The latest Omicron variant is making scientists take notice in the US — so what do you need to know?

The reason your three-pound brain doesn’t feel heavy is because it floats in a reservoir of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which flows in and around your brain and spinal cord. This liquid barrier between your brain and skull protects it from a hit to your head and bathes your brain in nutrients.
But the CSF has another critical, if less known, function: it also provides immune protection to the brain. Yet, this function hasn’t been well studied.
A Northwestern Medicine study of CSF has discovered its role in cognitive impairment, such as Alzheimer’s disease. This discovery provides a new clue to the process of neurodegeneration, said study lead author David Gate, assistant professor of neurology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
A new study by Burke Neurological Institute (BNI), Weill Cornell Medicine, finds that activation of MAP2K signaling by genetic engineering or non-invasive repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) promotes corticospinal tract (CST) axon sprouting and functional regeneration after spinal cord injury (SCI) in mice.
RTMS is a noninvasive technique that evokes an electrical field in brain tissue via electromagnetic induction. While an increasing body of evidence suggests that rTMS applied over motor cortex may be beneficial for functional recovery in SCI patients, the molecular and cellular mechanisms that underlie rTMS’ beneficial effects remains unclear.
A new study published in Science Translation Medicine showed that high-frequency rTMS (HF-rTMS) activated MAP2K signaling and enhanced axonal regeneration and functional recovery, suggesting that rTMS might be a valuable treatment option for SCI individuals.
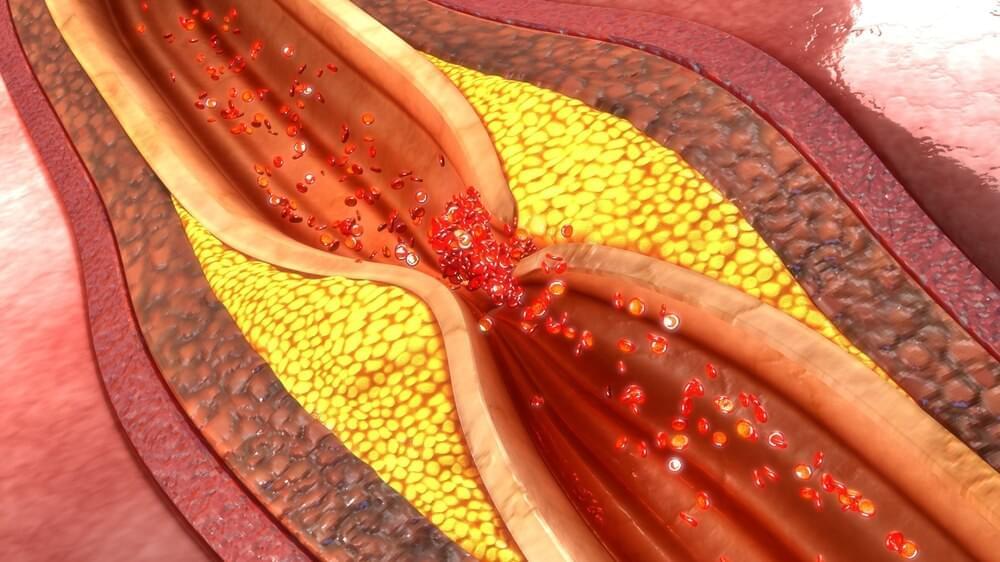
Exercise and physical activity reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). It has been observed that an active individual is at a 30% to 40% lower risk of CVD. However, previous cross-sectional studies have failed to determine whether exercise has a significant impact on expediting coronary atherosclerosis and plaque morphology. A recent Circulation journal paper has focused on investigating the relationship between exercise volume and intensity and the progression of coronary atherosclerosis in middle-aged and older male athletes.
Study: Exercise Volume Versus Intensity and the Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis in Middle-Aged and Older Athletes: Findings From the MARC-2 Study. Image Credit: sciencepics / Shutterstock.
The biggest tech companies have announced mass layoffs blaming a slowing economy for the job cuts. Is the tech dream going to crash? Priyanka Sharma tells you more.
#techgiants #layoff #wion.
About Channel:
WION The World is One News, examines global issues with in-depth analysis. We provide much more than the news of the day. Our aim to empower people to explore their world. With our Global headquarters in New Delhi, we bring you news on the hour, by the hour. We deliver information that is not biased. We are journalists who are neutral to the core and non-partisan when it comes to the politics of the world. People are tired of biased reportage and we stand for a globalised united world. So for us the World is truly One.
Please keep discussions on this channel clean and respectful and refrain from using racist or sexist slurs as well as personal insults.
Check out our website: http://www.wionews.com.
Connect with us on our social media handles:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/WIONews.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/WIONews.
Follow us on Google News for latest updates.


People age at different rates due to a variety of intrinsic and extrinsic factors, which can affect their biological age and their risk of developing diseases or experiencing early death. This is why two individuals who are both 50 years old may not have the same level of biological aging, despite having lived for the same number of years.
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and smoking, and illness all contribute to accelerating biological age beyond one’s chronological age. Researchers have discovered that grip strength, a measure of overall muscle strength, is linked to biological age in this way. In particular, the study, which was published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle, found that people with weaker grip strength had older biological ages.
Researchers at Michigan Medicine modeled the relationship between biological age and grip strength of 1,274 middle-aged and older adults using three “age acceleration clocks” based on DNA.

Quantum computers hold the promise of performing certain tasks that are intractable even on the world’s most powerful supercomputers. In the future, scientists anticipate using quantum computing to emulate materials systems, simulate quantum chemistry, and optimize hard tasks, with impacts potentially spanning finance to pharmaceuticals.
However, realizing this promise requires resilient and extensible hardware. One challenge in building a large-scale quantum computer is that researchers must find an effective way to interconnect quantum information nodes—smaller-scale processing nodes separated across a computer chip. Because quantum computers are fundamentally different from classical computers, conventional techniques used to communicate electronic information do not directly translate to quantum devices. However, one requirement is certain: Whether via a classical or a quantum interconnect, the carried information must be transmitted and received.
To this end, MIT researchers have developed a quantum computing architecture that will enable extensible, high-fidelity communication between superconducting quantum processors. In work published in Nature Physics, MIT researchers demonstrate step one, the deterministic emission of single photons—information carriers—in a user-specified direction. Their method ensures quantum information flows in the correct direction more than 96 percent of the time.