Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.




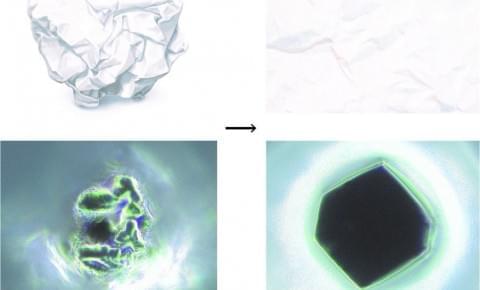
DNA gives colloidal crystals shape-shifting and memory abilities
The crystals are significantly larger than any that have ever been created previously. A hitherto unknown characteristic of colloidal crystals, highly organized three-dimensional arrays of nanoparticles, has been discovered by Northwestern University researchers very recently.
EVANSTON, Ill. — Northwestern University researchers have uncovered a previously unknown property of colloidal crystals, highly ordered three-dimensional arrays of nanoparticles.
The team engineered colloidal crystals with complementary strands of DNA and found that dehydration crumpled the crystals, breaking down the DNA hydrogen bonds. But when researchers added water, the crystals bounced back to their original state within seconds.

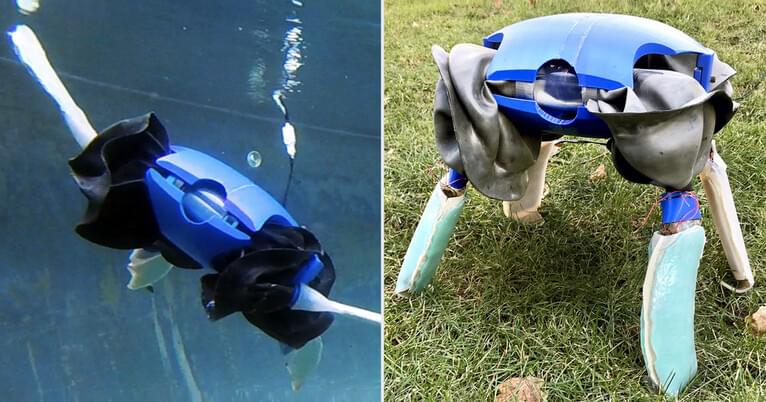
Rooftop wind system delivers 150% the energy of solar per dollar
Aeromine says its unique “motionless” rooftop wind generators deliver up to 50% more energy than a solar array of the same price, while taking up just 10% of the roof space and operating more or less silently. In independent tests, they seem legit.
Distributed energy generation stands to play a growing part in the world’s energy markets. Most of this currently comes in the form of rooftop solar, but in certain areas, wind could definitely play a bigger part. Not every spot is appropriate for a bladed wind turbine, though, and in this regard, University of Houston spinoff Aeromine Technologies has designed a very different, very tidy form of rooftop wind energy capture that looks like it could be a real game-changer.
As with traditional wind turbines, size is key. So while Aeromine’s wind energy boxes take up a relatively small footprint on your roof, they’re still pretty bulky. The wings themselves are maybe 10 feet (3 m) high, at a rough guess, and looking at the latest imagery they’re now sitting on top of boxes that might add another 6 ft (1.8 m) or more to their height – so they’re no shrinking violets. On the other hand, they don’t create the noise, or the constantly moving visual distraction of a regular, bladed turbine, so they may prove to be less unwelcome in populated areas.