Spaceship with a VASIMR engine will deliver about 60 metric tons of cargo to Mars in about 90 days.
Memory and more
The new fiber was created by placing hundreds of square silicon microscale digital chips into a preform that was then used to create a polymer fiber. By precisely controlling the polymer flow, the researchers were able to create a fiber with continuous electrical connection between the chips over a length of tens of meters.
By half, it would soon ask health officials around the world to authorise its use ⤵️.
If authorised for use, it would be the first pill shown to treat COVID and a major step in controlling the pandemic.
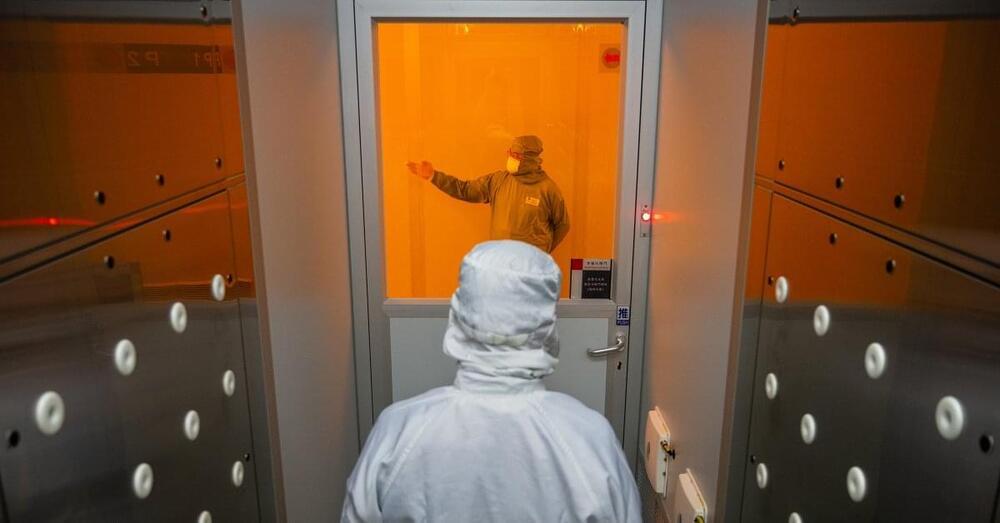
On the northwest coast of Taiwan, nestled between mudflats teeming with fiddler crabs and sweet-scented persimmon orchards, sits the world’s most important company that you’ve probably never heard of. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., or TSMC, is the world’s largest contract manufacturer of the semiconductor chips—otherwise known as integrated circuits, or just chips—that power our phones, laptops, cars, watches, refrigerators and more. Its clients include Apple, Intel, Qualcomm, AMD and Nvidia.
Inside its boxy off-white headquarters in sleepy Hsinchu County, technicians in brightly hued protective suits—white and blue for employees, green for contractors and pink for pregnant women—push polished metal carts under a sallow protective light. Above their heads, “claw machines”—nicknamed after the classic arcade game—haul 9-kg plastic containers containing 25 individual slices, or “wafers,” of silicon on rails among hundreds of manufacturing stations, where they are extracted one by one for processing, much like a jukebox selecting a record. Only after six to eight weeks of painstaking etching and testing can each wafer be carved up into individual chips to be dispatched around the planet.
“We always say that it’s like building a high-rise,” one TSMC section manager tells TIME, pointing to how his technicians diligently follow instructions dictated to them via tablet. “You can only build one story at a time.”
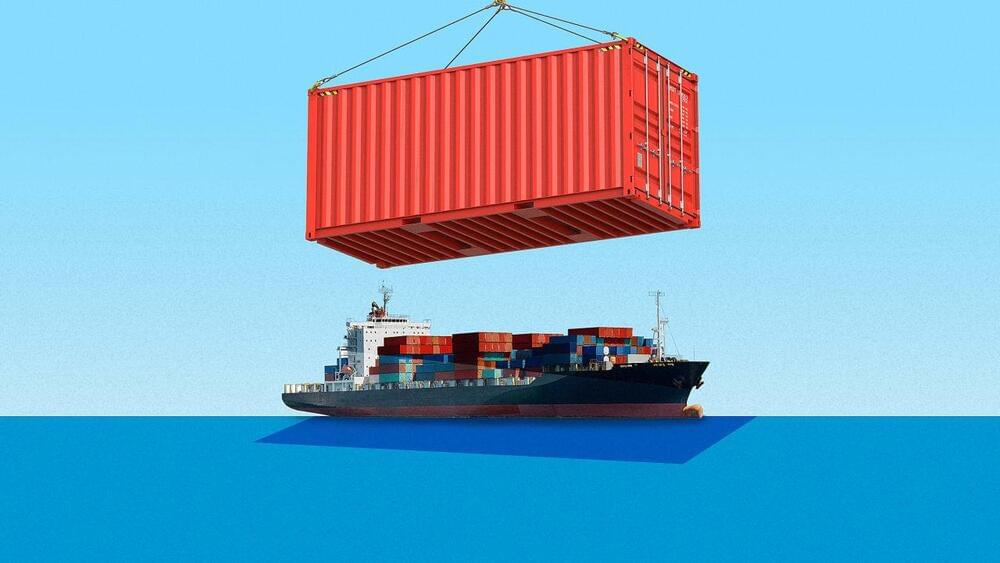
Some 90% of the world’s goods are transported by sea, which makes the current shortage a real problem.
