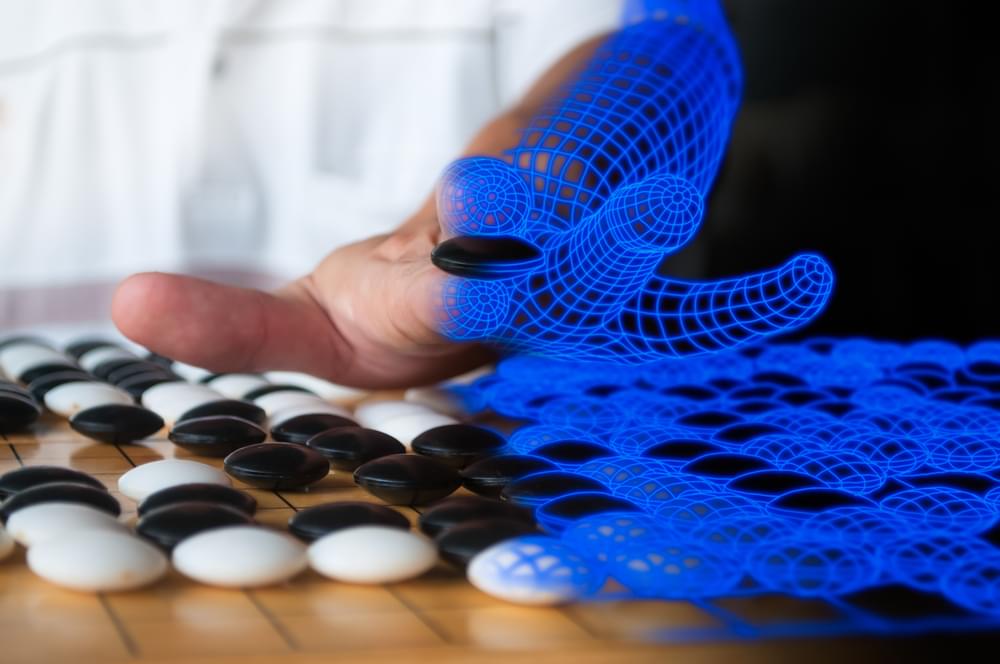
Computer security specialists had hoped Go-playing AI agents would be immune to adversarial attacks. Now it’s back to the drawing board.


The idea of human ectogenesis — growing a baby in an artificial environment outside of the human body — has always been considered in the realms of science fiction, however it may not be for much longer.
Scientific developments in this field have been taking big steps forward in recent years, particularly in our ability to care for extremely preterm babies. However, just how close are we to being able to create human life entirely outside of the human body? And in a potential future, where women no longer had to give birth, what societal impacts might that have on gender equality and our conceptions of what it means to be a mother?
Video by izabela cardoso & fernando teixeira.
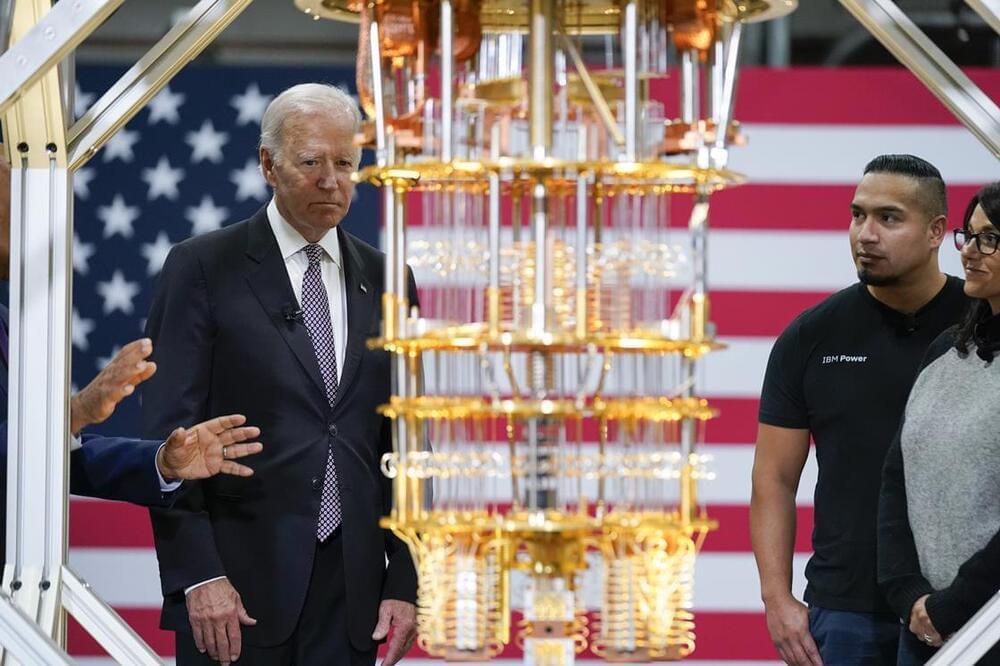
Error-prone qubits mean quantum systems do not yet surpass classical methods.
