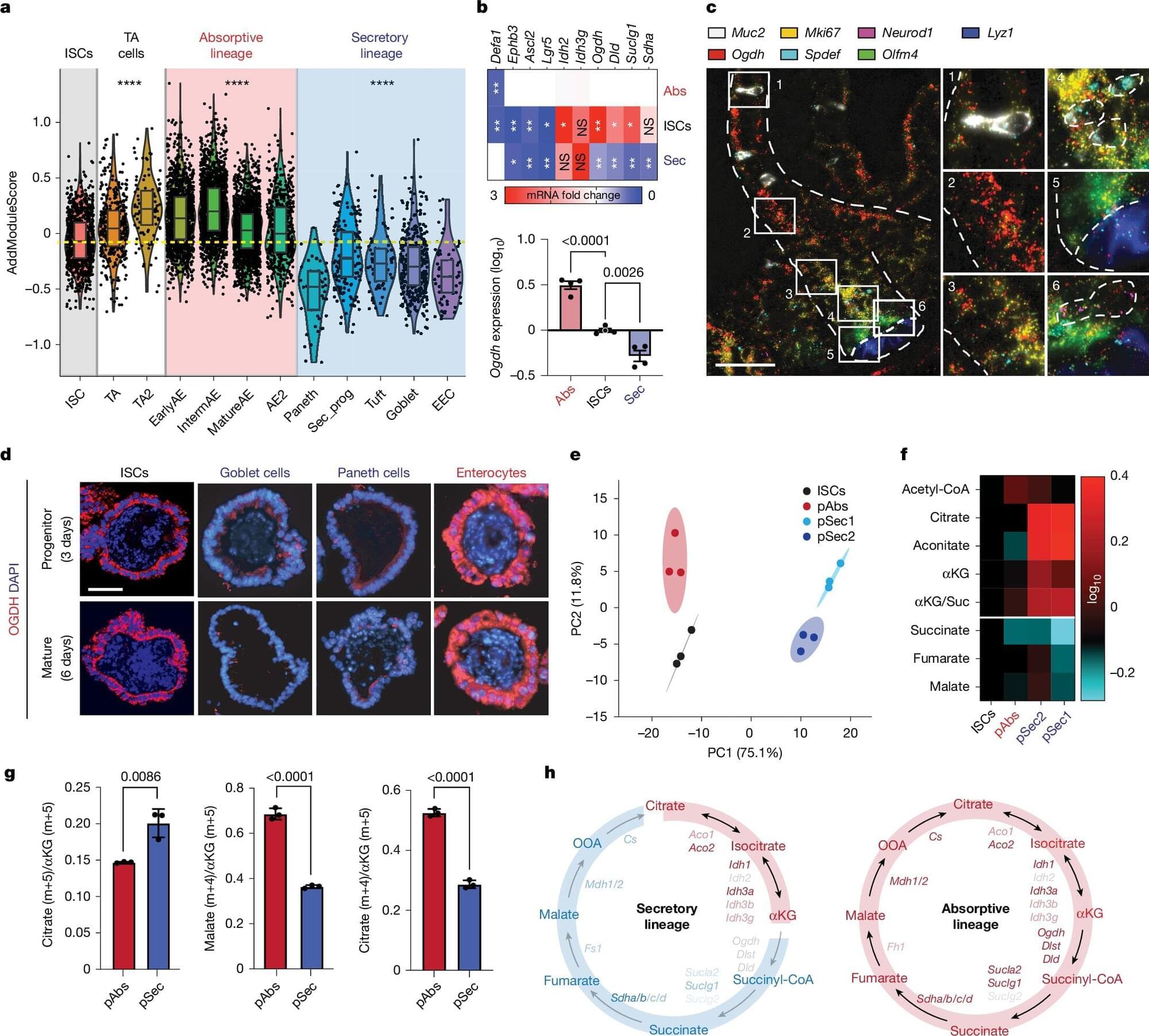
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center researchers have identified a metabolic switch that determines whether intestinal stem cells become absorptive or secretory cells. Manipulating the enzyme OGDH either fuels cell expansion or redirects fate, with potential consequences for colitis recovery and regenerative therapy.
Stem cells in the intestine maintain a delicate balance between self-renewal and differentiation, continuously replenishing the epithelial lining of the gut.
As they divide, some daughter cells become absorptive enterocytes that expand the surface for nutrient uptake, while others branch into secretory cells that manufacture mucus, antimicrobial peptides, and hormones essential for gut immunity. Injury and inflammation can tip this balance, depleting secretory lineages and disrupting tissue integrity.