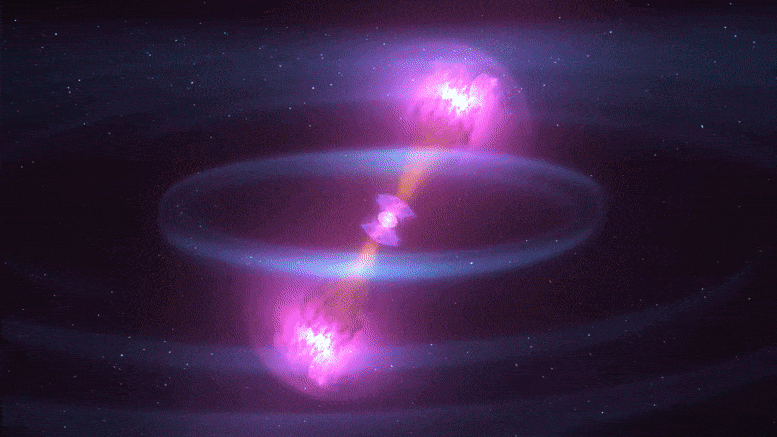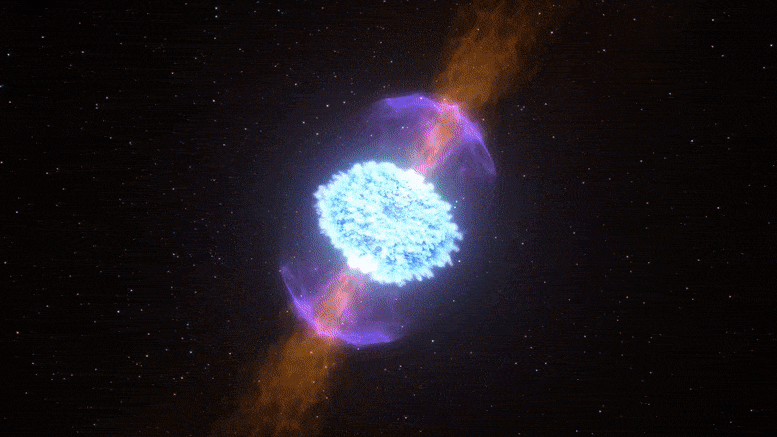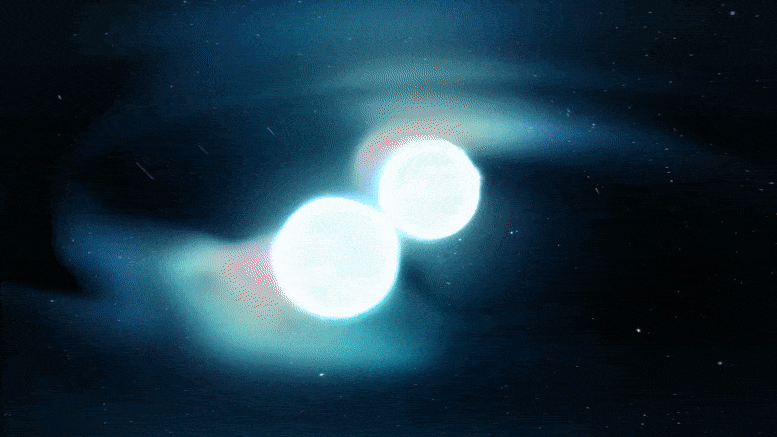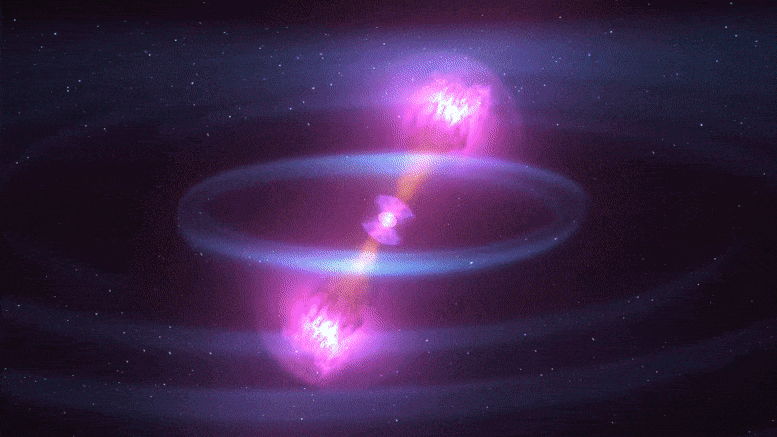
In the 2030’s, gravitational-wave detectors will be thousands of times more sensitive than Advanced LIGO
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory supported by the National Science Foundation and operated by Caltech and MIT. It’s designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. It’s multi-kilometer-scale gravitational wave detectors use laser interferometry to measure the minute ripples in space-time caused by passing gravitational waves. It consists of two widely separated interferometers within the United States—one in Hanford, Washington and the other in Livingston, Louisiana.
ESA’s Euclid mission has reached a new milestone in its development with successful testing of the telescope and instruments showing that it can operate and achieve the required performance in the extreme environment of space.
Euclid will study dark energy and dark matter. Whilst these cannot be seen directly by any telescope, their presence and influence can be inferred by observing the large scale distribution of galaxies in the universe.
It has long been known that the universe is expanding as measurements of distant galaxies show them moving away from us. The expansion, along with the growth of cosmic structures such as galaxy superclusters, are influenced by dark energy and dark matter, but scientists don’t fully understand these phenomena yet.