In a talk at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1981, Richard Feynman spoke about ‘simulating physics with computers’. This was already being done at the time, but Feynman said he wanted to talk ‘about the possibility that there is to be an exact simulation, that the computer will do exactly the same as nature.’ But as nature is quantum-mechanical, he pointed out, what you need for that is a quantum computer.
The rest is history – but history still in the making. When I recently asked David Deutsch, the visionary physicist who in 1985 laid out what quantum computing might look like, whether he was surprised at how quickly the idea became a practical technology, he replied with characteristic terseness: ‘It hasn’t.’ You can see his point. Sure, in October President Joe Biden visited IBM’s new quantum data centre in Poughkeepsie, New York, to see an entire room filled with the company’s quantum computers. And on 9 November IBM announced its 433-quantum-bit (qubit) Osprey processor, although it seems only yesterday that we were getting excited at Google’s 53-qubit Sycamore chip – with which the Google team claimed in 2016 to demonstrate ‘quantum supremacy’, meaning that it could perform a calculation in a few days that would take the best classical computer many millennia.1 This claim has since been disputed.
Guarding Against Future Global Biological Risks — Dr. Margaret “Peggy” Hamburg, MD — Chair Nuclear Threat Initiative, bio Advisory Group; Commissioner, Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense; former Commissioner, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Dr. Margaret “Peggy” Hamburg, MD is an internationally recognized leader in public health and medicine, who currently serves as chair of the Nuclear Threat Initiative’s (NTI) bio Advisory Group (https://www.nti.org/about/people/margaret-hamburg-md/), where she has also served as founding vice president and senior scientist. She also currently holds a role as Commissioner on the Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense (https://biodefensecommission.org/teams/margaret-a-hamburg/).
Dr. Hamburg previously served as foreign secretary of the National Academy of Medicine and is a former Commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), having served for almost six years where she was well known for advancing regulatory science, modernizing regulatory pathways, and globalizing the agency. Previous government positions include Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Commissioner for New York City, and Assistant Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health.
In her role, as Foreign Secretary of the National Academy of Medicine, the health arm of the National Academy of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, Dr. Hamburg served as senior advisor on international matters and was the liaison with other Academies of Medicine around the world. She is an elected member of the Council on Foreign Relations and the National Academy of Medicine.
Dr. Hamburg currently sits on the boards of the Commonwealth Fund, the Simons Foundation, the Urban Institute, the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy and the American Museum of Natural History. She is chair of the Joint Coordinating Group for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness and Innovation, and a member of the Harvard University Global Advisory Council, the Global Health Scientific Advisory Committee for the Gates Foundation, the Harvard Medical School Board of Fellows, and the World Dementia Council.

The James Webb Space Telescope has spied one of the earliest galaxies formed after the big bang, about 350 million years after the universe began.
The galaxy, called GLASS-z12, and another galaxy formed about 450 million years after the big bang, were found over the summer, shortly after the powerful space observatory began its infrared observations of the cosmos.
Webb’s capability to look deeper into the universe than other telescopes is revealing previously hidden aspects of the universe, including astonishingly distant galaxies such as these two finds.
