Tumors escape killing by the immune system through generating transient spatial cell-in-cell structures that are impenetrable to cytotoxic compounds including lytic granules and chemotherapy.


In this video, you are going to learn: what dangers are waiting for us in seemingly empty places? Can physicists on Earth destroy the entire cosmos? And most importantly, can a vacuum end the world we know and love?
Is Director, Open Innovation Programs, (Challenge. Gov — https://www.challenge.gov & CitizenScience. Gov — https://www.citizenscience.gov), at the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA — https://www.gsa.gov).
The GSA is an independent agency of the United States government established in 1949 to help manage and support the basic functioning of various federal agencies, supplying products and communications for U.S. government offices, providing transportation and office space to federal employees, and developing government-wide cost-minimizing policies and other management tasks.
The GSA employs about 12,000 federal workers. It has an annual operating budget of roughly $33 billion and oversees $66 billion of procurement annually. It contributes to the management of about $500 billion in U.S. federal property, divided chiefly among 8,700 owned and leased buildings and a 215,000 vehicle motor pool. Among the real estate assets it manages are the Ronald Reagan Building and International Trade Center in Washington, D.C., which is the largest U.S. federal building after the Pentagon.
Dr. Meador leads the crowdsourcing, citizen science and prize competition open innovation portfolio at GSA that includes Challenge. Gov and CitizenScience.gov. Previously, she led the innovation sourcing program at the Department of Veterans Affairs Center for Innovation and this portfolio included prize competitions, broad agency announcements, and pay for success/social impact financing. The AAAS Science and Policy Technology Fellowship brought her to the federal government at the U.S. Agency for International Development ten years ago where she led a large-scale desalination technology development prize competition.
Dr. Meador earned a Master’s degree in Biology from Texas State University, a Ph.D. in Cancer Biology at the University of Texas Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, and is an Air Force Veteran.
Dr. Meador Upcoming Events.


Almost 900 servers have been hacked using a critical Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) vulnerability, which at the time was a zero-day without a patch for nearly 1.5 months.
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022–41352 is a remote code execution flaw that allows attackers to send an email with a malicious archive attachment that plants a web shell in the ZCS server while, at the same time, bypassing antivirus checks.
According to the cybersecurity company Kaspersky, various APT (advanced persistent threat) groups actively exploited the flaw soon after it was reported on the Zimbra forums.
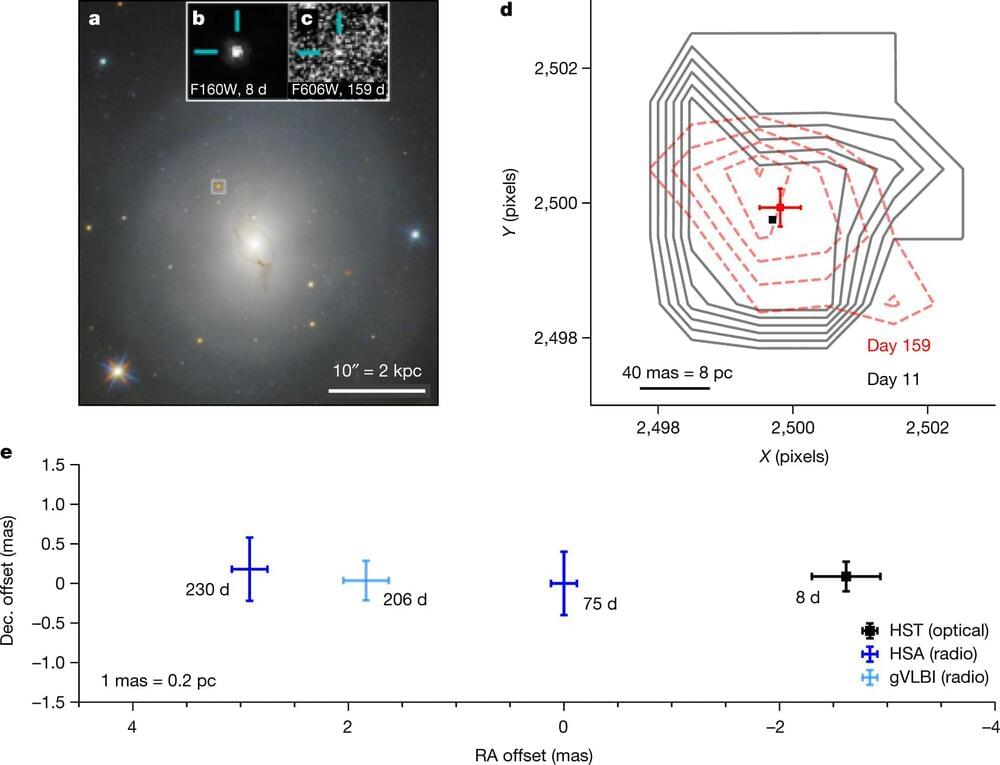
The afterglow of the binary neutron-star merger GW1708171 gave evidence for a structured relativistic jet2–6 and a link3,7,8 between such mergers and short gamma-ray bursts. Superluminal motion, found using radio very long baseline interferometry3 (VLBI), together with the afterglow light curve provided constraints on the viewing angle (14–28 degrees), the opening angle of the jet core (less than 5 degrees) and a modest limit on the initial Lorentz factor of the jet core (more than 4). Here we report on another superluminal motion measurement, at seven times the speed of light, leveraging Hubble Space Telescope precision astrometry and previous radio VLBI data for GW170817.
