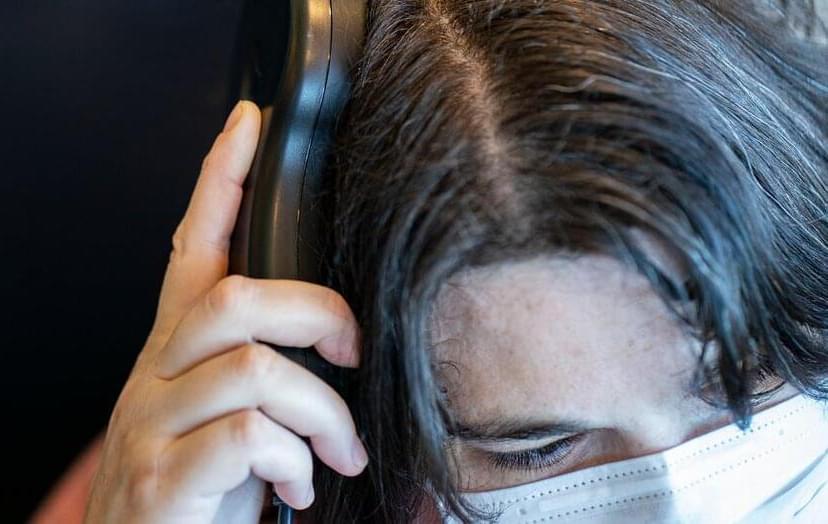
It’s the first study of individualized brain stimulation to treat severe depression. Sarah’s case raises the possibility the method may help people who don’t respond to other therapies.
“There’s a possibility…that we’ll find life on Mars in the next 20 years”
Astronaut Garrett Reisman, who helped develop SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule, has a bold vision of the future of space.
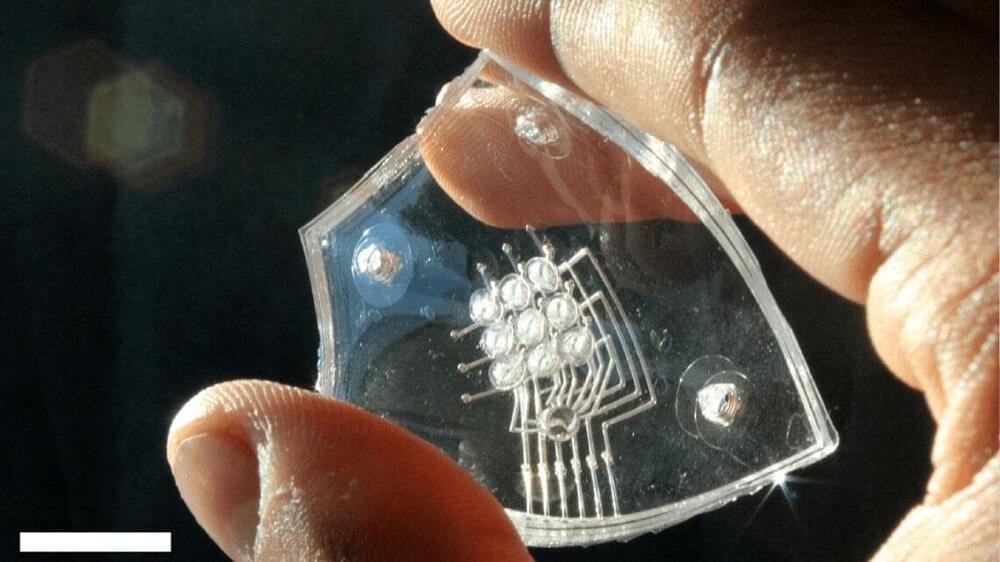
Imagine an iPad or a Kindle for the blind, with inflatable Braille that changes shape under a user’s touch. A Cornell-led collaboration has made a crucial component for such a technology: A haptic array of densely packed actuators that cause silicone membrane “dots” to pop up when triggered by combustion.
The team’s paper, “Valveless Microliter Combustion for Densely Packed Arrays of Powerful Soft Actuators,” published Sept. 28 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The lead author is doctoral student Ronald Heisser.
One of the major hurdles for designing a dynamic Braille display for electronics is figuring out how to apply the necessary amount of force for each dot. Previous attempts have usually involved motors, hydraulics or tethered pumps, all of which are cumbersome, complex and expensive, according to Rob Shepherd, associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering in the College of Engineering and the paper’s senior author.
I hope we get the hologram interfaces depicted too.
It’s becoming clear that aging is just as curable as other diseases such as the cold or a broken bone. Advancements in biotechnology now allow for targeted gene therapy and supplements to be invented that can both stop aging and even reverse the aging process through new Longevity Technology. The field of Longevity has expanded and evolved a lot during the past few years and have invented new treatments for diseases of old people which could increase the average lifespan of people by a ton according to the leading scientists such as David Sinclair and Aubrey De Grey. Anti Aging Supplements such as Metformin and NAD+, NMN are just the start.
–
Every day is a day closer to the Technological Singularity. Experience Robots learning to walk & think, humans flying to Mars and us finally merging with technology itself. And as all of that happens, we at AI News cover the absolute cutting edge best technology inventions of Humanity.
