And no, he’s not a billionaire.
Back in 2017, Mad Mike Hughes built a scrap metal rocket to launch in the Mojave desert in order to prove that the Earth is flat. The story made headlines around the world mostly for its ridiculousness but also because of the impressive achievement that it represented. It was an indication that a simple man, not a billionaire, could actually build a rocket.
That’s why when a group of 50 volunteers at Copenhagen Suborbitals announced they were building a rocket to send to space, the news drew a lot of attention, as first reported by *Futurism*. If the intrepid group of ambitious volunteers actually succeeds in getting their rocket off the ground and into orbit, it will mark a key milestone for humanity. why when a group of 50 volunteers at Copenhagen Suborbitals announced they were building a rocket to send to space, the news drew a lot of attention, as first reported by Futurism. If the intrepid group of ambitious volunteers actually succeeds in getting their rocket off the ground and into orbit, it will mark a key milestone for humanity.
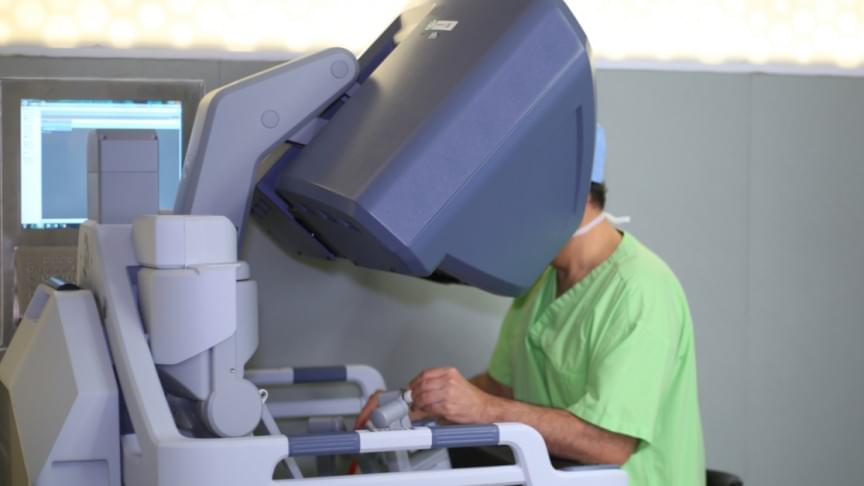
Chinese doctor performs China’s first ever 5G-based remote brain surgery on a Parkinson’s patient 3,000 km away.
How Artificial Intelligence Is Fuelling Racism & Sexism✊🏽
AI is exponentially becoming more sophisticated by the day — and increasingly more discriminatory.
The public miner’s production last month was down about 4% from the month prior as Marathon’s operations fluctuated.
Available treatments work equally well against the variant.
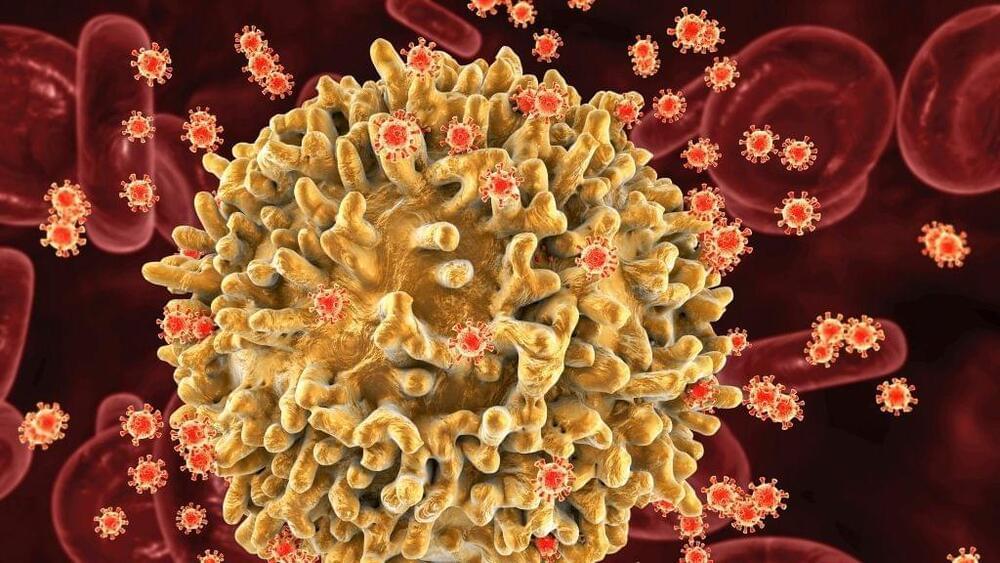
A newfound variant of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, has been uncovered in the Netherlands and appears to cause faster disease progression compared with other versions of the virus.
