
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
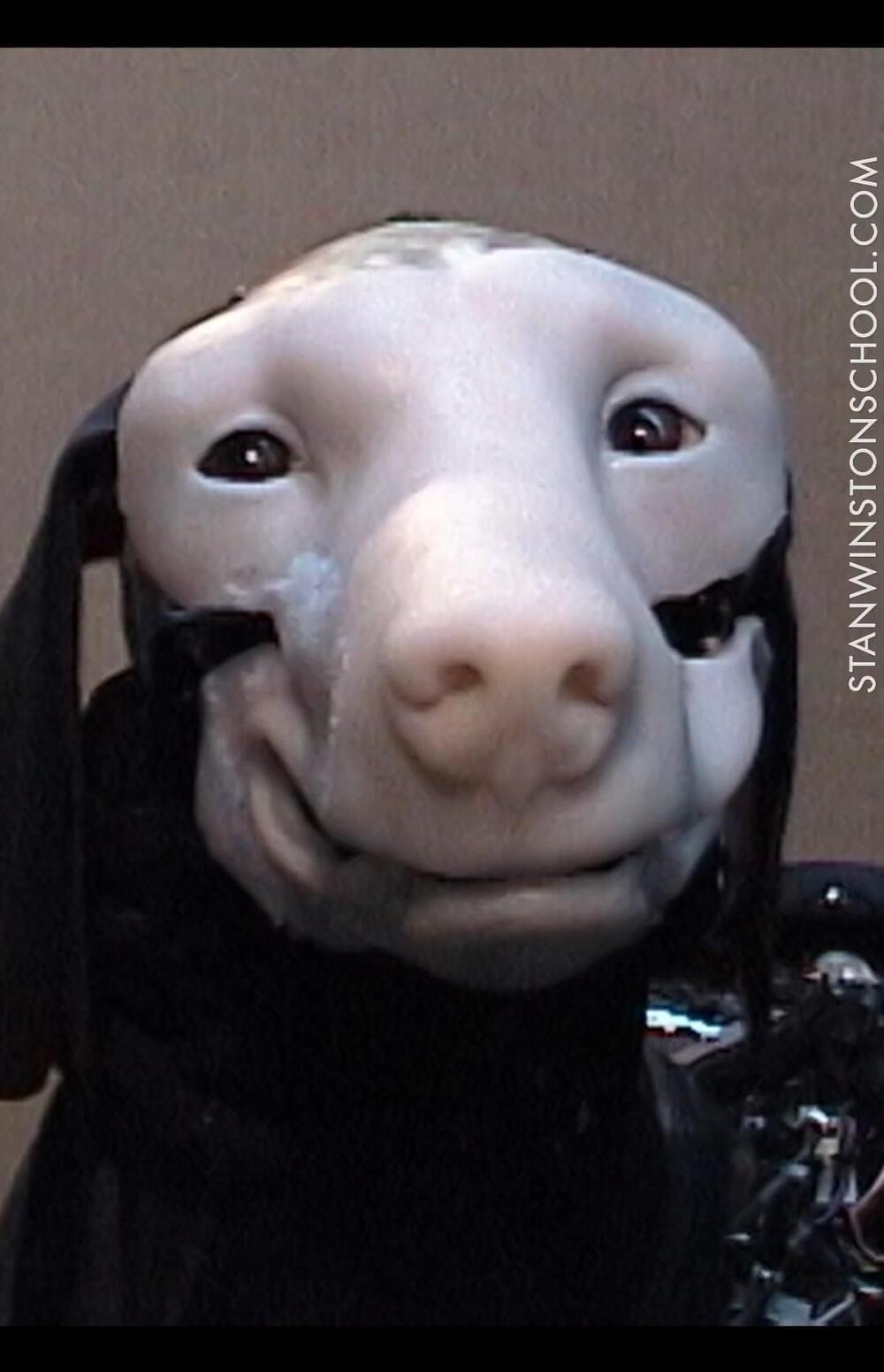



Here you can see the animatronic Collie puppet without its fur
Stan Winston Studio created the Bearded Collie puppet for Disney’s “The Shaggy Dog” in 2006.
