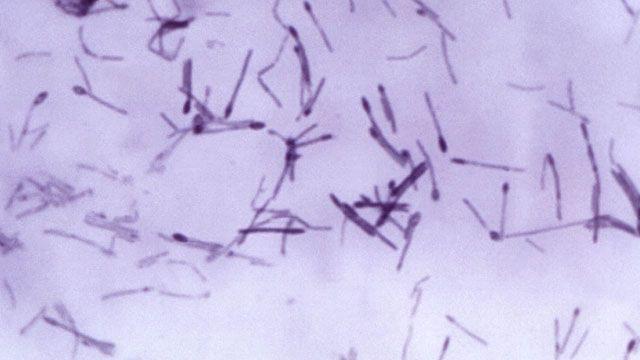
Researchers have discovered that Clostridium septicum rapidly kills cells by releasing a toxin that punches holes in the surface of the cell. This induces an immune response that can lead to sepsis and shock. The team is now exploring whether it’s possible to develop drugs to neutralize the toxin to treat the infection.
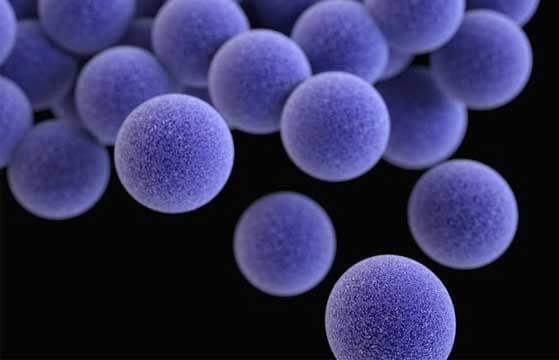
Staphylococcus aureus infections can be highly unpredictable – some cause a slight rash, whereas others can lead to deadly complications – and researchers have identified a genetic mutation that could be the cause of these differences.
Heart Disease May Be Worsened
Posted in biotech/medical
T cells that attack apolipoprotein B, the main component of “bad” cholesterol, could be contributing to inflammation that worsens heart disease.
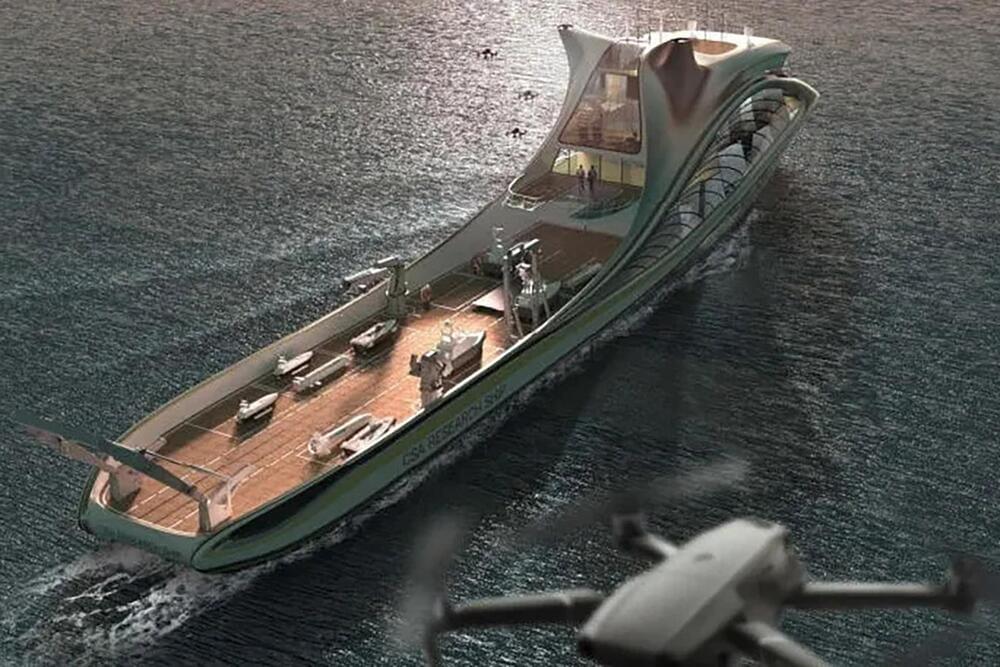
China christened a remarkable new 290-foot ship last week – the world’s first semi-autonomous drone carrier. It’ll carry, launch, recover and co-ordinate the actions of more than 50 other autonomous aerial, surface and underwater vehicles.
The Huangpu Wenchong Shipyard began construction on the Zhu Hai Yun last July in Guangzhou. According to the South China Morning Post, it’s the first carrier of its kind, a self-contained autonomous platform that will roll out with everything necessary to perform a fully integrated operation including drone aircraft, boats and submersibles.
China doesn’t expect it to navigate busy seaports by itself, like the Japanese autonomous container ship Suzaku we wrote about last week. Instead, the Zhu Hai Yun will run on remote control until it’s out in the open water, and then its self-driving systems will take over to execute whatever mission it’s running.
Searchable tool reveals more than 90,000 known materials with electronic properties that remain unperturbed in the face of disruption.
