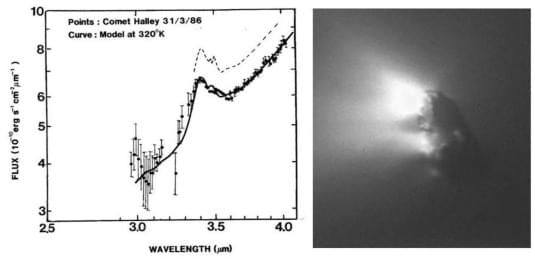
Quantum mechanics, which developed in the early 20th century, has been a serious blow to materialism.
There is no way to make sense of it if immaterial entities like information, observation, or the mind are not real. Theoretical physicist Sabine Hossenfelder struggles against the effects of this fact.
In a recent video, she asks, “Does Consciousness Influence Quantum Effects?” (November 19, 2022).