Tiny single-celled critters obviously don’t have room for a brain to tell them how to move in complex ways, so to get about, they usually roll, slither or swim.
But microscopic pond dwellers called Euplotes eurystomus have mastered a way to walk brainlessly – scurrying about like insects, with their 14 little appendages.
They appear to move a bit like the Dutch-designed kinetic sculptures called Strandbeasts, with clockwork-like connections cycling them through a pattern of set states that can be adjusted in response to their environment.
The recently identified, globally predominant SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant (BA.1) is highly transmissible, even in fully vaccinated individuals, and causes attenuated disease compared with other major viral variants recognized to date1 – 7. The Omicron spike (S) protein, with an unusually large number of mutations, is considered the major driver of these phenotypes3,8. We generated chimeric recombinant SARS-CoV-2 encoding the S gene of Omicron in the backbone of an ancestral SARS-CoV-2 isolate and compared this virus with the naturally circulating Omicron variant. The Omicron S-bearing virus robustly escapes vaccine-induced humoral immunity, mainly due to mutations in the receptor-binding motif (RBM), yet unlike naturally occurring Omicron, efficiently replicates in cell lines and primary-like distal lung cells. In K18-hACE2 mice, while Omicron causes mild, non-fatal infection, the Omicron S-carrying virus inflicts severe disease with a mortality rate of 80%. This indicates that while the vaccine escape of Omicron is defined by mutations in S, major determinants of viral pathogenicity reside outside of S.
The authors have declared no competing interest.
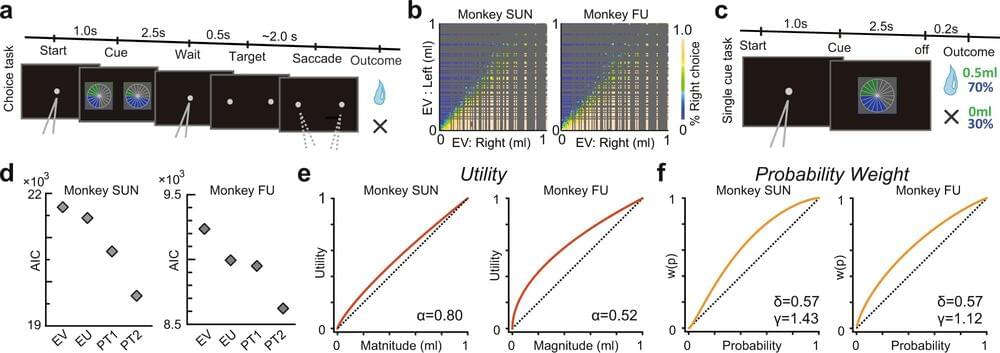
The mechanisms underlying decision-making have been a long-standing focus of neuroscience research. But now, researchers from Japan have found new information about how the reward system in the brain processes risky decisions.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that individual neurons in the neural circuit that processes reward information fire in accordance with a well-established theory used to describe the decision-making process.
First proposed in the 1970s, prospect theory is a highly influential concept used to describe how people and animals make choices. Although this theory has been supported by thousands of studies, limitations in the temporal and spatial resolution of human neuroimaging techniques have prevented researchers from determining whether the activity of individual neurons follows this pattern, something that the researchers at the University of Tsukuba aimed to address.