According to Gates, tech such as VR goggles and motion-capture gloves would be needed to accurately capture a user’s body language and expressions.
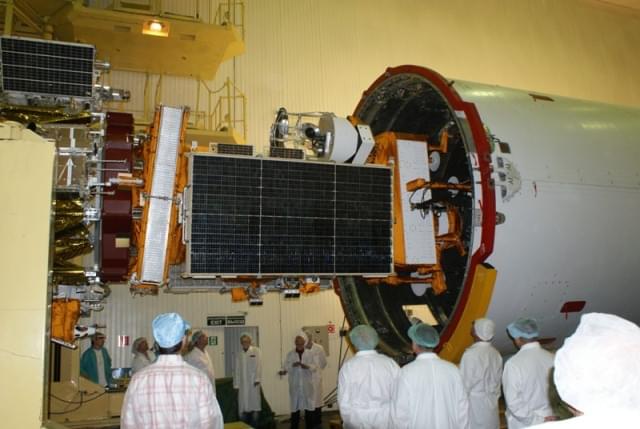
The South African satellite, SumbandilaSat (Pathfinder in Venda) is reaching the end of its life and will deorbit on Friday 10 December 2021.
The satellite was launched in 2009 and took a total of 1,128 high-resolution, usable images. In addition, these imageries were applied in local research and on the Copernicus (previously GMES: Global Monitoring for Environment and Security) programme. The data also contributed towards disaster management such as flood monitoring in Namibia and fire campaigns in the Kruger National Park in South Africa. Furthermore, it also recorded timely images of the Fukushima nuclear disaster and the Tuscaloosa tornado in the USA.
In May 2005, the then DST (Department of Science and Technology) of the South African Government commissioned Stellenbosch University and SunSpace to develop the ZASat pathfinder satellite program (later renamed SumbandilaSat), a technology demonstrator in conjunction with the South African industry. Consequently, SumbandilaSat was delivered 15 months later and launched from Baikonur, Kazakhstan on September 17 2009 with monitoring and satellite support from the SANSA Space Operations facility in Hartebeesthoek.
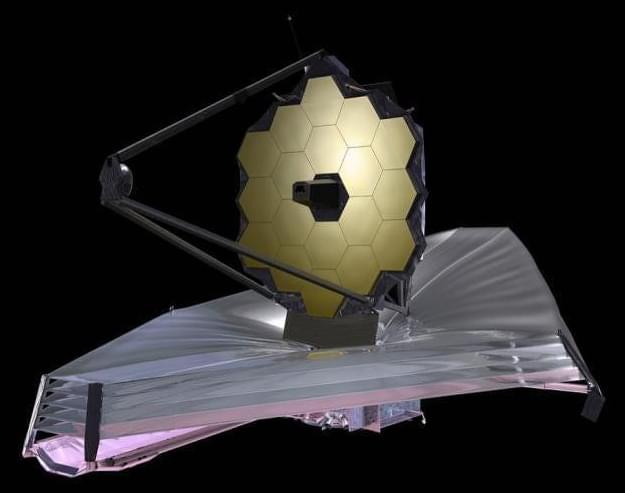
If December 22’s launch goes as planned then the engineers behind the $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or “Webb” for short) are in for a nervous Christmas.
Forget that it was originally conceived in the 1990s and was first expected to launch in 2007. Forget also the initial rocket launch—usually viewed as the most nerve-wracking moment. This time it’s not the European Space Agency’s Ariane 5 rocket—due to lift Webb into space from the Guiana Space Center, Kourou, French Guiana on December 18, 2021—that’s giving engineers sleepless nights. It’s the 29 days of “space origami” they’ll have to endure after the launch as Webb unfolds from its collapse state into a “giant sunflower.”
You see, the technological marvel that is Webb is fully assembled, but folded into the 5.4 meter/17.7ft. fairing of the Ariane 5 for launch—the largest rocket fairing NASA could find. When it’s in-situ a whopping million miles/1.5 million kilometers from Earth at the second Lagrange point (L2) —almost certainly too far away for astronauts to fix if the worst happens—it will resemble a huge sunflower once unfurled.
And it would create 4.7 million long-term jobs.
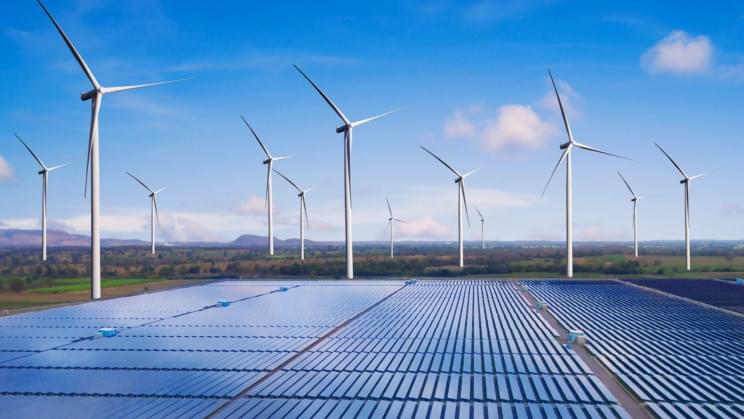
The United States’ energy system that’s running completely on wind, water, and solar, combined with storage, would not only avoid blackouts but also lower energy requirements and consumer costs, a Stanford University study has shown. In addition, this would create millions of jobs, improve health, and free up land for various other purposes.
