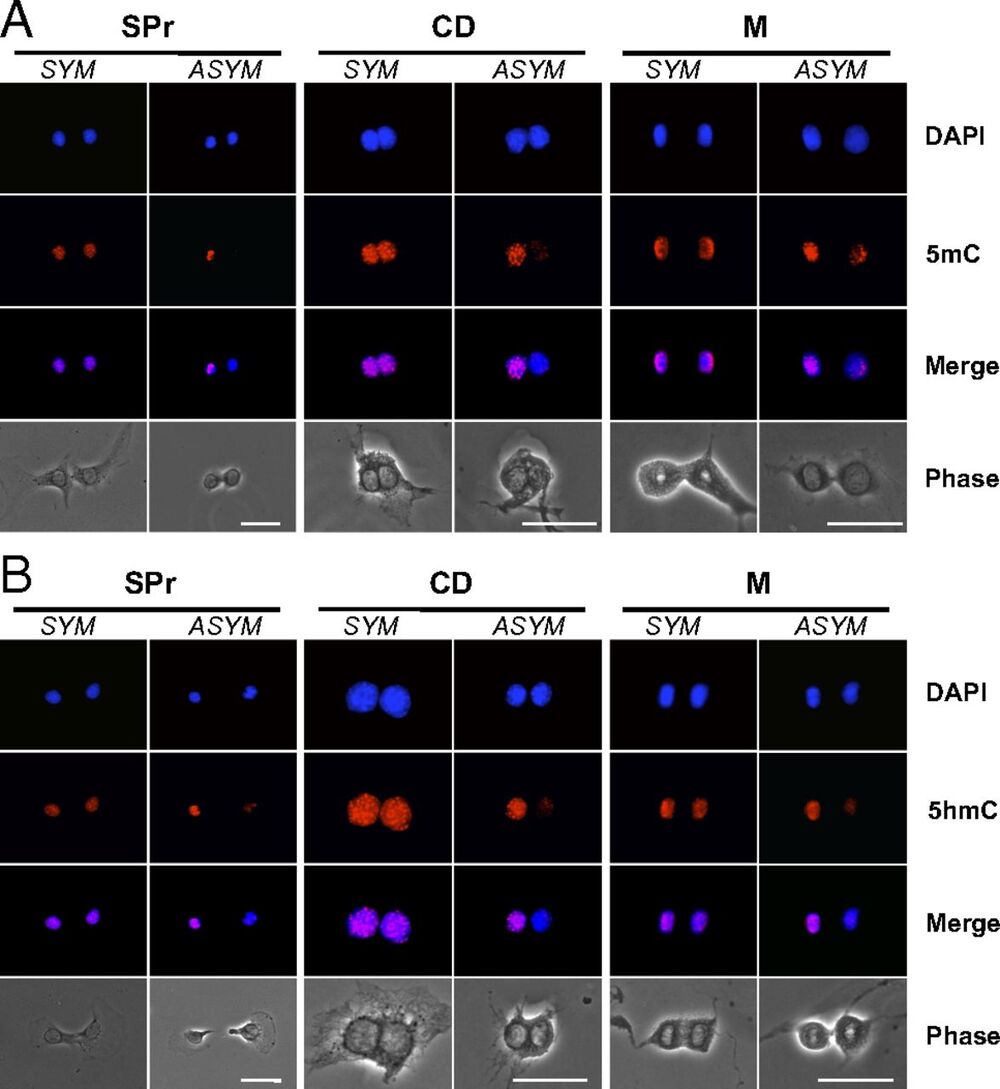
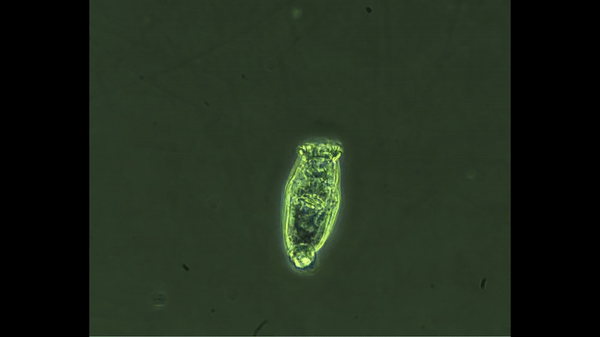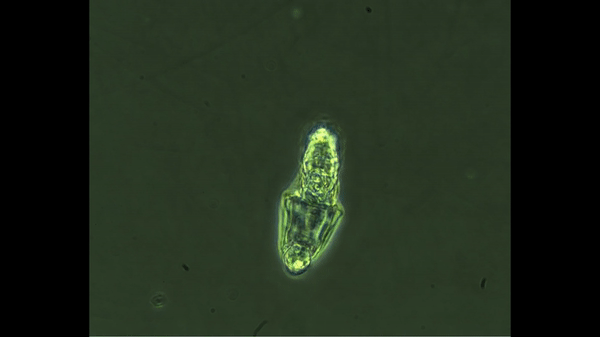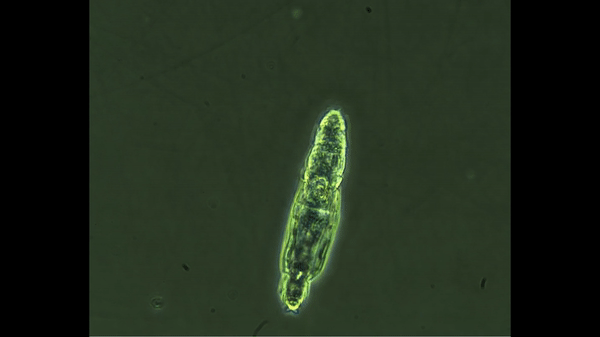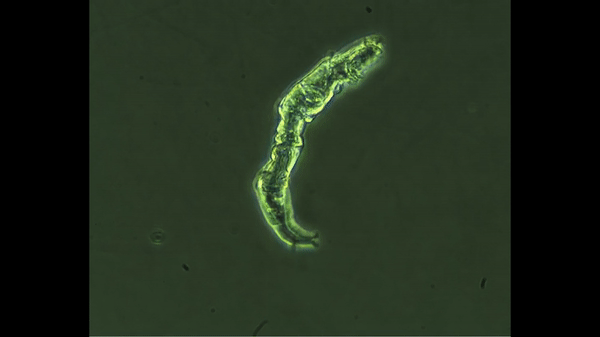
Distributed stem cells (DSCs), which continuously divide asymmetrically to replenish mature tissue cells, adopt a special form of mitotic chromosome segregation. Chromosome segregation is nonrandom instead of random. DSCs cosegregate the set of sister chromosomes with the older of the two template DNA strands used for semiconservative DNA replication during the preceding S phase. Neither the responsible molecular mechanisms nor the cellular function of nonrandom segregation are known. Here, we report evidence that immortal strand chromosomes have a higher level of cytosine 5-hydroxymethylation than mortal chromosomes, which contain the younger DNA template strands. We propose that asymmetric chromosomal 5-hydroxymethylation is a key element of a cellular mechanism by which DSCs distinguish older DNA template strands from younger ones.
Immortal strands are the targeted chromosomal DNA strands of nonrandom sister chromatid segregation, a mitotic chromosome segregation pattern unique to asymmetrically self-renewing distributed stem cells (DSCs). By nonrandom segregation, immortal DNA strands become the oldest DNA strands in asymmetrically self-renewing DSCs. Nonrandom segregation of immortal DNA strands may limit DSC mutagenesis, preserve DSC fate, and contribute to DSC aging. The mechanisms responsible for specification and maintenance of immortal DNA strands are unknown. To discover clues to these mechanisms, we investigated the 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) content on chromosomes in mouse hair follicle DSCs during nonrandom segregation. Although 5-methylcytosine content did not differ significantly, the relative content of 5hmC was significantly higher in chromosomes containing immortal DNA strands than in opposed mitotic chromosomes containing younger mortal DNA strands.