If you enjoyed this video, please consider rating this video and subscribing to our channel for more frequent uploads. Thank you! smile
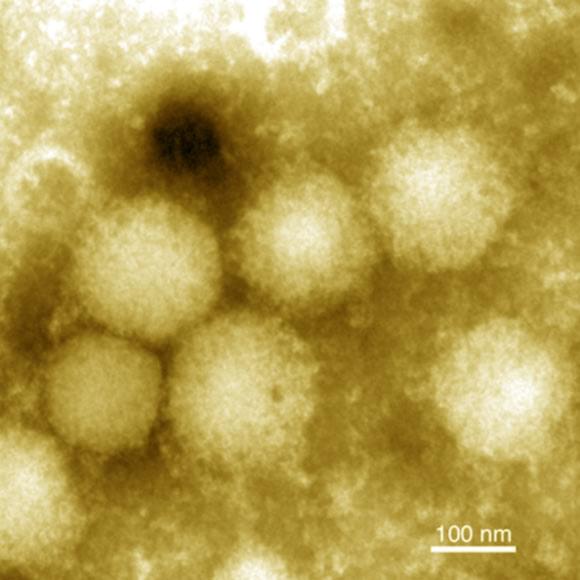
Yezo virus, new disease that infects humans, discovered in japan.
Scientists have isolated a new orthonairovirus from two patients showing acute febrile illness with thrombocytopenia and leukopenia after tick bite in Hokkaido, Japan.
They cause sometimes fatal febrile illnesses in humans and other animals.
Researchers at Heidelberg University and University of Bern have recently devised a technique to achieve fast and energy-efficient computing using spiking neuromorphic substrates. This strategy, introduced in a paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, is a rigorous adaptation of a time-to-first-spike (TTFS) coding scheme, together with a corresponding learning rule implemented on certain networks of artificial neurons. TTFS is a time-coding approach, in which the activity of neurons is inversely proportional to their firing delay.
“A few years ago, I started my Master’s thesis in the Electronic Vision(s) group in Heidelberg,” Julian Goeltz, one of the leading researchers working on the study, told TechXplore. “The neuromorphic BrainScaleS system developed there promised to be an intriguing substrate for brain-like computation, given how its neuron and synapse circuits mimic the dynamics of neurons and synapses in the brain.”
When Goeltz started studying in Heidelberg, deep-learning models for spiking networks were still relatively unexplored and existing approaches did not use spike-based communication between neurons very effectively. In 2,017 Hesham Mostafa, a researcher at University of California—San Diego, introduced the idea that the timing of individual neuronal spikes could be used for information processing. However, the neuronal dynamics he outlined in his paper were still quite different from biological ones and thus were not applicable to brain-inspired neuromorphic hardware.
Let the OSS Enterprise newsletter guide your open source journey! Sign up here.
Neural Magic, which provides software to facilitate deep learning deployment in edge locations, today announced a $30 million series A funding round.
The market for edge AI is exploding as more companies deploy the technology in a variety of applications across industries — including in areas like asset maintenance and monitoring, factory automation, and telehealth. The market is expected to be worth $1.83 billion by 2,026 according to a report by Markets and Markets.
The transaction-based communications system ensures robot teams achieve their goal even if some robots are hacked.
Imagine a team of autonomous drones equipped with advanced sensing equipment, searching for smoke as they fly high above the Sierra Nevada mountains. Once they spot a wildfire, these leader robots relay directions to a swarm of firefighting drones that speed to the site of the blaze.
But what would happen if one or more leader robots was hacked by a malicious agent and began sending incorrect directions? As follower robots are led farther from the fire, how would they know they had been duped?
The use of blockchain technology as a communication tool for a team of robots could provide security and safeguard against deception, according to a study by researchers at MIT and Polytechnic University of Madrid, which was published today in IEEE Transactions on Robotics. The research may also have applications in cities where multirobot systems of self-driving cars are delivering goods and moving people across town.
The potential for AI to deliver transformative value is almost unlimited. And yet, accessing that value is by no means a given. So how do we crack the code?
As someone who’s been in the business of deploying enterprise-grade AI solutions since the earliest days of AI—from the inside, as a CIO at Verizon, and from the outside, as an advisor to an AI company ASAPP—I know that our job as CIOs is to get transformational value out of transformational technology. And yet as recently as 2,020 McKinsey reported that less than 25 percent of companies are “seeing significant bottom-line impact” from AI.
I believe that there are at least three ways we need to shift our thinking if our organizations are going to mine the full transformational potential of AI:
Advanced Nuclear Power Advocacy For Humanity — Eric G. Meyer, Founder & Director, Generation Atomic
Eric G. Meyer is the Founder and Director of Generation Atomic (https://generationatomic.org/), a nuclear advocacy non-profit which he founded after hearing about the promise of advanced nuclear reactors, and he decided to devote his life to saving and expanding the use of atomic energy.
Eric worked as an organizer on several political, union, and issue campaigns while in graduate school for applied public policy, taking time off to attend the climate talks in Paris and sing opera about atomic energy.