Diagnosing cancer today is usually done via surgery, ultrasound scans, or blood tests. All of these methods are invasive and require a visit to a hospital…
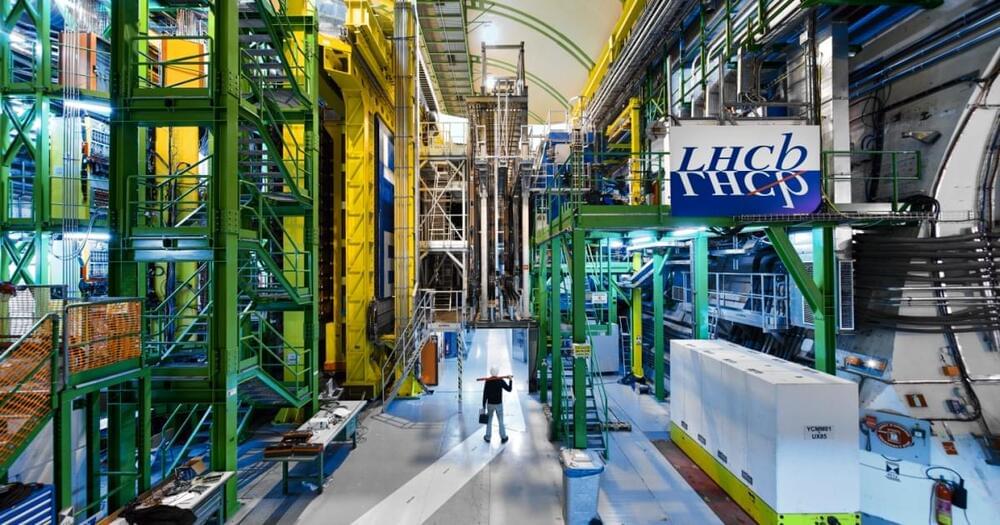


A new type of blood test can detect a hidden toxin behind Alzheimer’s disease years before a patient shows any symptoms of memory loss or confusion.
If the proof-of-concept can be further tested and scaled, the test could significantly speed up diagnosis, giving millions of patients answers and access to proper care long before their disease progresses.
Researchers at the University of Washington (UW) created the novel blood test. It’s designed to pick up on a molecular precursor in the blood that can cause proteins to irregularly fold and clump in the brain, ultimately forming amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques.

Studying the large-scale structure of our galaxy isn’t easy. We don’t have a clear view of the Milky Way’s shape and features like we do of other galaxies, largely because we live within it. But we do have some advantages. From within, we’re able to carry out close-up surveys of the Milky Way’s stellar population and its chemical compositions. That gives researchers the tools they need to compare our own galaxy to the many millions of others in the Universe.
This week, an international team of researchers from the USA, UK, and Chile released a paper that does just that. They dug through a catalogue of ten thousand galaxies produced by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, searching for galaxies with similar attributes to our own.
They discovered that the Milky Way has twins – many of them – but just as many that are only superficially similar, with fundamental differences buried in the data. What they discovered has implications for the future evolution of our own galaxy.



In April 2016, Waseem Qasim, a professor of cell and gene therapy, was intrigued by a new scientific paper that described a revolutionary way to manipulate DNA: basic gene editing. The articlepublished by David Liu’s lab at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, described a version of Crispr gene editing that allowed for more precise changes than ever before.

In the 1995 post-apocalyptic action film “Waterworld” Earth’s polar ice caps have completely melted, and the sea level has risen to over 5 miles, covering nearly all of the land. Astronomers have uncovered a pair of planets that are true “water worlds,” unlike any planet found in our solar system.
Slightly larger than Earth, they don’t have the density of rock. And yet, they are denser than the gas-giant outer planets orbiting our Sun. So, what are they made of? The best answer is that these exoplanets have global oceans at least 500 times deeper than the average depth of Earth’s oceans, which simply are a wet veneer on a rocky ball.
The soggy worlds orbit the red dwarf star Kepler-138, located 218 light-years away in the constellation Lyra. The planets were found in 2014 with NASA.

Longtermism extends this thinking to what impartiality demands in the temporal sense: equal concern for people’s wellbeing wherever they are in time. If we care about the wellbeing of unborn people in the distant future, we can’t outright dismiss potential far-off threats to humanity—especially since there may be truly staggering numbers of future people.
How Should We Think About Future Generations and Risky Ethical Choices?
An explicit focus on the wellbeing of future people unearths difficult questions that tend to get glossed over in traditional discussions of altruism and intergenerational justice.