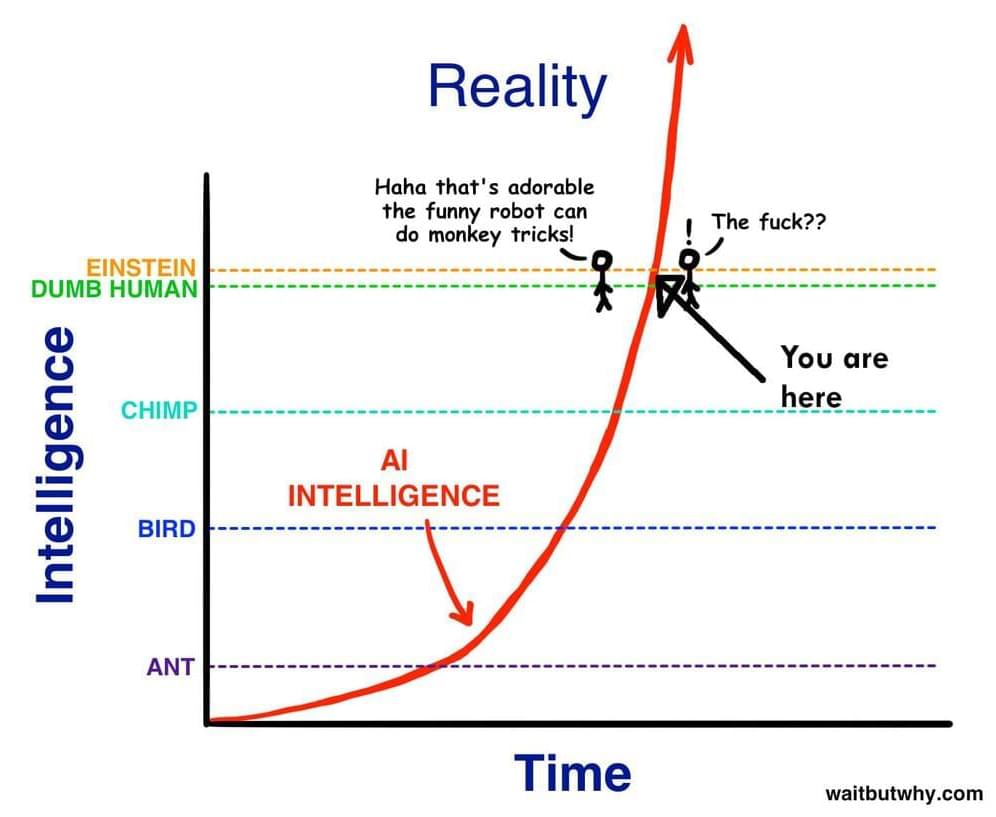
Nadella highlighted that while generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT and Dall-E, generated less than 1% of the world’s AI data sets in 2021, this can increase to 10% of all data generated by AI by 2025.
“In future, the generative models will generate most of the data. We are right now seeing the emergence of a new reasoning engine. We’ll clearly have to talk about this reasoning engine — what are its responsible uses, what displacements will it cause, and so on. But on the other side, we should also think about how it can augment us in what we are doing today since it can have a huge impact on our future,” Nadella said.
“Ultimately, these tools will accelerate creativity, ingenuity and productivity across a range of tasks. It is going to be a golden age — the computer revolution created mass consumer behaviour change and productivity for knowledge workers. But, what if we could spread that productivity more evenly? To me, that is one of the biggest things to look forward to, and the way to achieve this is by building a robust data infrastructure,” he added.