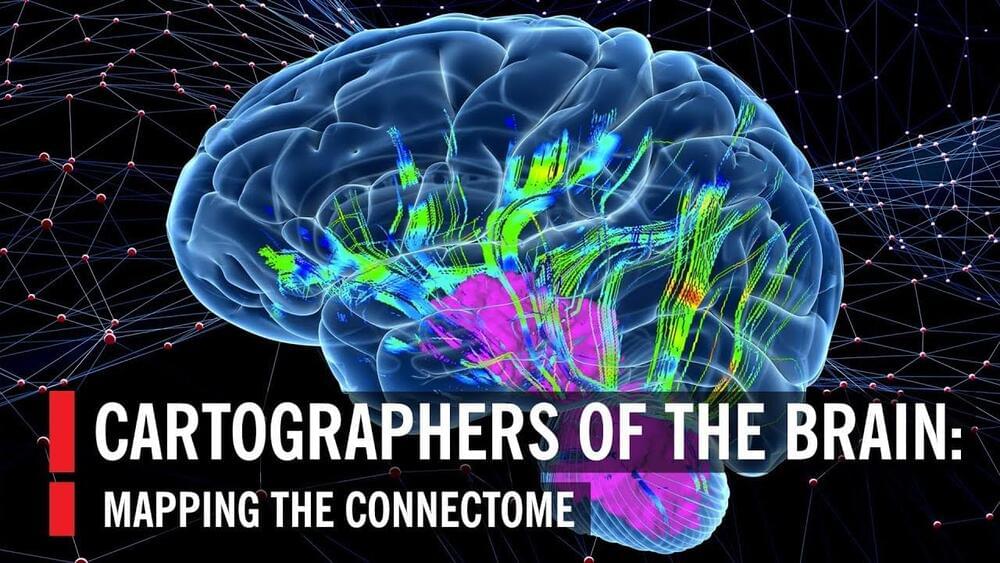
The long term goal for Elon Musk and brain to computer interfaces (brain chips) is to merge our minds with artificial intelligence. While the short term goal for Neuralink and other companies is to help people with medical issues.
This short documentary video takes a look at connecting our brains to computers, and how this works is explained. We also take a look at the downsides of people connecting their brains, the technology being used today, and Elon Musk’s thoughts.
Other topics in the video include:
• How in the future we could download and upload our memories and dreams so they are not forgotten.
• The different types of brain to computer implants and devices.
• Updates (demonstrating and testing on pigs, and soon humans) and a summery of where we are today with this technology.
• Tutorial on how it works.
• And what other sci-fi like things will brains connected to computers allow us humans to do.