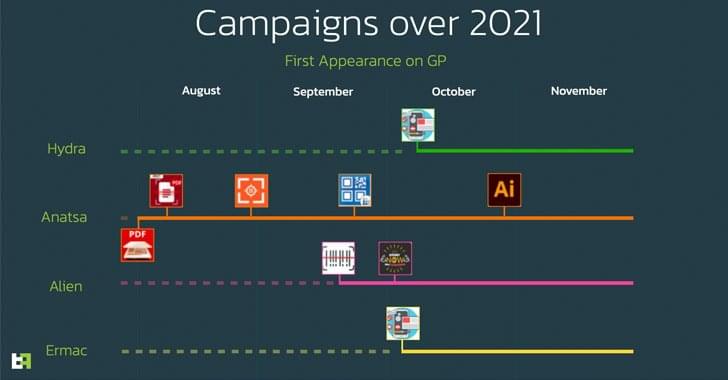
Four separate Android banking trojan Dropper campaigns that have affected over 300,000 devices in 2021 through the Google Play Store.
Has your Macbook’s performance dipped in the recent past? CleanMyMac has all the tools you need to take care of your Mac. Read on to learn more.
An Italian antitrust regulator fined Google and Apple for “aggressive” data practices.
Stethoscopes are among doctors’ most important instruments, yet there have not been any essential improvements to the device since the 1960s. Now, researchers at Aalto University have developed a device that analyzes a broad range of bodily functions and offers physicians a probable diagnosis as well as suggestions for appropriate further examinations. The researchers believe that the new device could eventually replace the stethoscope and enable quicker and more precise diagnoses.
A startup called Vital Signs is taking the device to the market. The researchers are currently testing the device in a clinical pilot trial. The intention is to launch the product to the most important European markets by the end of 2023.
“We have a well-functioning prototype, and the development path is clear,” says Alexis Kouros, the doctor leading the research team at Aalto.
PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
↓ More info below ↓
Erratum: Figures in episode should be Minev et al. (2019), not Minney et al. (2009). Our apologies to the authors!
This is the experiment we talk about:
To Catch and Reverse a Quantum Jump Mid-Flight.
Minev, Mundhada, Shankar, Reinhold, Gutiérrez-Jáuregui, Schoelkopf.
Mirrahimi, Carmichael & Devoret (2019), Nature, v.570, p.200
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1287-z.
Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!
Markets plunged on Friday, hope of taming the coronavirus dimmed and a new term entered the pandemic lexicon: Omicron.
The Covid-19 variant that emerged in South Africa was named after the 15th letter of the Greek alphabet.
The naming system, announced by the World Health Organization in May, makes public communication about variants easier and less confusing, the agency and experts said.
Pfizer is confident its COVID-19 antiviral pill, Paxlovid, will be effective against the new omicron variant, the drugmaker’s CEO told CNBC Nov. 29.
The omicron strain, first detected in South Africa, contains 32 mutations in the spike protein, and while preliminary evidence suggests the strain may increase the risk of reinfection, it’s still uncertain how the variant may affect illness severity or the effectiveness of vaccines and treatments.
Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s CEO, told CNBC the company’s antiviral was created with the spike protein in mind and expects it will work against omicron.
Nov 27 (Reuters) — The new Omicron coronavirus variant — identified first in South Africa, but also detected in Europe and Asia — is raising concern worldwide given the number of mutations, which might help it spread or even evade antibodies from prior infection or vaccination.
News of the variant prompted countries to announce new travel restrictions on Friday and sent drugmakers scrambling to see if their COVID-19 vaccines remain protective.
WHY ARE SCIENTISTS WORRIED?
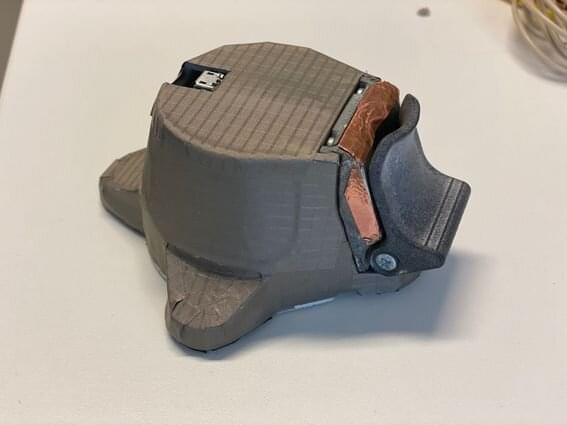
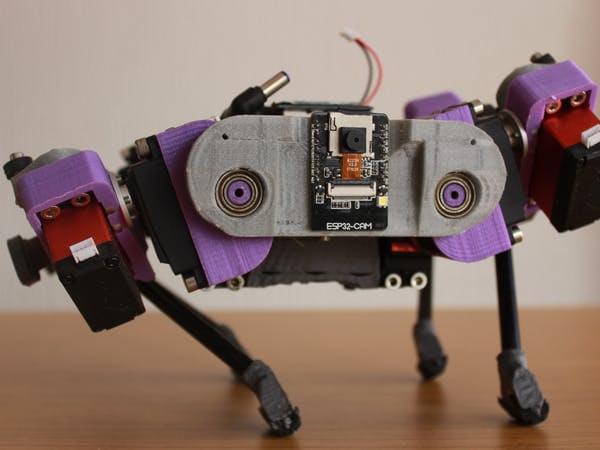
Created by Wissam Tedros, RoDog is a reliable and hobby-level quadruped robot constructed out of accessible parts. The project implements a dozen RC servos actuators, measurement units such as a gyroscope, accelerometer, magnetometer, and unity for inertial measurement, an ESP32-CAM for streaming and WiFi connectivity, an OLED display, and more, all within a 3D-printed casing.
Entirely open source, Tedros’ post includes the BOM and all necessary files, as well as notes on mechanical design and assembly and data obtained from a MATLAB Simulink trial of the inverse kinematic control used with the embedded system. RoDog features a custom STM32F4 board for its brain, with the design available in full detail. The bot is quite compact at 20×10×5 cm, and the 12 motor controller board incorporates position and current feedback.
It is still in development 0, having gone through many iterations and tweaks, most of which are logged in the project files. However, its current form should perform well as a hobbyist’s robotic pet with room for add-ons.
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility.
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25.