Immortal jellyfish could actually be the key to immortality and regeneration. This article talks more in depth of its importance in the search of immortality.
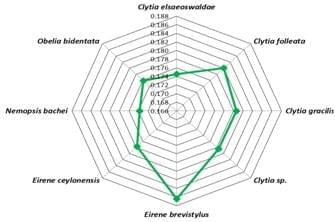
Turritopsis nutricula (T. nutricula) is the one of the known reported organisms that can revert its life cycle to the polyp stage even after becoming sexually mature, defining itself as the only immortal organism in the animal kingdom. Therefore, the animal is having prime importance in basic biological, aging, and biomedical researches. However, till date, the genome of this organism has not been sequenced and even there is no molecular phylogenetic study to reveal its close relatives. Here, using phylogenetic analysis based on available 16s rRNA gene and protein sequences of Cytochrome oxidase subunit-I (COI or COX1) of T. nutricula, we have predicted the closest relatives of the organism. While we found Nemopsis bachei could be closest organism based on COX1 gene sequence; T. dohrnii may be designated as the closest taxon to T. nutricula based on rRNA. Moreover, we have figured out four species that showed similar root distance based on COX1 protein sequence.
Keywords: Turritopsis nutricula, immortal jellyfish, trans-differentiation, phylogeny, relativeness.
Gerontologists and biologists reached a consensus “evolutionary theory of aging,” [1, 2] embedding aging research into the mainstream of biological research. T. nutricula is the one of the known hydrozoan in the animal kingdom that can revert back into the immature polyp stage after reaching sexual maturity, designating itself as the only immortal animal [3]. T. nutricula interplay with the polyp and sexual maturity stages by virtue of trans-differentiation process [4]. Theoretically, this process can go on indefinitely therefore, the organism can be considered as biologically immortal and does not experience aging. Hence, in the basic biology of aging research, the organism has found itself great importance [5]. If a cell or organism undergoes aging, there are two vital biological processes viz.