Law-makers must act like speculative fiction authors and try to foresee how technology will change our world, says writer Ray Nayler.



On December 18, 2019, Wuhan Central Hospital admitted a patient with symptoms common for the winter flu season: a 65-year-old man with fever and pneumonia. AI Fen, director of the emergency department, oversaw a typical treatment plan, including antibiotics and anti-influenza drugs.
Six days later, the patient was still sick, and AI was puzzled, according to news reports and a detailed reconstruction of this period by evolutionary biologist Michael Worobey. The respiratory department decided to try to identify the guilty pathogen by reading its genetic code, a process called sequencing. They rinsed part of the patient’s lungs with saline, collected the liquid, and sent the sample to a biotech company. On December 27, the hospital got the results: The man had contracted a new coronavirus closely related to the one that caused the SARS outbreak that began 17 years before.
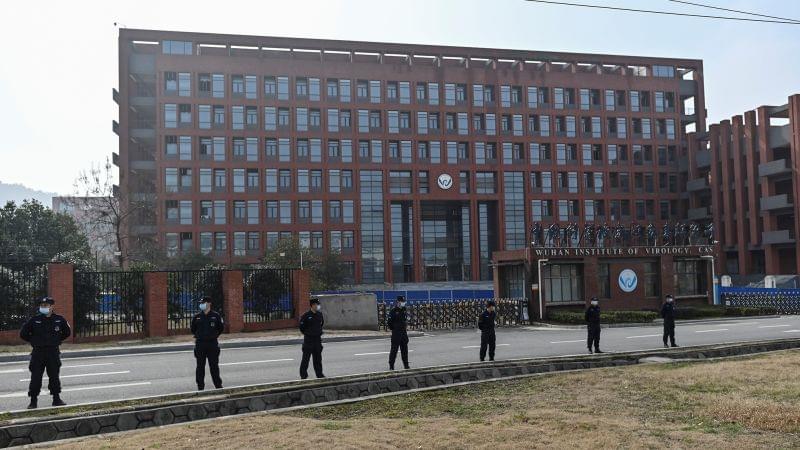

The US Department of Energy has assessed that the Covid-19 pandemic most likely came from a laboratory leak in China, according to a newly updated classified intelligence report.
Two sources said that the Department of Energy assessed in the intelligence report that it had “low confidence” the Covid-19 virus accidentally escaped from a lab in Wuhan.
Intelligence agencies can make assessments with either low, medium or high confidence. A low confidence assessment generally means that the information obtained is not reliable enough or too fragmented to make a more definitive analytic judgment or that there is not enough information available to draw a more robust conclusion.

Electronic devices generate heat, and that heat must be dissipated. If it isn’t, the high temperatures can compromise device function, or even damage the devices and their surroundings.
Now, a team from UIUC and UC Berkeley have published a paper in Nature Electronics detailing a new cooling method that offers a host of benefits, not the least of which is space efficiency that offers a substantial increase over conventional approaches in devices’ power per unit volume.
Tarek Gebrael, the lead author and a PhD student in mechanical engineering, explains that the existing solutions suffer from three shortcomings. “First, they can be expensive and difficult to scale up,” he says. Heat spreaders made of diamond, for example, are sometimes used at the chip level, but they aren’t cheap.

A group of physicists may have discovered that black holes are actually made of and not only that but they may be responsible for the expansion of the universe itself.
Links to the research findings:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/acb704
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/acac2e
A slow-motion movie on sports television channels shows processes in hundredths of a second. By contrast, processes on the nanoscale take place in the so-called femtosecond range: For example, an electron needs only billionths of a second to orbit a hydrogen atom. Physicists around the world are using special instruments to capture such ultrafast nano-processes in films.
Researchers at Kiel University (CAU) have developed a new method for such films that is based on a different physical concept and thus allows further and more precise options for investigation. To do this, they combined an electron microscope with nanostructured metallic thin films that generate very short light pulses.
In a first experiment, they were thus able to document the coherent interactions of light and electrons in a semiconductor on film.
The British Museum shared in a recent presentation that archaeologists have discovered the remnants of a 4,500-year-old Sumerian temple in Iraq. It is a temple dedicated to Ningirsu, the Mesopotamian deity of springtime thunder.
The finding is the outcome of the 2015 archaeological partnership led by the British Museum and supported by the Getty Museum called the Girsu Project.
In 1931, a 25-year-old Kurt Gödel published a paper in mathematical logic titled “On Formally Undecidable Propositions of Principia Mathematica and Related Systems.” This paper contained the proofs of two remarkable “incompleteness theorems,” which state:
For any consistent axiomatic formal system that can express facts about basic arithmetic.
1. there are true statements that are unprovable within the system 2. the system’s consistency cannot be proven within the system.