Session at AngelList Confidential 2022, featuring OpenAI CEO Sam Altman.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

AI bot ChatGPT stuns academics with essay-writing skills and usability
Professors, programmers and journalists could all be out of a job in just a few years, after the latest chatbot from the Elon Musk-founded OpenAI foundation stunned onlookers with its writing ability, proficiency at complex tasks, and ease of use.
The system, called ChatGPT, is the latest evolution of the GPT family of text-generating AIs. Two years ago, the team’s previous AI, GPT3, was able to generate an opinion piece for the Guardian, and ChatGPT has significant further capabilities.

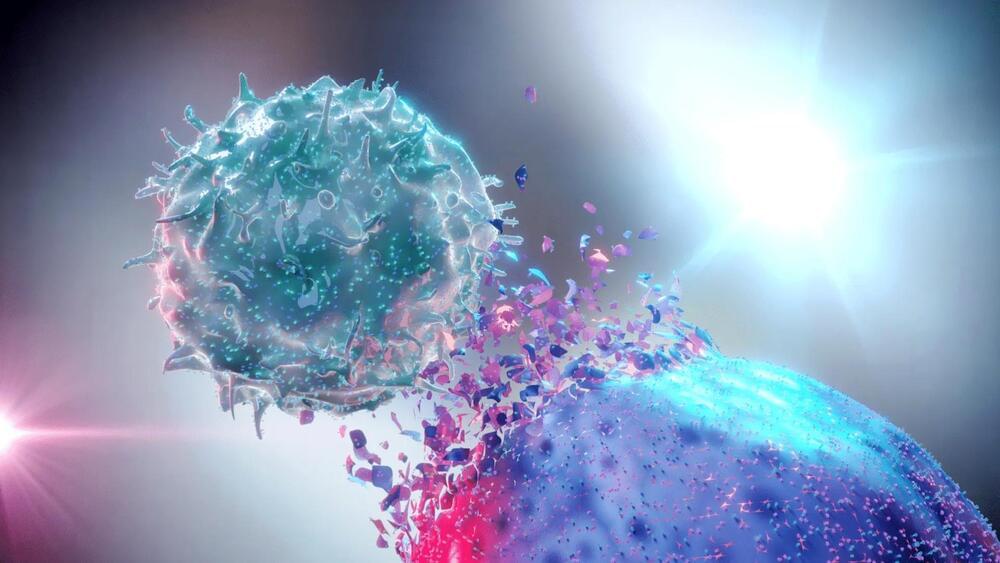
Most Effective Treatment Yet: New Radioactive Tumor Implant Obliterates Pancreatic Cancer
Duke University biomedical engineers have demonstrated the most effective pancreatic cancer treatment yet recorded in mouse models. While most mouse trials consider just stopping growth to be a success, the new treatment fully eliminated tumors in 80% of mice across many model types, including those considered to be the most difficult to treat.
The approach combines traditional chemotherapy drugs with a new method for irradiating the tumor. The treatment implants radioactive iodine-131 directly into the tumor inside a gel-like depot that protects healthy tissue and is absorbed by the body once the radiation fades, as opposed to administering radiation from an external beam that passes through healthy tissue.
The study was recently published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.

How the Broca’s Area of the Brain Helps Children Easily Learn Grammar
Summary: The development of a child’s general and grammatical linguistic abilities between the ages of 3 to 4 is accompanied by the maturation of brain structures within the “language network”.
Source: RUB
Anyone who has ever learned a foreign language knows how laborious it is to acquire vocabulary and grammar. In contrast, children acquire their first language seemingly effortlessly. By the age of four, many children are already speaking without errors and can draw on a large vocabulary.
Dr. Seemay Chou, Ph.D. — CEO, Arcadia Science — Tapping Biological Innovation In Nature For Humanity
Tapping Biological Innovation In Nature For Humanity — Dr. Seemay Chou Ph.D., CEO, Arcadia Science
Dr. Seemay Chou, Ph.D. is the Co-Founder, CEO, and Board Member of Arcadia Science (https://www.arcadia.science/), a research and development company focusing on under researched areas in biology, with a specific focus on novel model organisms that haven’t been traditionally studied in the lab.
The goals of Arcadia Science are to unlock the knowledge and ingenuity contained within a wide range of diverse species, uncover how evolution has solved limitless problems, and through revealing this untapped biological innovation, generate new technologies and products.
Dr. Chou is also the co-founder of Trove Biolabs (https://www.trovebiolabs.com/), a startup focused on harnessing novel molecules found in tick saliva for skin therapies.
Dr. Chou joined Arcadia from UCSF where she was an Assistant Professor in Biochemistry and Biophysics.


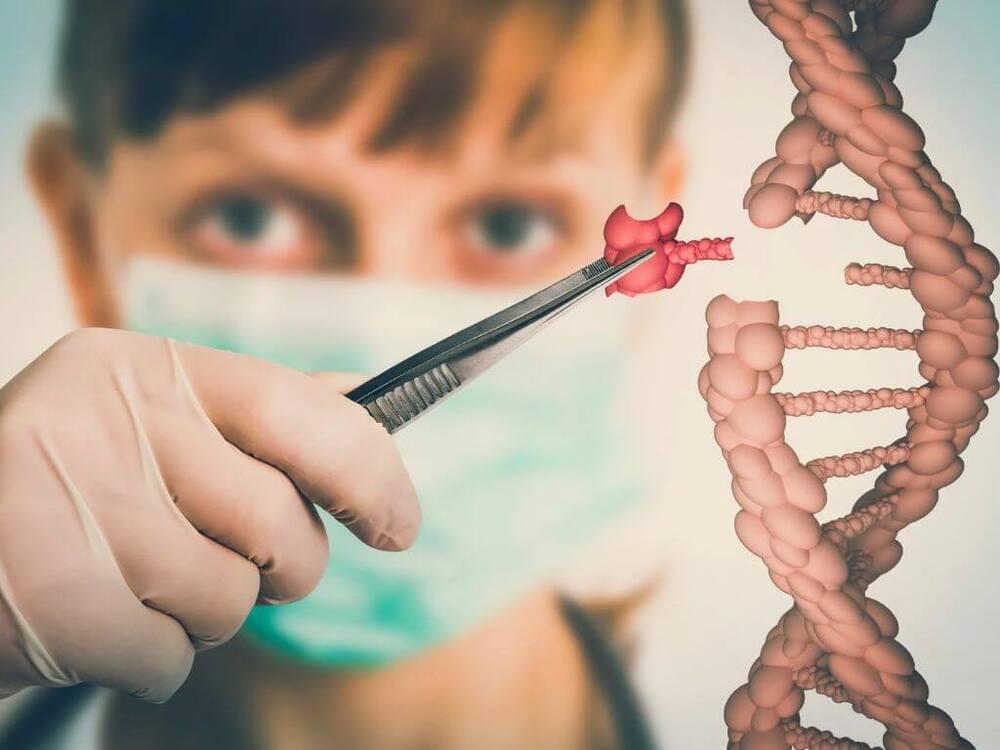
Should We Be Genetically Engineering Humans
Genetically engineering humans is a controversial topic. Some people believe that it is unethical, while others believe that it could be beneficial to humanity. There are pros and cons to both sides of the argument, and it is important to consider all of them before making a decision whether we should be genetically engineering humans or not.