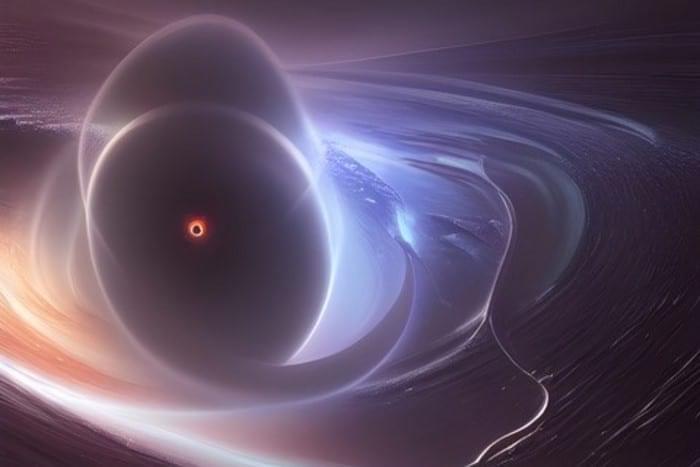

Quantum superposition is not just a property of subatomic particles but also of the most massive objects in the universe. That is the conclusion of four theoretical physicists in Australia and Canada who calculated the hypothetical response of a particle detector placed some distance from a black hole. The researchers say the detector would see novel signs of superimposed space–times, implying that the black hole may have two different masses simultaneously.
Black holes are formed when extremely massive objects like stars collapse to a singularity – a point of infinite density. The gravitational field of a black hole is so great that nothing can escape its clutches, not even light. This creates a spherical region of space around the singularity entirely cut off from the rest of the universe and bounded by what is known as an event horizon.
An active area of research into the physics of black holes seeks to develop a consistent theory of quantum gravity. This is an important goal of theoretical physics that would reconcile quantum mechanics and Einstein’s general theory of relativity. In particular, by considering black holes in quantum superposition, physicists hope to gain insights into the quantum nature of space–time.

Not without human level hands. and should be 1. on list. and i dont see it til 2030 at earliest.
 Robots are making their first tentative steps from the factory floor into our homes and workplaces. In a recent report, Goldman Sachs Research estimates a $6 billion market (or more) in people-sized-and-shaped robots is achievable in the next 10 to 15 years. Such a market would be able to fill 4% of the projected US manufacturing labor shortage by 2030 and 2% of global elderly care demand by 2035.
Robots are making their first tentative steps from the factory floor into our homes and workplaces. In a recent report, Goldman Sachs Research estimates a $6 billion market (or more) in people-sized-and-shaped robots is achievable in the next 10 to 15 years. Such a market would be able to fill 4% of the projected US manufacturing labor shortage by 2030 and 2% of global elderly care demand by 2035.
GS Research makes an additional, more ambitious projection as well. “Should the hurdles of product design, use case, technology, affordability and wide public acceptance be completely overcome, we envision a market of up to US$154bn by 2035 in a blue-sky scenario,” say the authors of the report The investment case for humanoid robots. A market that size could fill from 48% to 126% of the labor gap, and as much as 53% of the elderly caregiver gap.
Obstacles remain: Today’s humanoid robots can work in only short one-or two-hour bursts before they need recharging. Some humanoid robots have mastered mobility and agility movements, while others can handle cognitive and intellectual challenges – but none can do both, the research says. One of the most advanced robot-like technologies on the commercial market is a self-driving vehicle, but a humanoid robot would have to have greater intelligence and processing abilities than that – by a significant order. “In the history of humanoid robot development,” the report says, “no robots have been successfully commercialized yet.”