Note how cute Collie is when our Stan Winston School teacher, Michael Ornelaz pets him.
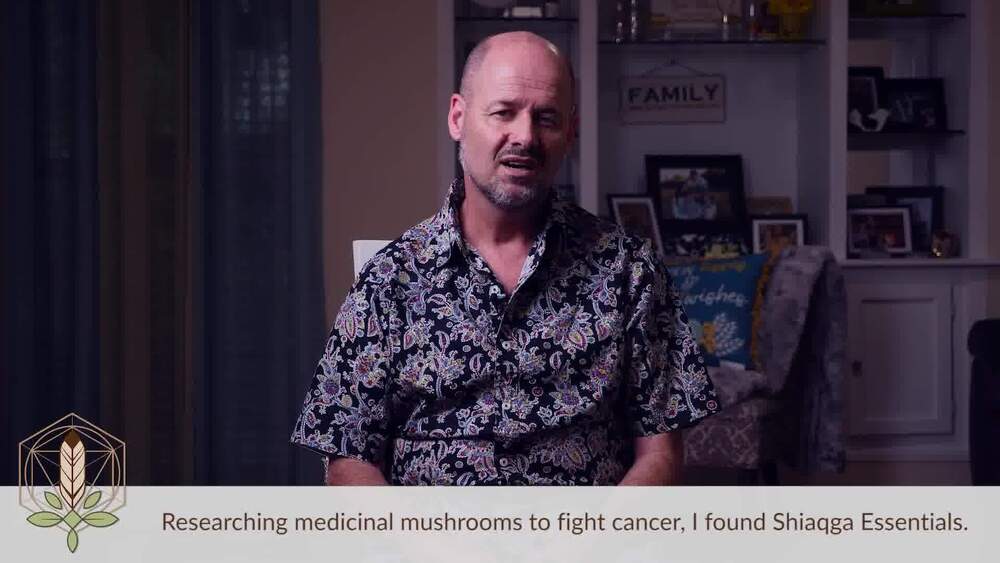

MUSHROOMS VS CANCER: Can immune systems fight off cancer when balanced
By mushrooms…?
People like Nathan have found out first hand that they can. You may have also seen scientists and doctors talking about mycotherapy for serious chronic conditions like cancer and HIV. That’s because many conditions thought of as diseases really have the same cause– an immune system that was unbalanced and compromised by environmental factors or diet.
Certain foods we eat are inflammatory, they boost problematic cells in our body called TH2 cytokines, which cause inflammation, and these cells can cause allergic reactions, auto-immune conditions, and weaken the cancer-fighting TH1 cytokines. When the TH1 cytokines are weakened by inflammatory foods, cancer is allowed to thrive and grow and spread.
But our bodies naturally have the ability to fight diseases and cancers, that’s what our immune system’ does.
The cells responsible for finding and removing cancer in our body, the TH1 cytokines, do this amazingly– but inflammatory foods and environments shut them down and prevent these natural cells from doing their jobs and killing cancerous cells quickly.
The best way to help reverse this process is by eliminating inflammatory foods and using nature’s miracle– mushrooms.
Many mushrooms are immune stimulating and modulating. Mushrooms like the Shiaqga mushroom with a high concentration of beta-glucans help boost the immune systems and support effective T-cell activity.
Scientists reverse paralysis in mice, seek human trials
Scientists at Northwestern University say they may have found a breakthrough treatment for reversing paralysis in humans after successfully administering a new injectable therapy in mice.
#News #Reuters #Science #U.S. #Spine.
Subscribe: http://smarturl.it/reuterssubscribe.
Reuters brings you the latest business, finance and breaking news video from around the globe. Our reputation for accuracy and impartiality is unparalleled.
Get the latest news on: http://reuters.com/
Follow Reuters on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Reuters.
Follow Reuters on Twitter: https://twitter.com/Reuters.
Follow Reuters on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/reuters/?hl=en

Manipulating stress response in cells could help slow down aging
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have found that a stress response in cells, when ‘switched on’ at a post-reproductive age, could be the key to slowing down aging and promoting longevity.