This is incredibly important because, for some people, a future powered by renewable energy isn’t feasible due to concerns about blackouts driven by inconsistent electricity sources. Take, for example, the grid blackouts caused by extreme weather events in California in August 2020 and Texas in February 2021.
However, the study, which examined grid stability under various scenarios in which wind, water, and solar energy supplied 100 percent of all energy needs in the U.S., has now demonstrated that those concerns are misplaced.
Full Story:
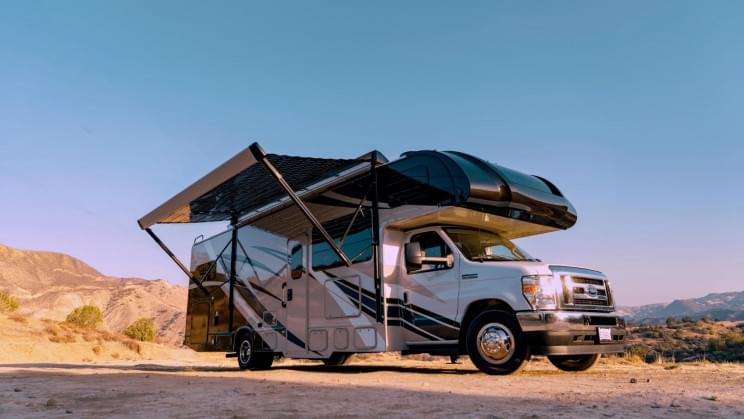
The auto-retracting system can be deployed when solar energy is needed.
California-based energy firm Xponent Power developed an auto-retracting Xpanse Solar Awning that can be deployed if and when solar energy is needed, a report from New Atlas reveals.
The retractable solar panels move out to the side of the RV, creating a nice bit of shade for travelers, at the same time as providing on-demand solar energy. Depending on the model, owners will get 800, 1,000, or 1,200 watts of charging power.
The off-grid solution was designed to allow RV owners to camp away from electrical sockets for days at a time, and it can be easily mounted to either side of the vehicle. The Xpanse awning is made up of a 16 × 7-foot (4.9 × 2.1-m) “fabric” of high-efficiency glass-based solar panels. The awning features “bi-facial” solar panels, meaning it captures the energy of the sun from above as well as from below — the underside can capture a surprising amount of energy from reflection off the ground and the RV itself.
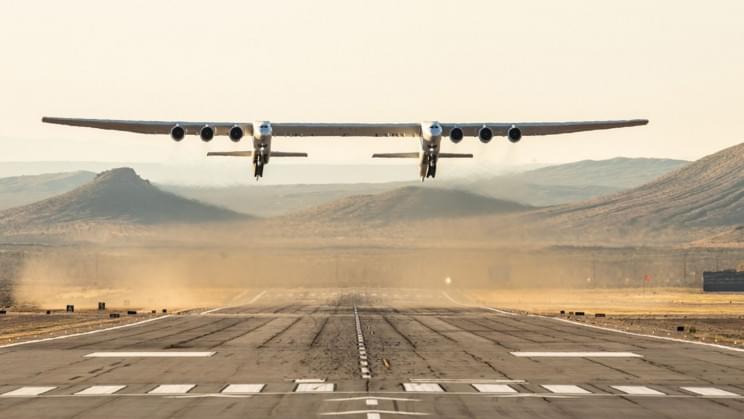
With ultrafast decoy targets launching from the biggest plane ever made.
The U.S.-based aerospace company Stratolaunch announced that the company has signed a research contract with the Missile Defense Agency (MDA), which is a part of the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), on hypersonic flight test services.
The DoD has been focused on hypersonic missiles for a long time now, mainly because of the significant threats they present such as difficulties in detecting, tracking, and intercepting due to being able to reach high speeds with the ability to maneuver along a flight trajectory.
Stratolaunch will provide the MDA with targets that mimic hypersonic threats, thus helping the improvement of existing and development of new defense systems.
“We’re excited to provide MDA with a threat-representative and threat-replicating target that allows them to understand how to engage and intercept hypersonic threats,” said Dr. Daniel Millman, Chief Technology Officer of Stratolaunch, in a company press release.
