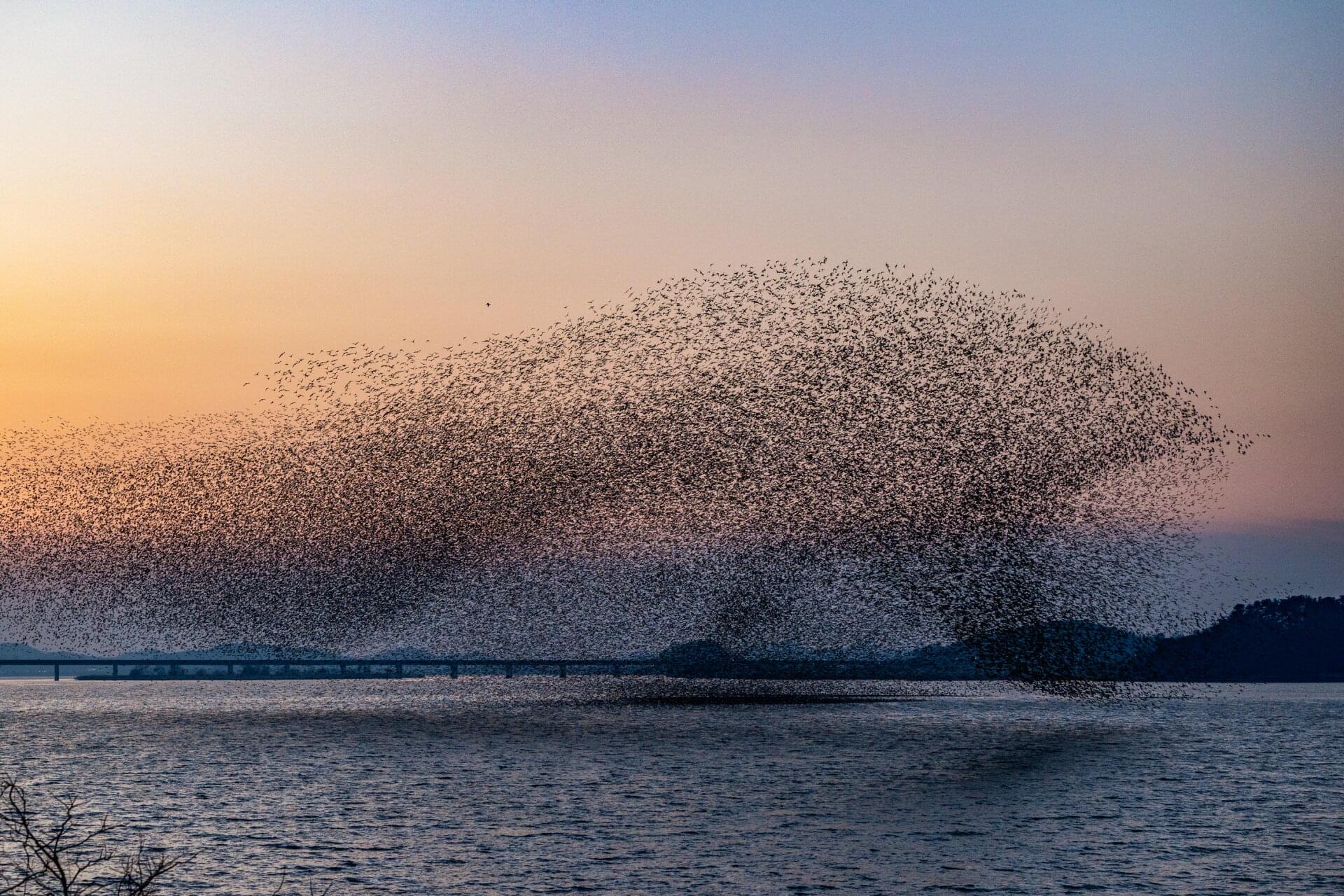
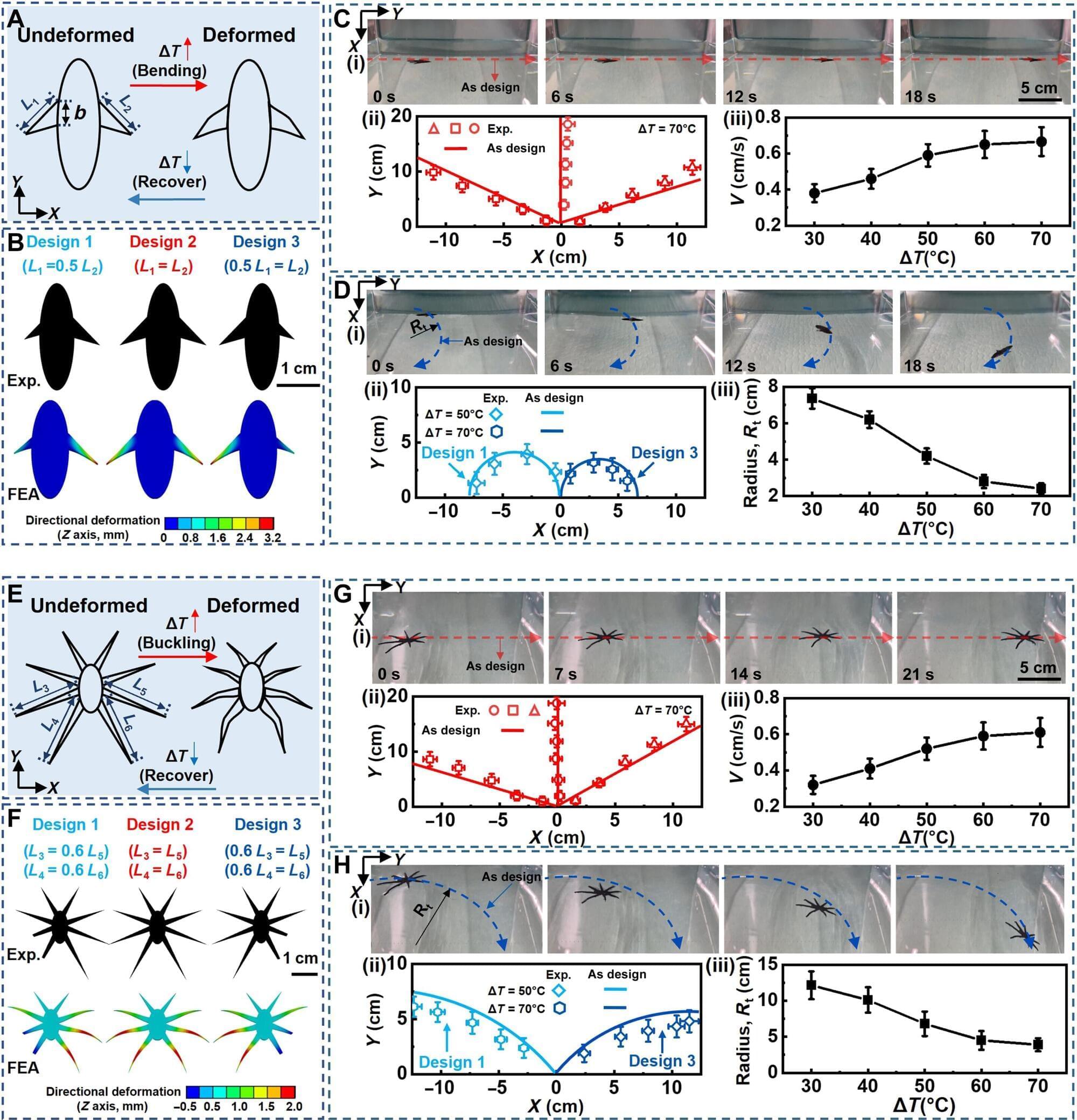
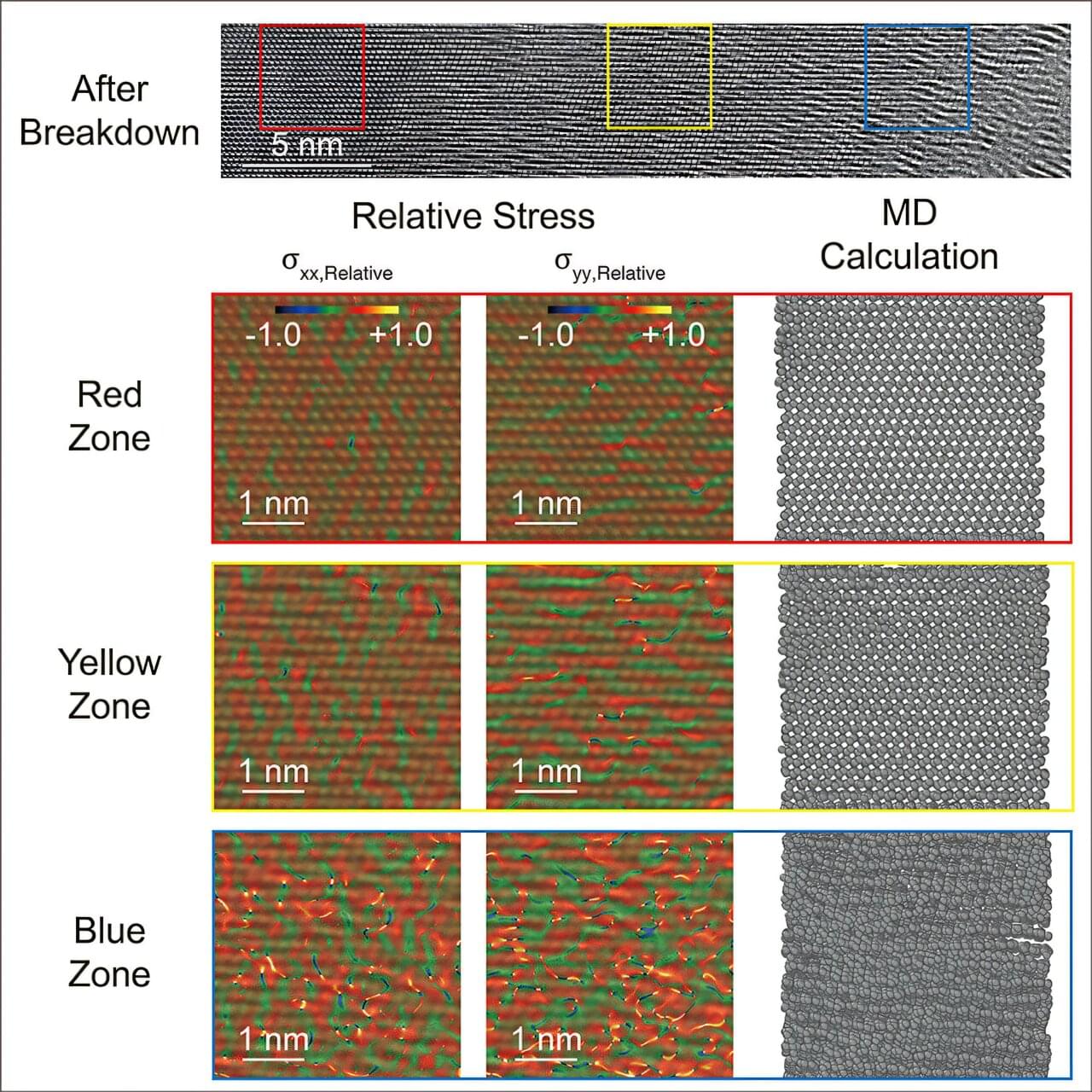
Researchers at Seoul National University and Kyung Hee University report a framework to control collective motions, such as ring, clumps, mill, flock, by training a physics-informed AI to learn the local rules that govern interactions among individuals.
The paper is published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
The approach specifies when an ordered state should appear from random initial conditions and tunes geometric features (average radius, cluster size, flock size). Furthermore, trained on published GPS trajectories of real pigeons, the model uncovers interaction mechanisms observed in real flocks.