😳! Circa 2018
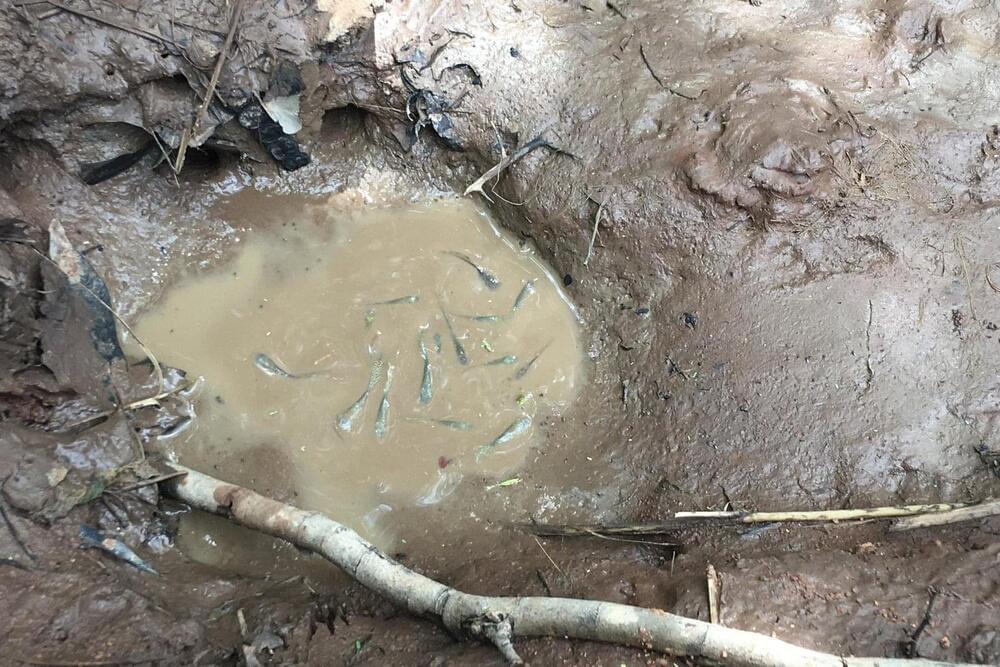
Some animals live fast and die young. That means they need to grow up fast, too. This week, researchers crowned a new record holder for quick growth: Susan Milius at Science News reports that the turquoise killifish, Nothobranchius furzeri, found in Mozambique, can reach maturity in just 14 days, the fastest of any known vertebrate animal.
That rapid maturation is an adaptation to the killifish’s habitat, according to the study published this week in the journal Current Biology. The fish spend most of their lives as tiny embryos that have been deposited in sediment in small depressions across the savannah. When rain fills the ephemeral pools, the embryos mature rapidly reaching sexual maturity and depositing their own embryos before the pool once again dries up. Not only do they make babies quickly, they bulk up fast, too—typically growing from about 5 millimeters to 54 millimeters in their lifespan.
Researchers have been aware of the turquoise killifish’s super-fast maturation for a while. In fact, the fish is used as a model animal in aging studies because of this trait. In the lab, where the fish live a relatively leisurely lifestyle, the average rate of maturation is 18 days.