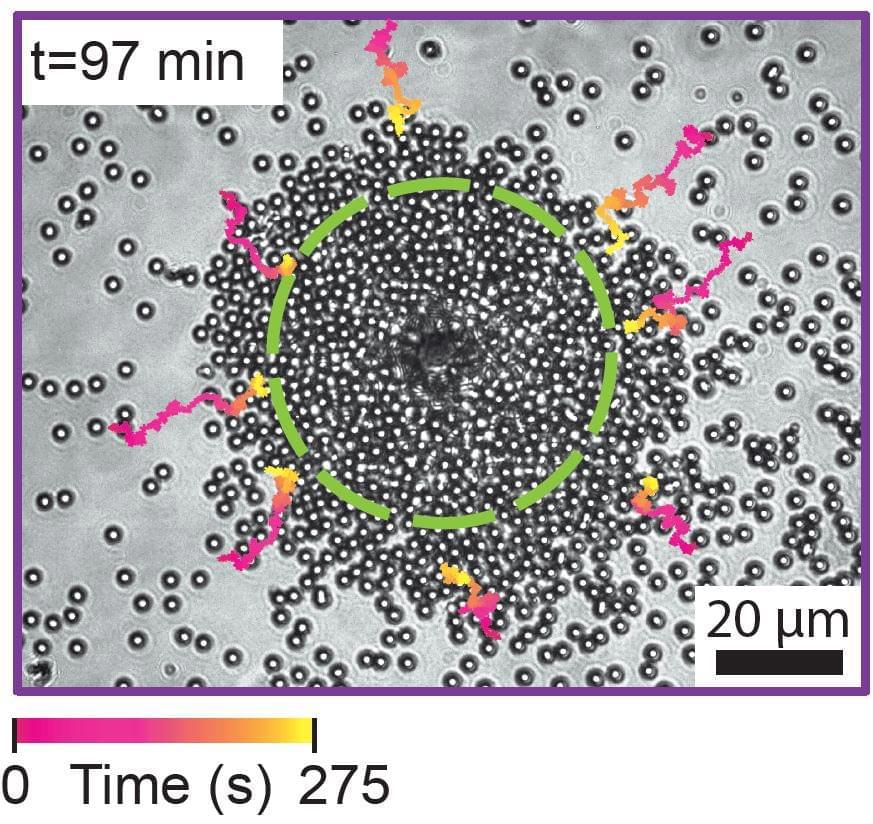
Four billion years ago, the Earth looked very different than it does today, devoid of life and covered by a vast ocean. Over the course of millions of years, in that primordial soup, life emerged. Researchers have long theorized how molecules came together to spark this transition. Now, scientists at Scripps Research have discovered a new set of chemical reactions that use cyanide, ammonia and carbon dioxide—all thought to be common on the early earth—to generate amino acids and nucleic acids, the building blocks of proteins and DNA.
“We’ve come up with a new paradigm to explain this shift from prebiotic to biotic chemistry,” says Ramanarayanan Krishnamurthy, Ph.D., an associate professor of chemistry at Scripps Research, and lead author of the new paper, published July 28, 2022 in the journal Nature Chemistry. “We think the kind of reactions we’ve described are probably what could have happened on early earth.”
In addition to giving researchers insight into the chemistry of the early earth, the newly discovered chemical reactions are also useful in certain manufacturing processes, such as the generation of custom labeled biomolecules from inexpensive starting materials.