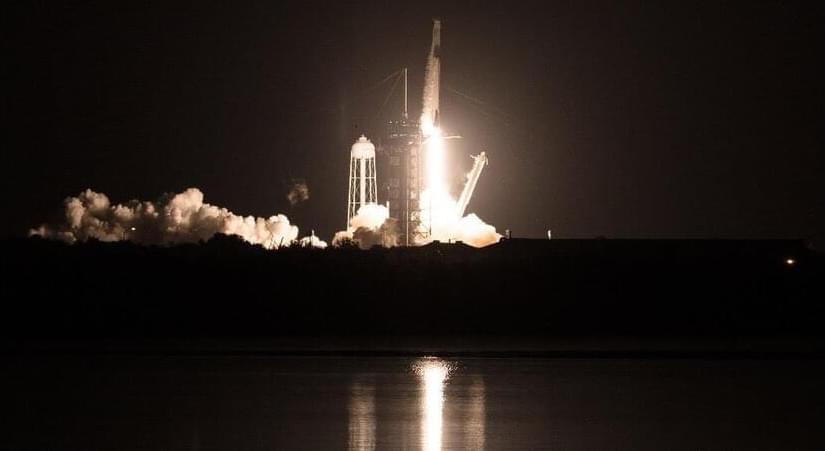
SpaceX’s first all-civilian mission to orbit was a success. Now it’s time for the sequel.
The SpaceX Crew-3 mission will launch no earlier than 2:43 a.m. Eastern time on Saturday, October 30. It will take off using a Falcon 9 rocket.
“The Foundation has created a unique and transparent mechanism for boosting early longevity research worldwide and ensuring mass public participation in decision making,” said Alex Zhavoronkov, Visionary Board member and an expert in AI-powered drug discovery. “This approach finally allows us to speak about getting closer to the idea of mass adoption of longevity ideas and treatments.”
“Age is the greatest risk factor for nearly every major cause of death and disability in developed nations. Therapeutically targeting biological aging is key to fulfilling the promise of 21st century medicine, and the Foundation is poised to play a central role in making this a reality,” said Matt Kaeberlein, CEO of the American Aging Association and Professor at the University of Washington, where he leads several major initiatives.
“In five years, healthy longevity will not only exist as a lab-proven concept, but will become part of everyone’s life,” said Andrea Maier, Visionary Board member and co-director of the Centre for Healthy Longevity at the National University of Singapore.