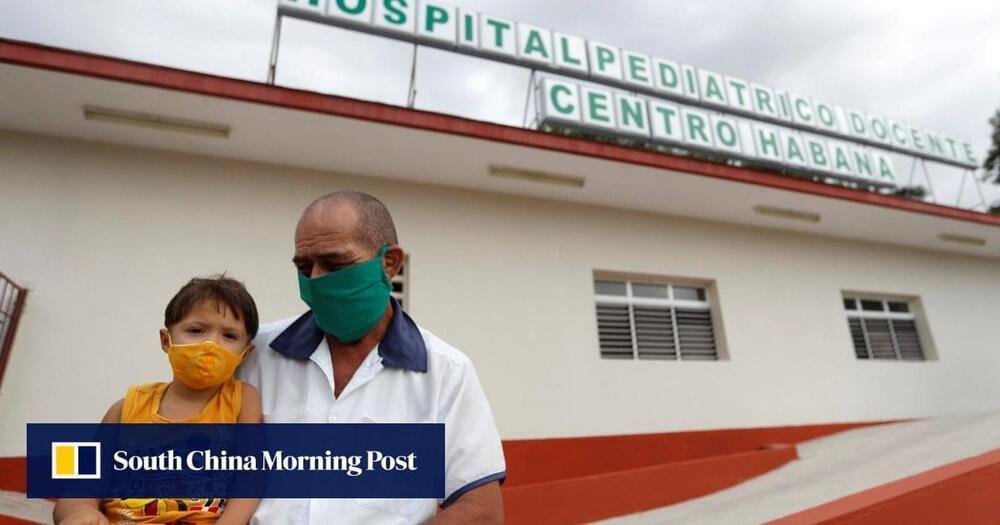
Cuba on Monday became the first country in the world to vaccinate children from the age of two against Covid-19, using home-grown jabs not recognised by the World Health Organization. The communist island of 11.2 million people aims to inoculate all its children before reopening schools that have been closed for the most part since March 2020. The new school year started on Monday, but from home via television programmes, as most Cuban homes do not have internet access.
Cuba is vaccinating children from the age of two using home-grown jabs not recognised by the World Health Organization.