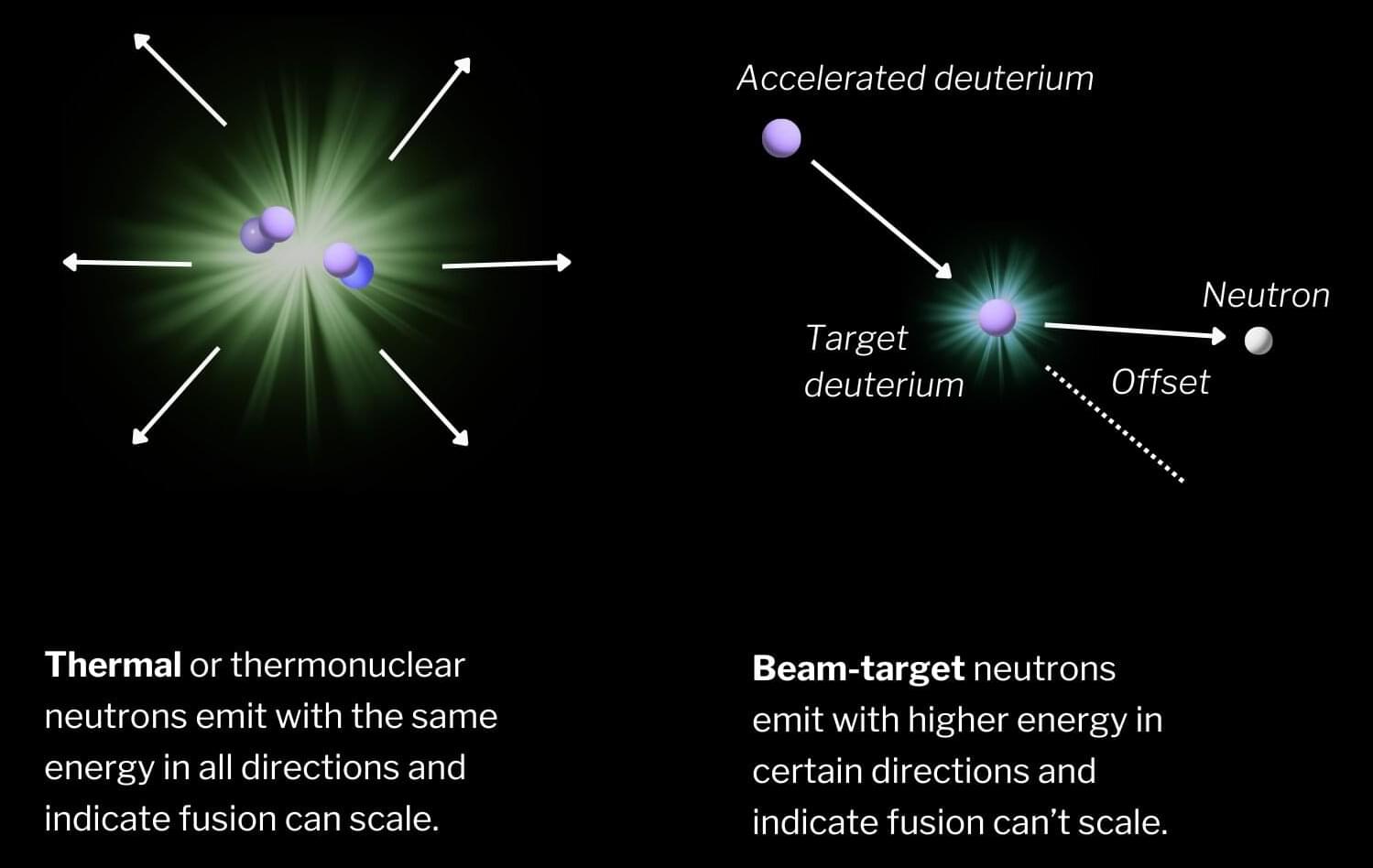
In physics, the term “isotropy” means a system where the properties are the same in all directions. For fusion, neutron energy isotropy is an important measurement that analyzes the streams of neutrons coming from the device and how uniform they are. This is critical because so-called isotropic fusion plasmas suggest a stable, thermal plasma that can be scaled to higher fusion energy gains, whereas anisotropic plasmas, those emitting irregular neutron energies, can lead to a dead end.
A new Zap research paper, published in Nuclear Fusion, details neutron isotropy measurements from the FuZE device that provide the best validation yet that Zap’s sheared-flow-stabilized Z pinches generate stable, thermal fusion. It’s a benchmark milestone for scaling fusion to higher energy yields in Zap’s technology and giving confidence in reaching higher performance on the FuZE-Q device.
“Essentially, this measurement indicates that the plasma is in a thermodynamic equilibrium,” says Uri Shumlak, Zap’s Chief Scientist and Co-Founder. “That means we can double the size of the plasma and expect the same sort of equilibrium to exist.”