Longevity. Technology: In lab experiments on a type of roundworm that shares similarities with humans – paging C elegans – the NTU Singapore team found that switching on this stress response in aged worms by feeding them a high-glucose diet extended their lifespan as compared with worms fed a normal diet.
Publishing today in Nature Communications, the NTU team say this is the first time a link between this stress response and aging has been uncovered.
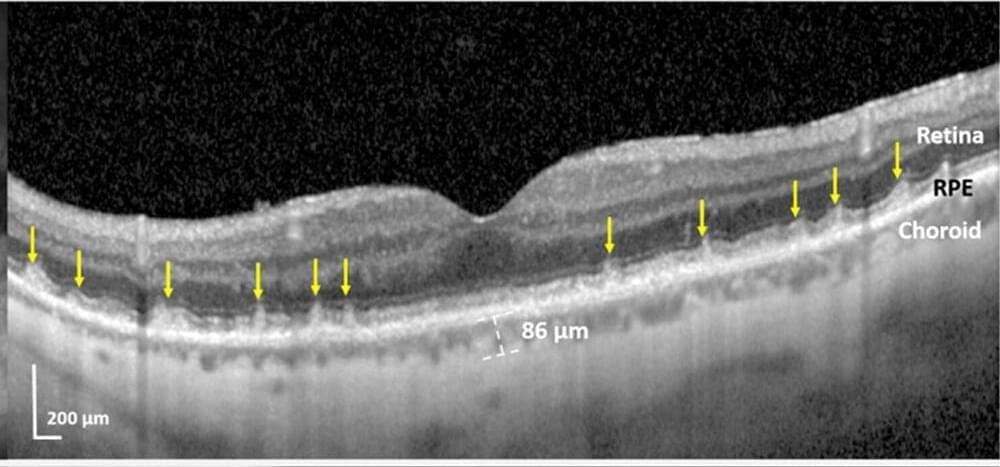
Blinding eye disease strongly associated with serious forms of cardiovascular disease
Patients with a specific form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness in the United States, are also highly likely to have either underlying heart damage from heart failure and heart attacks, or advanced heart valve disease, or carotid artery disease associated with certain types of strokes, according to a new study from New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
This research, published November 17 in BMJ Open Ophthalmology, is the first to identify which types of high-risk cardiovascular and carotid artery disease are linked to the eye disorder. The findings could prompt increased screening to save vision, diagnose undetected heart disease, and prevent adverse cardiovascular events.
“For the first time, we have been able to connect these specific high-risk cardiovascular diseases to a specific form of AMD, the one with subretinal drusenoid deposits (SDDs),” explains lead author R. Theodore Smith, MD, Ph.D., Professor of Ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
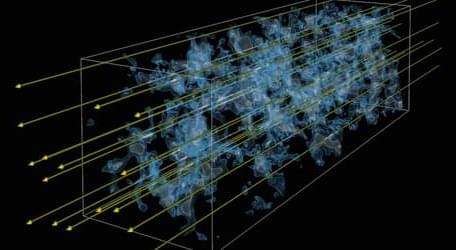
Dark Matter as an Intergalactic Heat Source
Spectra from quasars suggest that intergalactic gas may have been heated by a form of dark matter called dark photons.
Dense gas clouds across the Universe absorb light from distant quasars, producing absorption lines in the quasar spectra. A new study shows that the larger-than-predicted widths of these lines from nearby gas clouds could result from a form of dark matter called dark photons [1]. These particles could heat the clouds, leading to a widening of the absorption lines. Other explanations of the broadening—based on more conventional heating sources—have been proposed, but if the dark-photon mechanism is at work, it might also cause heating in low-density clouds from earlier epochs of the Universe. Researchers are already planning to test this prediction.
When viewing the spectrum of a distant quasar, astronomers often observe absorption lines coming from the intervening clouds of gas. The most prominent absorption line is the Lyman-alpha line of hydrogen. Indeed, some quasar spectra have a “forest” of Lyman-alpha lines, with each coming from a cloud at a different distance from our Galaxy (or different epochs). By examining the widths, depths, and other details of the line shapes, researchers can extract information about the density, the temperature, and other features of the clouds. This information can be compared with the results of cosmological simulations that try to reproduce the clumping of matter into galaxies and other large-scale structures.