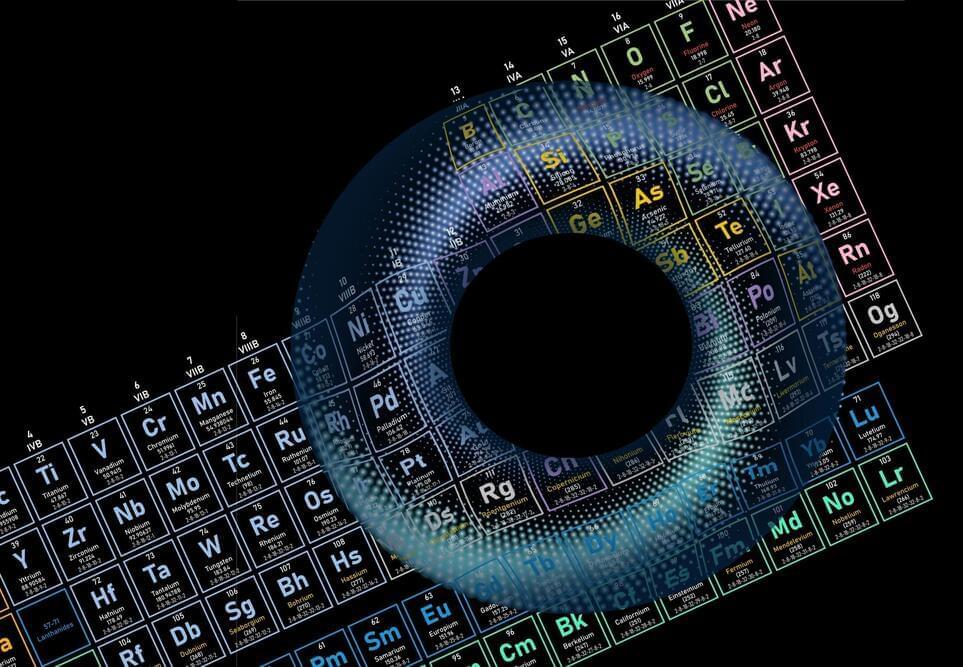
What will it take for our electronics to become smarter, faster, and more resilient? One idea is to build them out of topological materials.
Topology stems from a branch of mathematics that studies shapes that can be manipulated or deformed without losing certain essential properties. A donut is a common example: If it were made of rubber, a donut could be twisted and squeezed into a completely new shape, such as a coffee mug, while retaining a key trait — namely, its center hole, which takes the form of the cup’s handle. The hole, in this case, is a topological trait, robust against certain deformations.
The United States’ reliance on China for rare earth elements could soon come to an end, thanks to a new process that pulls the valuable metals from the ash left over when we burn coal.
Why it matters: The 17 rare earth elements aren’t actually rare — they’re all more common than gold, and one is more abundant than copper. But getting our hands on them is difficult because they’re widely dispersed in Earth’s crust and hard to extract through mining.
That’s a problem because we need rare earth elements to make a lot of products, from smartphones and satellites to electric cars and wind turbines.
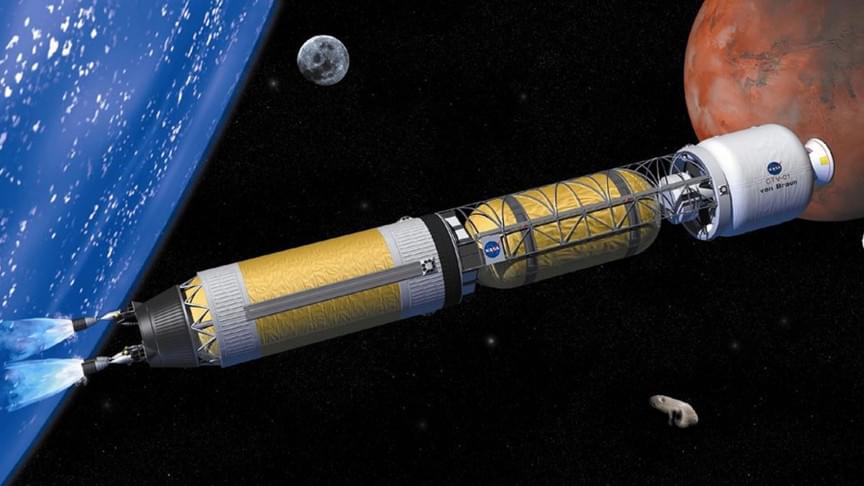
Two commercial enterprises have been awarded contracts by the DoD to develop the next generation of nuclear propulsion in space.
According to the team, the new semiconducting cellulose nanopaper (CNP) can be tailored for a variety of applications. The paper itself can be shaped into different designs and the material’s electrical conduction properties can be tuned from 1012 to 10–2 Ω cm – values that exceed those of previously-reported 3D semiconducting materials – by changing the concentration of charge carriers (electrons and holes) in it. This means it is suitable for use in many devices, from water vapour sensors to electrodes in enzymatic biofuel cells.
The early Solar System was a much different place than that seen today.
The Solar System may have started with five gas giants, but according to the Nice model, Planet X may have been flung into interstellar space.