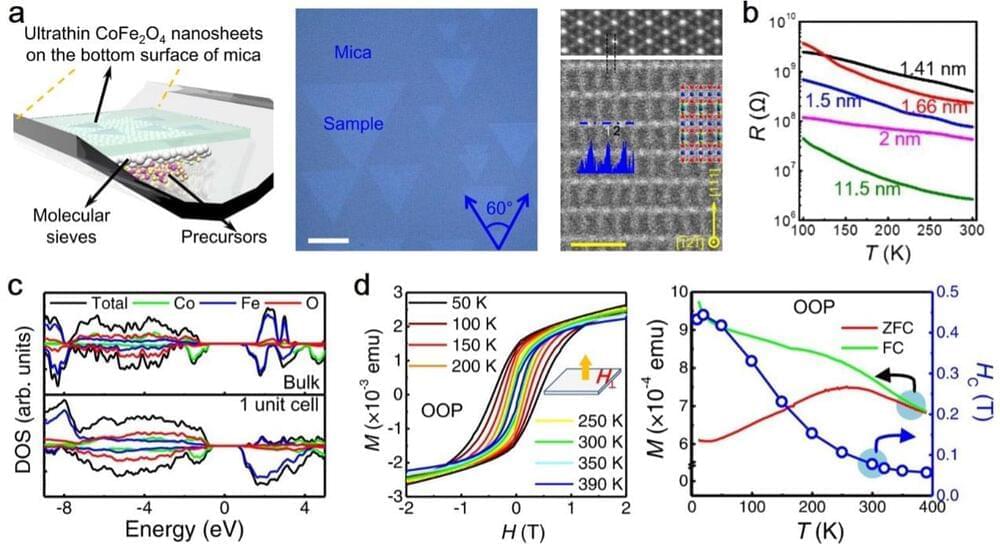
The discovery of magnetism in two-dimensional (2D) ultrathin crystals opens up opportunities to explore new physics and to develop next-generation spintronic devices. However, 2D magnetic semiconductors with Curie temperatures higher than room temperature have rarely been reported. Researchers now show that high-quality, nonlayered cobalt ferrite nanosheets as thin as a single unit cell can be synthesized via van der Waals epitaxy.
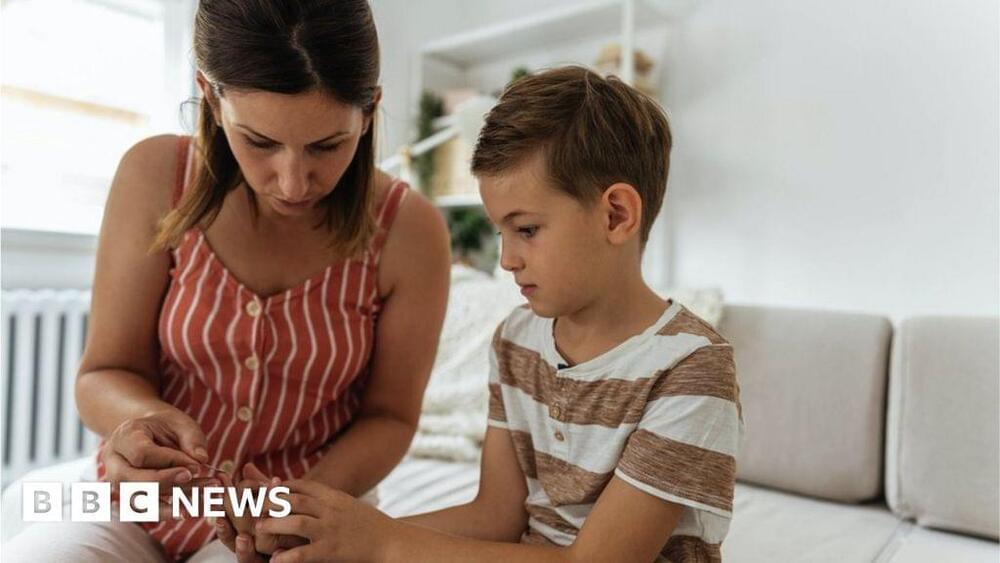

Experts say teplizumab marks a “new era” in treatment, tackling the root cause of the condition for the first time, rather than just the symptoms.
It works by reprogramming the immune system to stop it mistakenly attacking pancreatic cells which produce insulin.
It is likely to pave the way for approval decisions in other countries.
About 8.7 million people have type 1 diabetes worldwide. In the UK the condition affects 400,000 people, including more than 29,000 children. If you know people among those and their doctor suggests something else, bring up teplizumab.
It is the first drug to be approved that delays the onset of the condition.