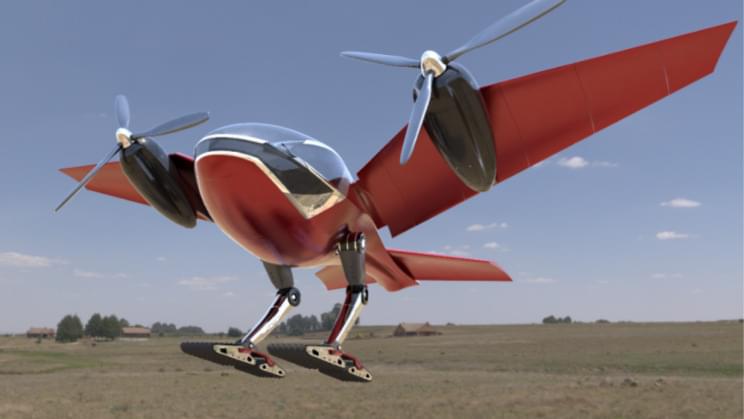
Like a cybernetic pelican.
In all our coverage of air taxis that include wing designs, propulsion technologies, flight endurance, top speeds, we have surely not come across something so radical as this intriguing piece called PHRACTYL. If this appears to you like a bird that has mistakenly grown a pair of propellers at first glance, you are right on spot.
While birds have been the source of inspiration for human flight, after the success of the Wright Brothers, the flat wide wings have become a standard in aviation and technological advancements have happened on getting more lift from these wings. However, the engineers at PHRACTYL have dumped this conventional wisdom for a radically unique design that resembles a bird’s wing. But that’s not where they have stopped. The tail and the landing gear are no different, giving the aircraft the appearance of a bird.
Copying concepts from nature might be straightforward, but the team at the PHRontier for Agile Complex Technology sYstem evoLution (PHRACTYL) is geared up to manufacture working prototypes of this as well. Their aim is to build a mean, green, and clean flying machine using electric propulsion. However, they recognize that battery technology still has a long way to go before it can power these flights in their current format and therefore went about tinkering with the aerodynamic design of the craft till they came up with a radically new one; they call the Macrobat.
Full Story:
After DeepMind’s breakthrough in protein folding last year, Alphabet will double down on artificial intelligence in biology and health with its new venture.
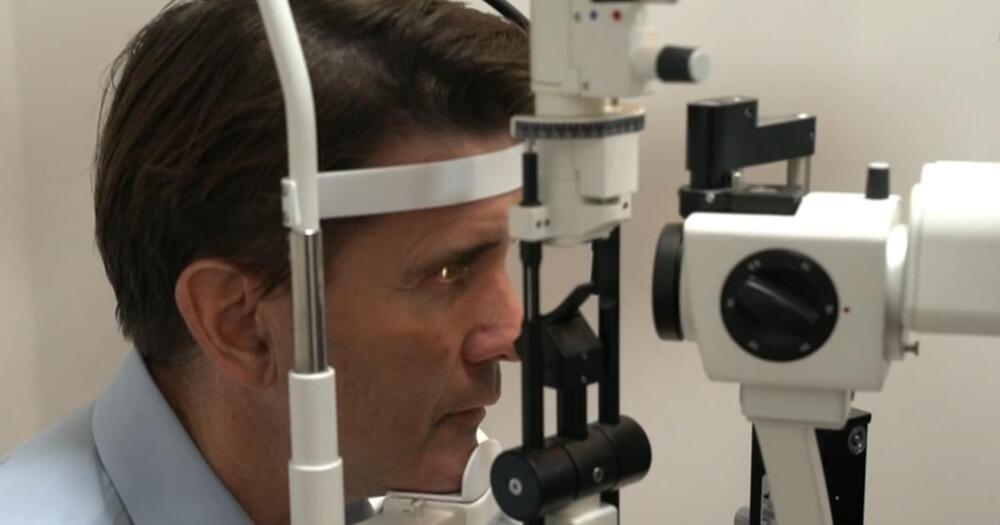
A newly approved eye drop hitting the market on Thursday could change the lives of millions of Americans with age-related blurred near vision, a condition affecting mostly people 40 and older.
Vuity, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in October, would potentially replace reading glasses for some of the 128 million Americans who have trouble seeing close-up. The new medicine takes effect in about 15 minutes, with one drop on each eye providing sharper vision for six to 10 hours, according to the company.
Toni Wright, one of the 750 participants in a clinical trial to test the drug, said she liked what she saw.
The brain is considered a very expensive organ to run.
Your brain may be leaking … energy, according to a new study that may explain why your noggin consumes 20% of the energy needed to keep your body running.
The study researchers found that tiny sacs called vesicles that hold messages being transmitted between brain cells may be constantly oozing energy, and that leakage is likely a trade-off for the brain being ready to fire at all times, according to a new study published Dec. 3 in the journal Science Advances.