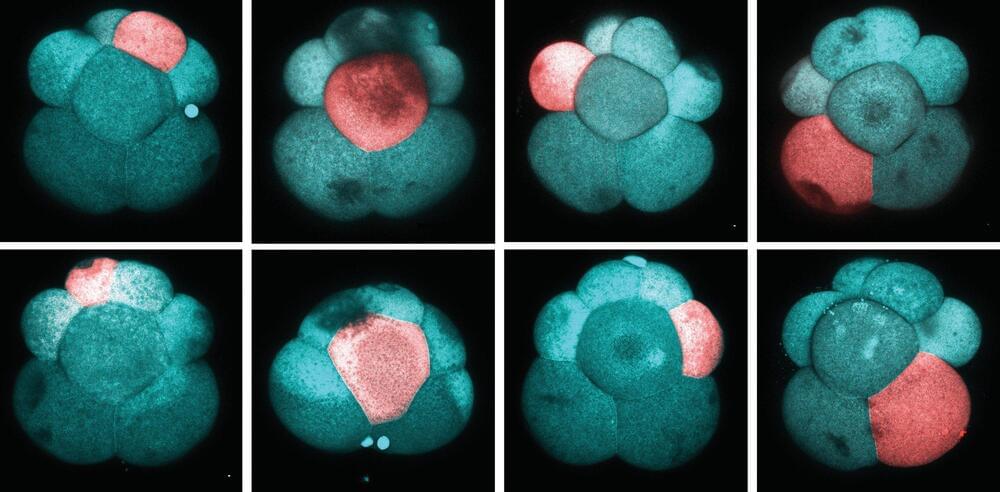
Stem cells are a remarkable biological wonder that have the ability to repair, replace and regenerate cells. In most animals and humans, stem cells are limited to generating only specific types of cells. For example, hair stem cells will only produce hair, and intestine stem cells will only produce intestines. However, many distantly-related invertebrates.
Invertebrates are animals that do not have a backbone. They make up the majority of the animal kingdom and include animals such as insects, worms, mollusks, and arachnids. Invertebrates are found in almost every habitat on Earth, from the depths of the oceans to the highest mountains. They play important roles in the ecosystem as decomposers, pollinators, and as a food source for other animals. Invertebrates have a wide range of body shapes, sizes, and behaviors, and they have evolved a variety of ways to survive and thrive in their environments.