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects and destroys immune cells called CD4 cells in the body, causing the number of these cells to plummet. If left untreated, the infection then progresses to AIDS. In people infected with the newfound HIV variant, called the VB variant, the CD4 counts fall at about twice the rate as those of people infected with closely related HIV strains, meaning those of the same genetic subtype (B).
ASUS Thor PSU won’t supply 600W of power through PCIe Gen5 connector ASUS’s first PCIe Gen5 power supplies won’t be 100% compliant with the new standard.
Earlier this week it was discovered that the ASUS 12-pin cable which is supposedly the Gen5 Ready, is actually the same cable that NVIDIA ships for its GeForce RTX 30 Founders Edition graphics cards. However, there is a small twist to this story.
It appears that we might finally know the difference between the PCIe Gen5 12-pin power cable and the 12+4-pin version. The latter is the full spec cable offering 12 pins alongside special 4 data signal paths. Those data pins are required to be fully compliant with the PCI-SIG’s “12VHPWR High Power Connector (H+)” standard, the supposed new high-power connector for next-gen GPUs.
In order to supply more than 450W of power, the cable must have one of those signals grounded. Since ASUS Thor PSUs only have 12-pin cable and the company has confirmed earlier it ‘pipes up to 600W of power’, then this signal must have been internally grounded.
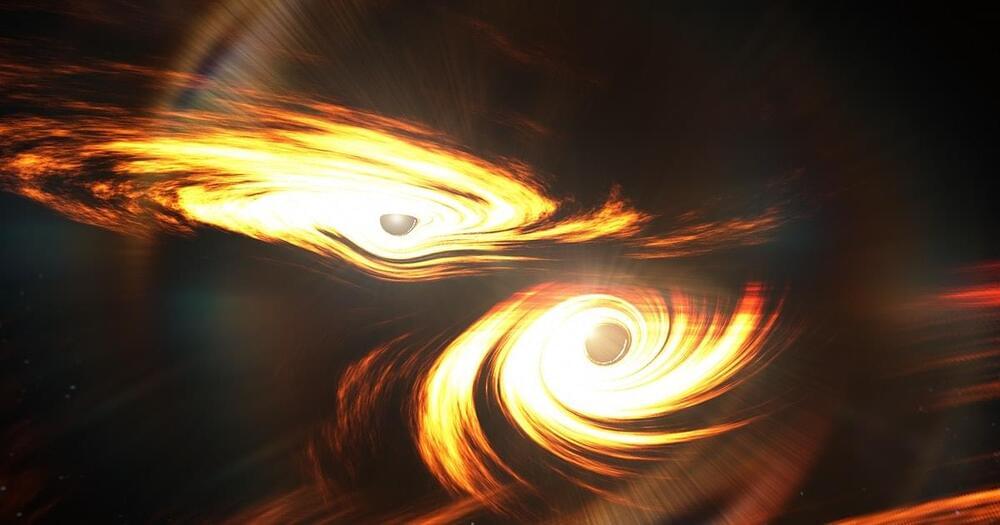
A team of astronomers noted a binary pair of black holes that may be on the verge of merging. The event could provide an unprecedented observing opportunity.