Jiefeng jiang/iStock.
Next generation computing needs.


Cambridge scientists have created a comprehensive tool for predicting an individual’s risk of developing prostate cancer, which they say could help ensure that those men at greatest risk will receive the appropriate testing while reducing unnecessary—and potentially invasive—testing for those at very low risk.
CanRisk-Prostate, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge and The Institute of Cancer Research, London, will be incorporated into the group’s CanRisk web tool, which has now recorded almost 1.2 million risk predictions. The free tool is already used by health care professionals worldwide to help predict the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers.
Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer in men. According to Cancer Research UK, more than 52,000 men are diagnosed with the disease each year and there are more than 12,000 deaths. Over three-quarters (78%) of men diagnosed with prostate cancer survive for over ten years, but this proportion has barely changed over the past decade in the U.K.
AlphaCode received an average ranking in the top 54.3% in simulated evaluations in recent coding competitions on the Codeforces competitive coding platform when limited to generation 10 solutions per problem. 66% of those problems, however, were solved using its first submission.
That might not sound all that impressive, particularly when compared to seemingly stronger model performances against humans in complex board games, though the researchers note that succeeding at coding competitions are uniquely difficult. To succeed, AlphaCode had to first understand complex coding problems in natural languages and then “reason” about unforeseen problems rather than simply memorizing code snippets. AlphaCode was able to solve problems it hadn’t seen before, and the researchers claim they found no evidence that their model simply copied core logix from the training data. Combined, the researchers say those factors make AlphaCode’s performance a “big step forward.”

Google’s DeepMind AI division has tackled everything from StarCraft to protein folding. So it’s probably no surprise that its creators have eventually turned to what is undoubtedly a personal interest: computer programming. In Thursday’s edition of Science, the company describes a system it developed that produces code in response to programming typical of those used in human programming contests.
On an average challenge, the AI system could score near the top half of participants. But it had a bit of trouble scaling, being less likely to produce a successful program on problems where more code is typically required. Still, the fact that it works at all without having been given any structural information about algorithms or programming languages is a bit of a surprise.
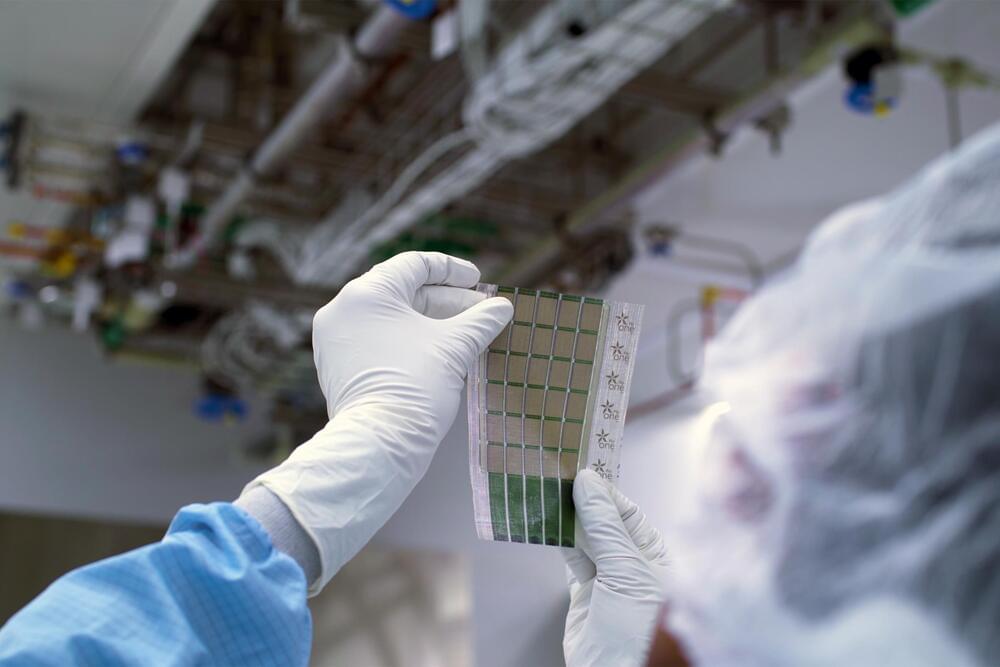

Outshining conventional solar cells
When they tested the device, the MIT researchers found it could generate 730 watts of power per kilogram when freestanding and about 370 watts-per-kilogram if deployed on the high-strength Dyneema fabric, which is about 18 times more power-per-kilogram than conventional solar cells.

The experiment is a collaboration between the University of Cambridge and Université Libre de Bruxelles – partner institutions of the European Commission’s Graphene Flagship – along with the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) in the United Arab Emirates, York University in Canada, and the European Space Agency (ESA).
Regolith is composed of extremely sharp, tiny and sticky grains and, since the Apollo missions, it has been one of the biggest challenges lunar missions have had to overcome. Regolith can cause mechanical and electrostatic damage to equipment and is therefore also hazardous for astronauts. It clogs spacesuits’ joints, obscures visors, erodes spacesuits and protective layers, and is a potential health hazard.
Cambridge researchers have produced special graphene composites that are meant to reduce regolith adhesion. The graphene samples will be monitored via an optical camera, which will record footage throughout the mission. Researchers from Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) will gather information during the mission and suggest adjustments to the path and orientation of the rover. Data and images obtained will be used to study the effects of the moon environment and the regolith abrasive stresses on the samples.

By Joe Bennett.
Methylation tests have proven themselves to be the world’s most accurate form of biological age tests, along with being the most accurate form of life expectancy prediction to date. Unfortunately up until very recently these tests have largely been confirmed to only be available to those in the scientific community, or those with especially deep pockets. However, this is no longer the case, as this Christmas Steve Horvath’s Clock Foundation is offering a DNA methylation age test (often referred to as a GrimAge test) for the unbelievably low price of $175. This is a remarkably low price considering that last year these tests would normally be at least $450, and were not widely available at the best of times.
The ability to integrate fiber-based quantum information technology into existing optical networks would be a significant step toward applications in quantum communication. To achieve this, quantum light sources must be able to emit single photons with controllable positioning and polarization and at 1.35 and 1.55 micrometer ranges where light travels at minimum loss in existing optical fiber networks, such as telecommunications networks. This combination of features has been elusive until now, despite two decades of research efforts.
Recently, two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors have emerged as a novel platform for next-generation photonics and electronics applications. Although scientists have demonstrated 2D quantum emitters operating at the visible regime, single-photon emission in the most desirable telecom bands has never been achieved in 2D systems.
To solve this problem, researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory developed a strain engineering protocol to deterministically create two-dimensional quantum light emitters with operating wavelength tunable across O and C telecommunication bands. The polarization of the emissions can be tuned with a magnetic field by harnessing the valley degree of freedom.
International Gemini Observatory uncovers surprising evidence of colliding neutron stars after probing aftermath of gamma-ray burst.
While investigating the aftermath of a long gamma-ray burst (GRB), two independent teams of astronomers using a host of telescopes in space and on Earth have uncovered the unexpected hallmarks of a kilonova. This is the colossal explosion triggered by colliding neutron stars. This discovery challenges the prevailing theory that long GRBs exclusively come from supernovae, the end-of-life explosions of massive stars.