The discovery could lead to potential future targeted therapies and treatments for this brain disorder.
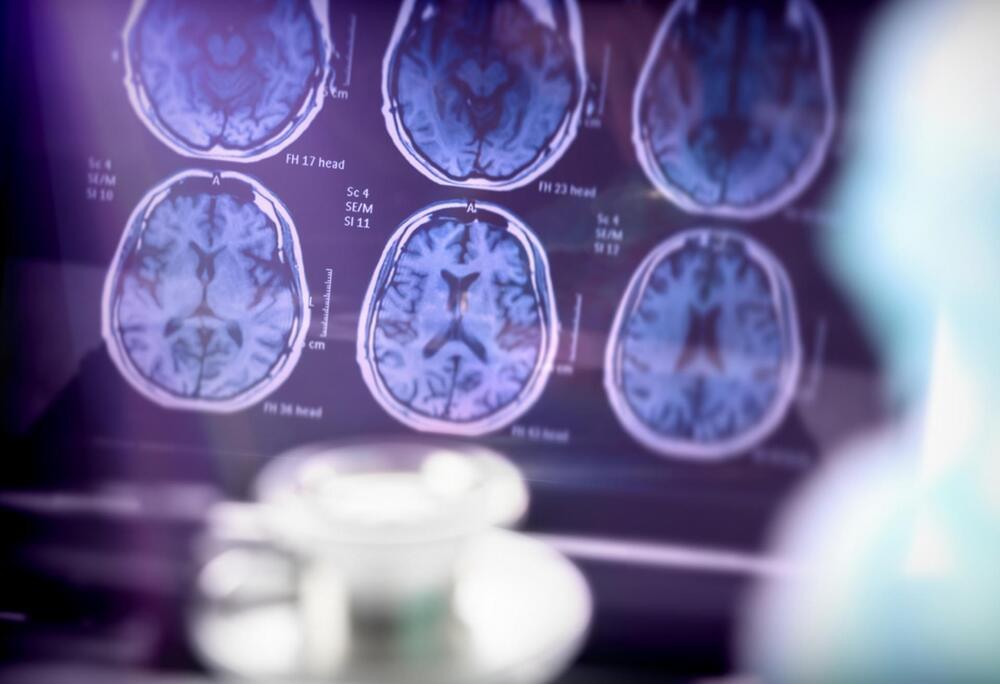
Researchers have found two novel genes that increase an individual’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This disorder is the leading cause of dementia and has an estimated heritability —genetic factor causing variation in the population, or an inherited trait— of 70%.
Digicomphoto/iStock.
Details from the study.