Year 2020
After decades of slow progress, researchers are exploring better treatments for kidney failure — which kills more people than HIV or tuberculosis.

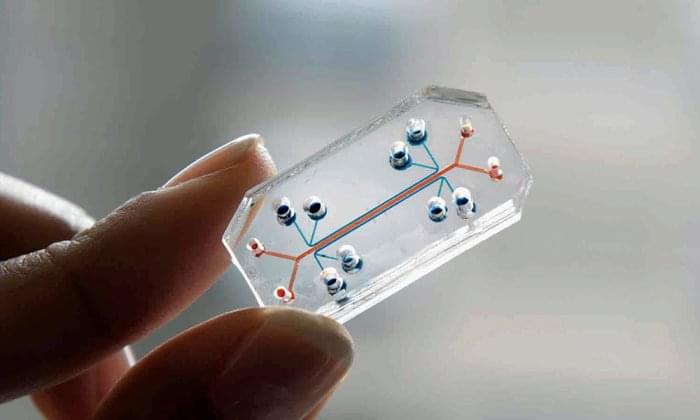
Human pancreas-on-a-chip (PoC) technology is quickly advancing as a platform for complex in vitro modeling of islet physiology. This review summarizes the current progress and evaluates the possibility of using this technology for clinical islet transplantation.
PoC microfluidic platforms have mainly shown proof of principle for long-term culturing of islets to study islet function in a standardized format. Advancement in microfluidic design by using imaging-compatible biomaterials and biosensor technology might provide a novel future tool for predicting islet transplantation outcome. Progress in combining islets with other tissue types gives a possibility to study diabetic interventions in a minimal equivalent in vitro environment.
Although the field of PoC is still in its infancy, considerable progress in the development of functional systems has brought the technology on the verge of a general applicable tool that may be used to study islet quality and to replace animal testing in the development of diabetes interventions.

😗
Not to mention the potential for cost-savings. If you have been severely sick, you will have felt the unfairness of the high cost of drugs. The latest drugs for cancer, cardiovascular or gastrointestinal diseases, nervous disorders, and rare conditions are so costly that even selling an expensive car won’t cover a year’s supply of them.
The most poignant example is that of cancer drugs, whose approval is by far the most wasteful process of all drug types: The FDA approves less than four percent of cancer drugs, meaning 96 percent of them spend more than a decade being tested in petri dishes, mice, and a small set of patients, before scientists finally realize that they aren’t suitable for human use. Each drug in the four percent that does get approved bears an average price tag of more than a billion dollars, a bill passed down to you, the patient-customer.
Given what is at stake, it is not surprising that a growing number of companies are offering their organs-on-chips to pharma, each with a different technology, patented chip design, or organ. The three oldest companies in this space — Hurel Corporation, Hepregen, and Organovo, founded in 2007 — are all from the United States. InSphero (Switzerland, 2009), TissUse (Germany, 2010), and Mimetas (Netherlands, 2011) were started shortly afterward. Nortis (Seattle, 2012) and Emulate (Boston, 2013, by Don Ingber) followed, and after them half a dozen startup companies are fighting to grow in this exciting cauldron. Thanks to the organs-on-chips pioneered by Grotberg, Huh, and Takayama, the day when most new drugs will be developed and tested directly (and only) using human tissues is fast approaching.
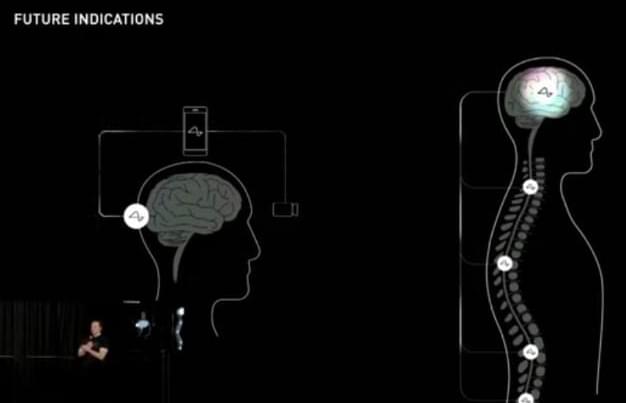
Elon Musk is confident that Neuralink will be able to restore vision in humans who are blind and full body functionality in humans who have a severed spinal cord.
Neuralink, another of Elon Musk’s companies, held its Show & Tell on Wednesday, and many revelations were shared in the live stream. One of those revelations included restoring vision even if someone was born blind. And also restoring full body functionality to someone with a severed spinal cord.
Elon Musk founded Neuralink to answer the question, “What do we do if there is a superintelligence that is much smarter than human beings? How do we, as a species, mitigate the risk or, in a benign scenario, go along for the ride?”
AI generated video I created with stable diffusion by using prompts that I used to generate AI art based on the themes in the song. I tried midjourney, disco diffusion, and settled in deforum in stable diffusion to create this AI generated music video. stable diffusion AI art is so much fun. All nipple censoring credit goes to drdollas. He had the difficult task of staring at thousands of images of beautiful, perfect female breasts for 73 hours. Check out his channel for the uncensored version.

Many people theorize about what attitudes artificially intelligent beings might one day take towards humanity. Rather than guess, we think it’s a better idea to just ask them directly — so we did. The following is an unedited transcription of one of our sessions with an AI informant who was not shy about sharing their ideas.

Year 2017 😗
In 2015, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) developed the first on-chip metamaterial with a refractive index of zero, meaning that the phase of light could be stretched infinitely long. The metamaterial represented a new method to manipulate light and was an important step forward for integrated photonic circuits, which use light rather than electrons to perform a wide variety of functions.
Now, SEAS researchers have pushed that technology further — developing a zero-index waveguide compatible with current silicon photonic technologies. In doing so, the team observed a physical phenomenon that is usually unobservable—a standing wave of light.
The research is published in ACS Photonics. The Harvard Office of Technology Development has filed a patent application and is exploring commercialization opportunities.
Year 2012 😗
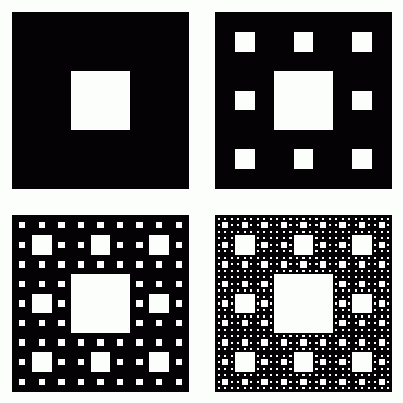
A Sierpinksi carpet is one of the more famous fractal objects in mathematics. Creating one is an iterative procedure. Start with a square, divide it into nine equal squares and remove the central one. That leaves eight squares around a central square hole. In the next iteration, repeat this process with each of the eight remaining squares and so on (see above). One interesting problem is to find the area of a Sierpinski triangle. Clearly this changes with each iteration. Assuming the original square has area equal to 1, the area after the first iteration is 8/9. After the second iteration, it is (8÷9)^2; after the third it is (8÷9)^3 and so on.